Question: help please D Question 1 1.95 pts 1. Consider the following PPFs for countries A and B, and their respective autarkic output levels. B YA
help please
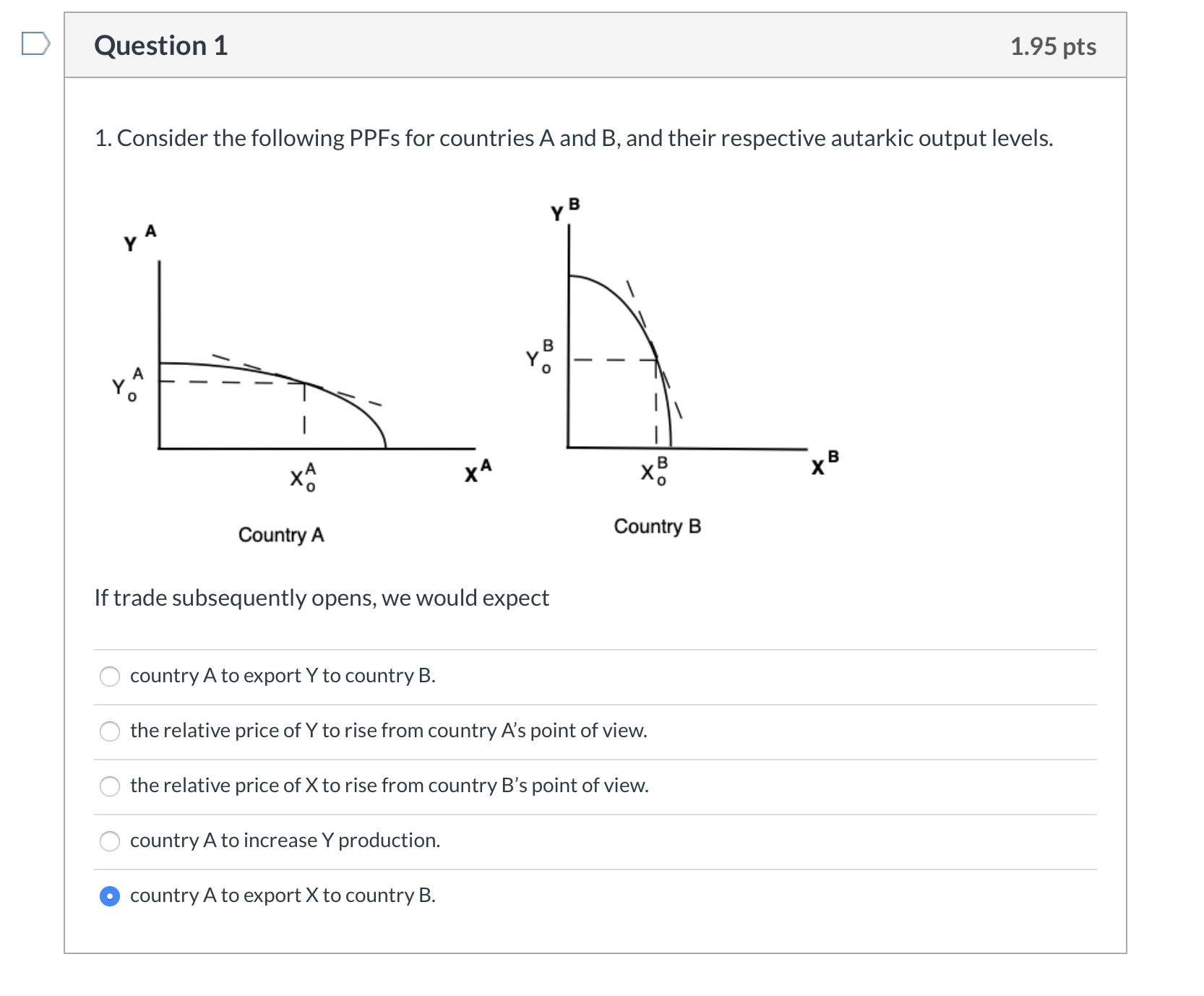
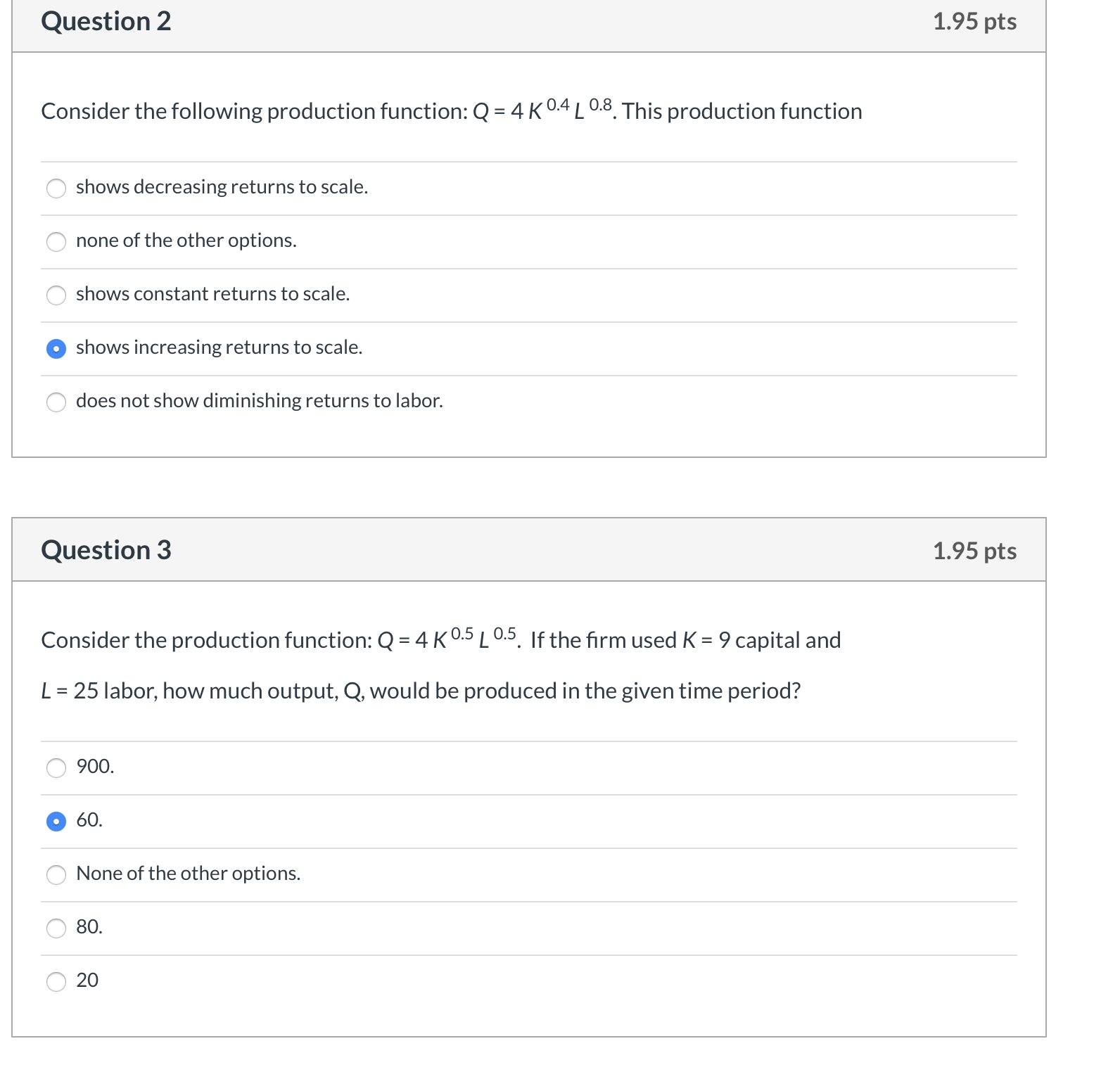

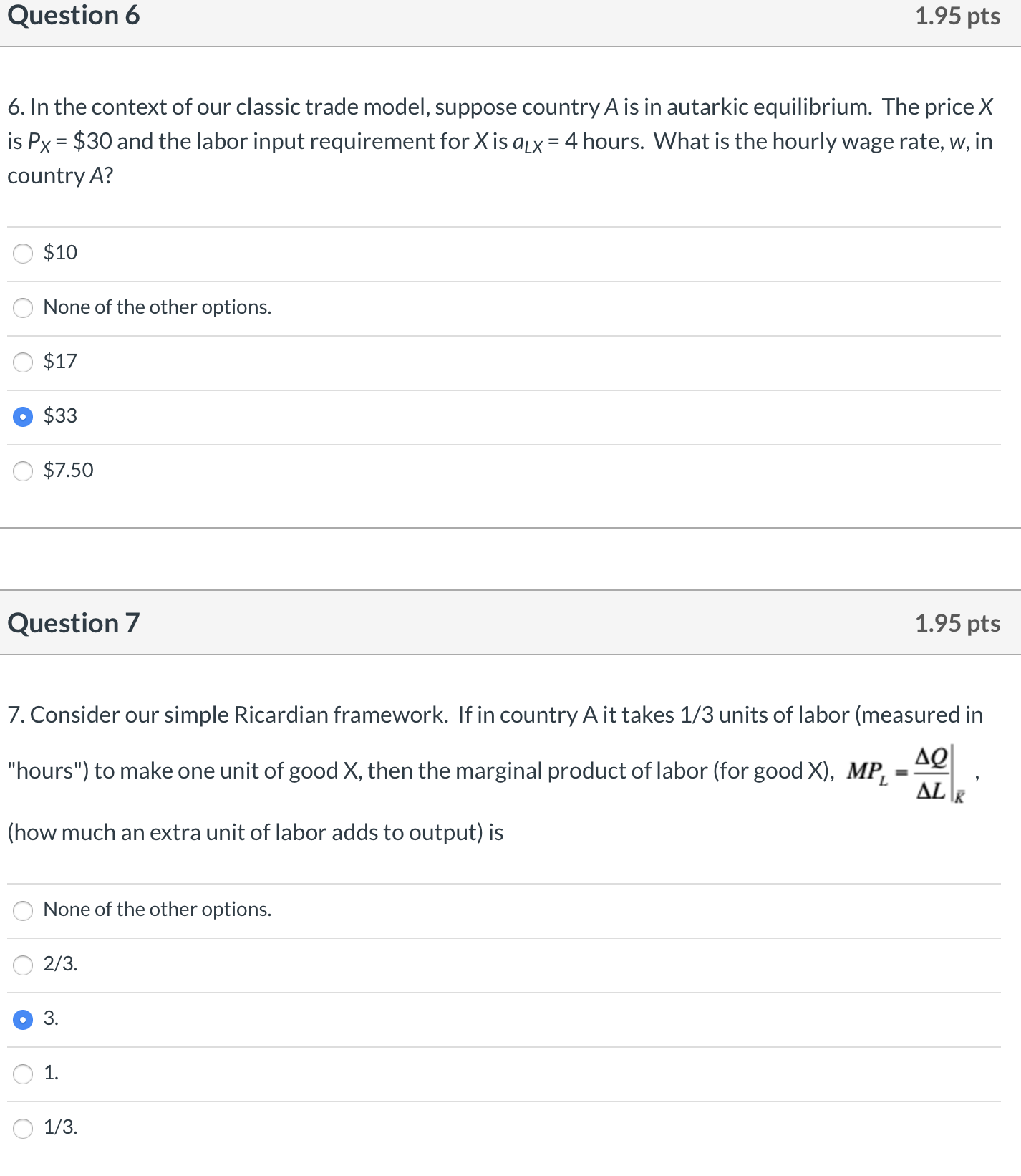
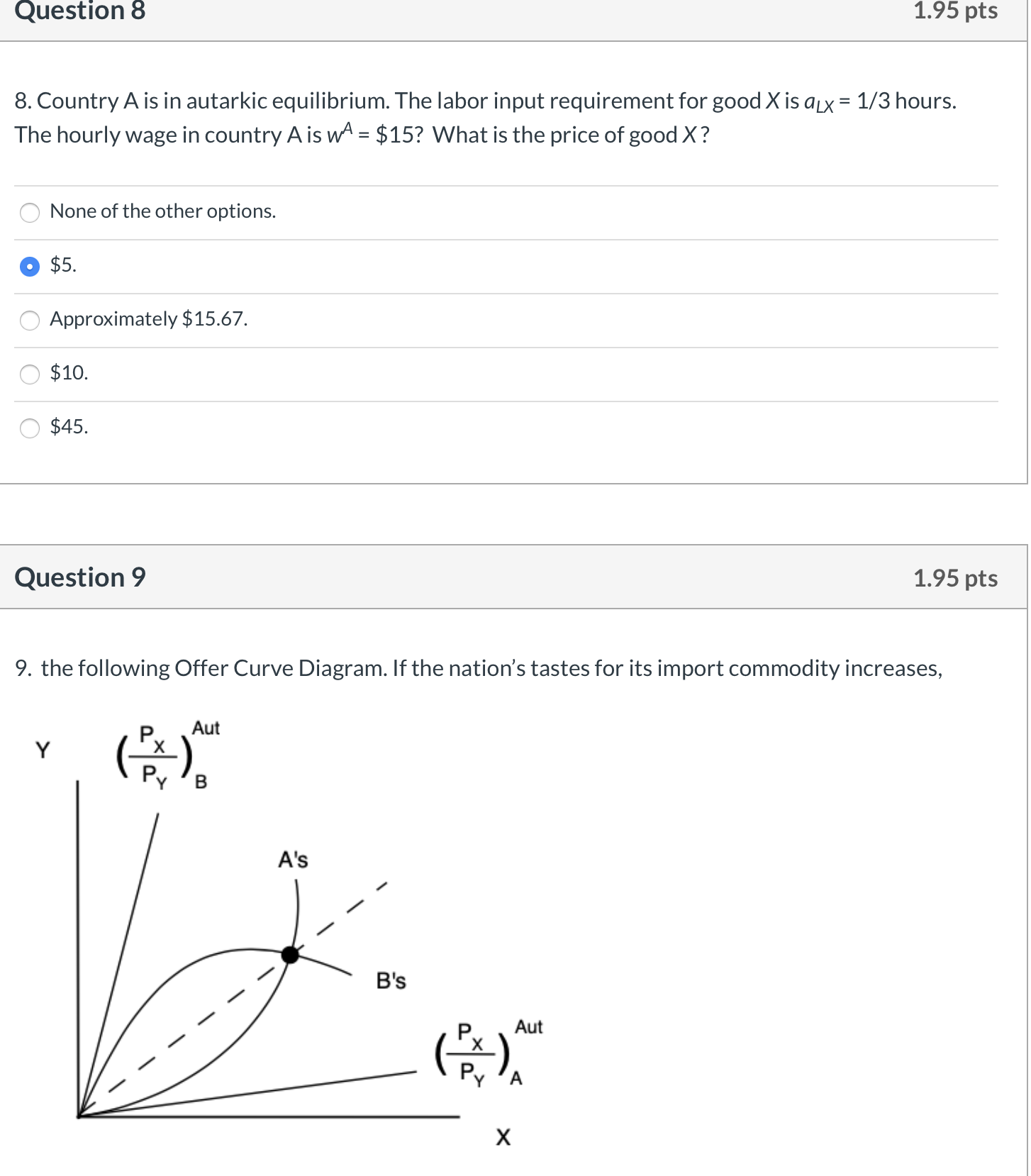

D Question 1 1.95 pts 1. Consider the following PPFs for countries A and B, and their respective autarkic output levels. B YA XA X B x B Country A Country B If trade subsequently opens, we would expect country A to export Y to country B. the relative price of Y to rise from country A's point of view. the relative price of X to rise from country B's point of view. country A to increase Y production. country A to export X to country B.Question 2 1.95 pts Consider the following production function: Q = 4 K 0-4 L 0-8. This production function (7 shows decreasing returns to scale. (7 none of the other options. 