Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
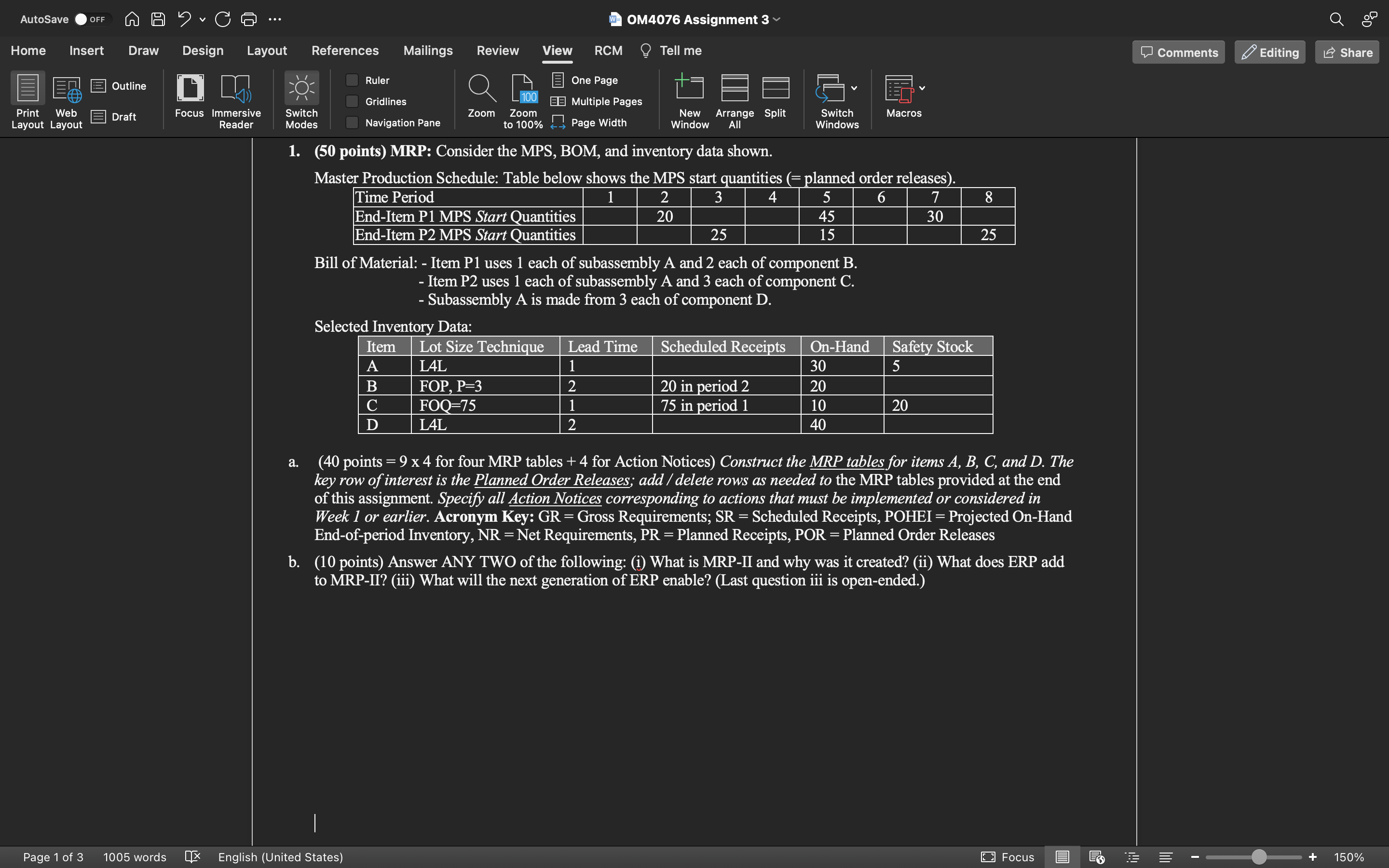
help on question 2, any and all parts is beneficial, thank you 1. (50 points) MRP: Consider the MPS, BOM, and inventory data shown. Master
help on question 2, any and all parts is beneficial, thank you
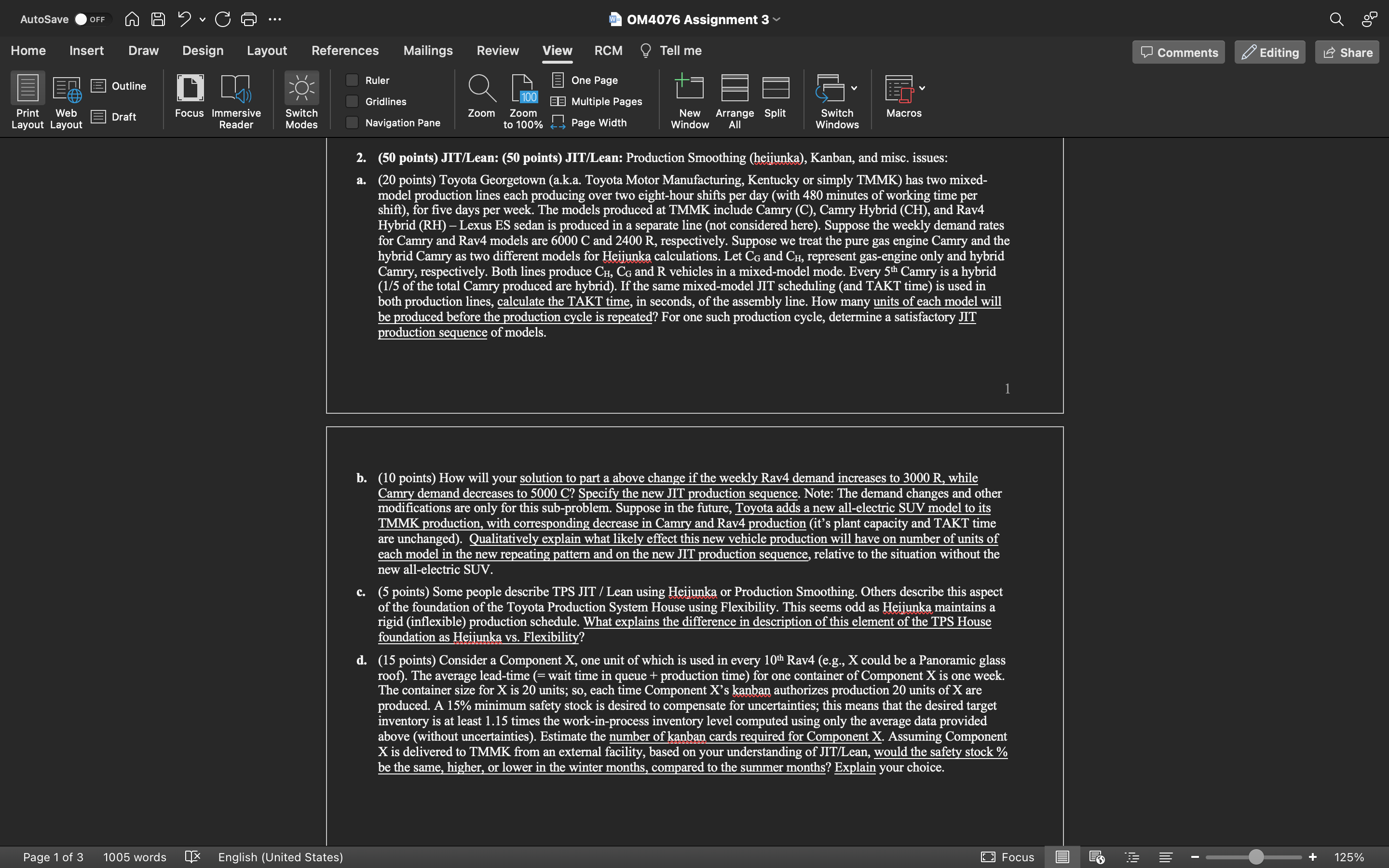
1. (50 points) MRP: Consider the MPS, BOM, and inventory data shown. Master Production Schedule: Table below shows the MPS start_auantities(= planned order releases). Bill of Material: - Item P1 uses 1 each of subassembly A and 2 each of component B. - Item P2 uses 1 each of subassembly A and 3 each of component C. - Subassembly A is made from 3 each of component D. a. (40 points =94 for four MRP tables +4 for Action Notices) Construct the MRP tables for items A,B,C, and D. The key row of interest is the Planned Order Releases; add / delete rows as needed to the MRP tables provided at the end of this assignment. Specify all Action Notices corresponding to actions that must be implemented or considered in Week 1 or earlier. Acronym Key: GR = Gross Requirements; SR = Scheduled Receipts, POHEI = Projected On-Hand End-of-period Inventory, NR = Net Requirements, PR = Planned Receipts, POR = Planned Order Releases b. (10 points) Answer ANY TWO of the following: (i) What is MRP-II and why was it created? (ii) What does ERP add to MRP-II? (iii) What will the next generation of ERP enable? (Last question iii is open-ended.) 