Question
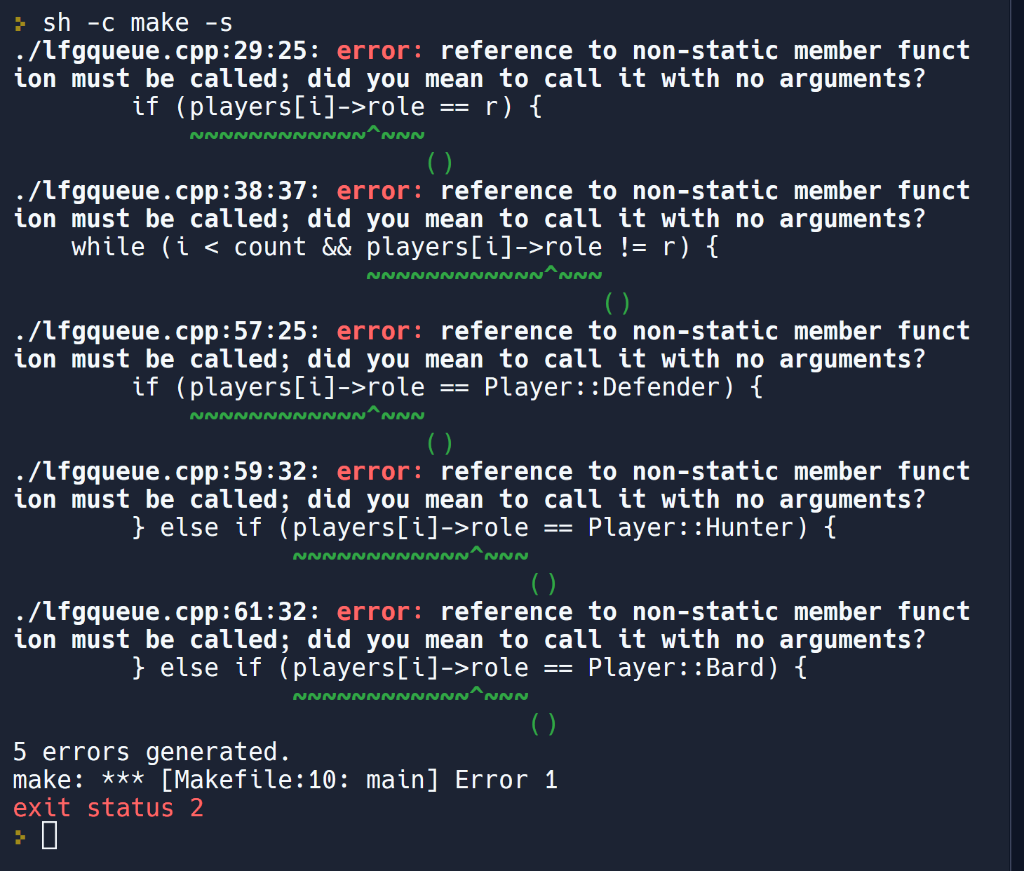
Hi, Can someone help me fix this error? I would appreciate it if you run it to ensure the error is fixed because I do
Hi, Can someone help me fix this error? I would appreciate it if you run it to ensure the error is fixed because I do not know how to fix it:(.
This is what the code is supposed to do:."
In many multiplayer online games, theres a looking for group feature for being automatically matched with other players. Such a feature behaves like a queue: players join the queue and removed in complete groups, and players who join the queue first are the first to be grouped. Here youll implement a looking-for-group queue for a game where players can be one of three roles (Defender, Hunter, and Bard) and each group consists of one Defender, one Hunter, and one Bard."
YOU CAN ONLY CHANGE lfgqueue.cpp file. Do not change anything else.
-------------ifgqueue.cpp----------------------
#include "lfgqueue.h"
LFGQueue::LFGQueue() { count = 0; capacity = 100; players = new Player*[capacity]; }
int LFGQueue::size() { return count; }
void LFGQueue::push_player(Player* p) { if (count == capacity) { capacity *= 2; Player** new_players = new Player*[capacity]; for (int i = 0; i
Player* LFGQueue::front_player(Player::Role r) { for (int i = 0; i role == r) { return players[i]; } } return nullptr; }
void LFGQueue::pop_player(Player::Role r) { int i = 0; while (i role != r) { i++; } if (i
bool LFGQueue::front_group(Player** group) { if (count role == Player::Defender) { defender = players[i]; } else if (players[i]->role == Player::Hunter) { hunter = players[i]; } else if (players[i]->role == Player::Bard) { bard = players[i]; } if (defender != nullptr && hunter != nullptr && bard != nullptr) { group[0] = defender; group[1] = hunter; group[2] = bard; return true; } } return false; }
void LFGQueue::pop_group() { Player* group[3]; if (front_group(group)) { pop_player(Player::Defender); pop_player(Player::Hunter); pop_player(Player::Bard); } }
-----lfgqueue.h------
#ifndef LFGQUEUE_H #define LFGQUEUE_H #include "player.h" class LFGQueue { public: // Constructs a new empty queue LFGQueue(); // Returns the number of players in the queue. int size(); // Adds a (pointer to a) player to the back of the queue void push_player(Player* p); // Returns a pointer to the frontmost player // with the specified role. If no such player // exists, returns 0. Player* front_player(Player::Role r); // Removes the frontmost player with the // specified role. If no such player exists // does nothing. void pop_player(Player::Role r); // Returns whether the queue contains a complete group // (a Defender, a Hunter, and a Bard). // // If the queue contains a complete group, the method // sets the first three elements of the array parameter // equal to the addresses of the frontmost: // 1. Defender (index 0) // 2. Hunter (index 1) // 3. Bard (index 2) bool front_group(Player** group); // Removes the frontmost Defender, Hunter, // and Bard from the queue. If some role // has no player with that role, then // no players are removed. void pop_group(); private: Player** players; int count; int capacity; }; -------------main.cpp-----------
#include#include #include #include "lfgqueue.h" using namespace std; inline void _test(const char* expression, const char* file, int line) { cerr name() == oss.str()); oss.str(""); oss name() == oss.str()); oss.str(""); oss name() == oss.str()); q.pop_group(); test(q.size() == 999 - 3 * (i+1)); } test(q.size() == 0); test(!q.front_group(group)); for (int i = 0; i player.h
#ifndef PLAYER_H #define PLAYER_H #includeusing namespace std; class Player { public: // This works like a custom type with just four values. // Outside of Player methods, reference them like: // "if (p->role == Player::Defender)", etc. enum Role {Defender, Hunter, Bard}; // Initializes a player with the given name and role Player(string name, Role role); // Returns the name of the player string name(); // Returns the role of the player Role role(); private: string _name; Role _role; }; #endif player.cpp
#include "player.h" Player :: Player(string name, Role role) { _name = name; _role = role; } string Player :: name() { return _name; } Player::Role Player :: role() { return _role; }
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