0 shows constant returns to scale. 0 shows increasing returns to scale. Q does not show diminishing returns to labor. Question 3 1.95 pts Consider the production function: Q = 4 KO-5 L05. If the rm used K = 9 capital and L = 25 labor, how much output, Q, would be produced in the given time period? Q 900. o 60. 0 None of the other options. a 80. Question 4 1.95 pts 4. If the Total Cost of production is C = $540, the number of units of capital is K = 10, the rental price of capital is r = $40, and the units of labor is L = 20, then what must be the wage rate, w (assuming that L and K are the only two inputs to production)? \"1' None of the other options. Question 5 1.95 pts 5. Suppose a rm is currently using capital (K) and labor (L) such that the marginal product of capital is MPK = 40 and the marginal product of labor is MPL = 18. If the rental price of capital is r = $20 and the wage rate is w = $10, then this rm is minimizing cost of its current level of production. can reduce the cost of its current level of output by using a bit more L and a bit more K. o can reduce the cost of its current level of output by using a bit more K and a bit less L (in such a way to keep output constant). must be maximizing its prot. A can reduce the cost of its current level of output by using a bit more L and a bit less K (in such a way to keep output constant). Question 6 1.95 pts 6. In the context of our classic trade model, suppose country A is in autarkic equilibrium. The price X is Px = $30 and the labor input requirement for X is aLx = 4 hours. What is the hourly wage rate, w, in country A? O $10 None of the other options. O $17 $33 O $7.50 Question 7 1.95 pts 7. Consider