2. (50 points) JIT/Lean: (50 points) JIT/Lean: Production Smoothing (heijunka), Kanban, and misc. issues: a. (20 points) Toyota Georgetown (a.k.a. Toyota Motor Manufacturing, Kentucky or simply TMMK) has two mixedmodel production lines each producing over two eight-hour shifts per day (with 480 minutes of working time per shift), for five days per week. The models produced at TMMK include Camry (C), Camry Hybrid (CH), and Rav4 Hybrid (RH) - Lexus ES sedan is produced in a separate line (not considered here). Suppose the weekly demand rates for Camry and Rav4 models are 6000C and 2400R, respectively. Suppose we treat the pure gas engine Camry and the hybrid Camry as two different models for Heijunka calculations. Let CG and CH, represent gas-engine only and hybrid Camry, respectively. Both lines produce CH,CG and R vehicles in a mixed-model mode. Every 5th Camry is a hybrid (1/5 of the total Camry produced are hybrid). If the same mixed-model JT scheduling (and TAKT time) is used in both production lines, calculate the TAKT time, in seconds, of the assembly line. How many units of each model will be produced before the production cycle is repeated? For one such production cycle, determine a satisfactory JIT production sequence of models. b. (10 points) How will your solution to part a above change if the weekly Rav4 demand increases to 3000R, while Camry demand decreases to 5000C ? Specify the new JIT production sequence. Note: The demand changes and other modifications are only for this sub-problem. Suppose in the future, Toyota adds a new all-electric SUV model to its TMMK production, with corresponding decrease in Camry and Rav4 production (it's plant capacity and TAKT time are unchanged). Qualitatively explain what likely effect this new vehicle production will have on number of units of each model in the new repeating pattern and on the new JIT production sequence, relative to the situation without the new all-electric SUV. c. (5 points) Some people describe TPS JIT / Lean using Heijunka or Production Smoothing. Others describe this aspect of the foundation of the Toyota Production System House using Flexibility. This seems odd as Heijunka maintains a rigid (inflexible) production schedule. What explains the difference in description of this element of the TPS House foundation as Heijunka vs. Flexibility? d. (15 points) Consider a Component X, one unit of which is used in every 10th Rav4 (e.g., X could be a Panoramic glass roof). The average lead-time (= wait time in queue + production time) for one container of Component X is one week. The container size for X is 20 units; so, each time Component X 's kanban authorizes production 20 units of X are produced. A 15% minimum safety stock is desired to compensate for uncertainties; this means that the desired target inventory is at least 1.15 times the work-in-process inventory level computed using only the average data provided above (without uncertainties). Estimate the number of kanban cards required for Component X. Assuming Component X is delivered to TMMK from an external facility, based on your understanding of JT/Lean, would the safety stock % be the same, higher, or lower in the winter months, compared to the summer months? Explain your choiceStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