our simple Ricardian framework. If in country A it takes 1/3 units of labor (measured in "hours") to make one unit of good X, then the marginal product of labor (for good X), MP, =- ALR (how much an extra unit of labor adds to output) is O None of the other options. O 2/3. 3. O 1. O 1/3.Question 8 1.95 pts 8. CountryA is in autarkic equilibrium. The labor input requirement for good X is aLX = 1/3 hours. The hourly wage in country A is w\" = $15? What is the price of good X? F\" None of the other options. 0 $5. F\" Approximately $15.67. A $10. A $45. Question 9 1.95 pts 9. the following Offer Curve Diagram. If the nation's tastes for its import commodity increases, p Aut Y 7:) o the nation's offer curve rotates toward the axis measuring its export commodity. C the partner's offer curve rotates toward the axis measuring its import commodity. IAI \\ 2 none of the other options. C the partner's offer curve rotates toward the axis measuring its export commodity. C the nation's offer curve rotates toward the axis measuring its import commodity. Question 10 1.95 pts 10. Consider the Offer Curve Graph in the previous question. If the nation's tastes for its import commodity d_ecreases, ICI none of the other options. C the partner's terms of trade deteriorate. C it will necessarily produce more exports. C the nation's terms of trade remain unchanged. 0 the nation's terms of trade deteriorate. Question 11 1.95 pts 1 1. The offer curve of a nation shows 0 the nation's demand for imports and supply of exports. O the demand for a nation's exports. 0 none of the other options. O only the supply of a nation's exports. O the trade partner's demand for imports and supply of exports
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


