Hii can you answer from question 1 to 11 I have no idea how to do them
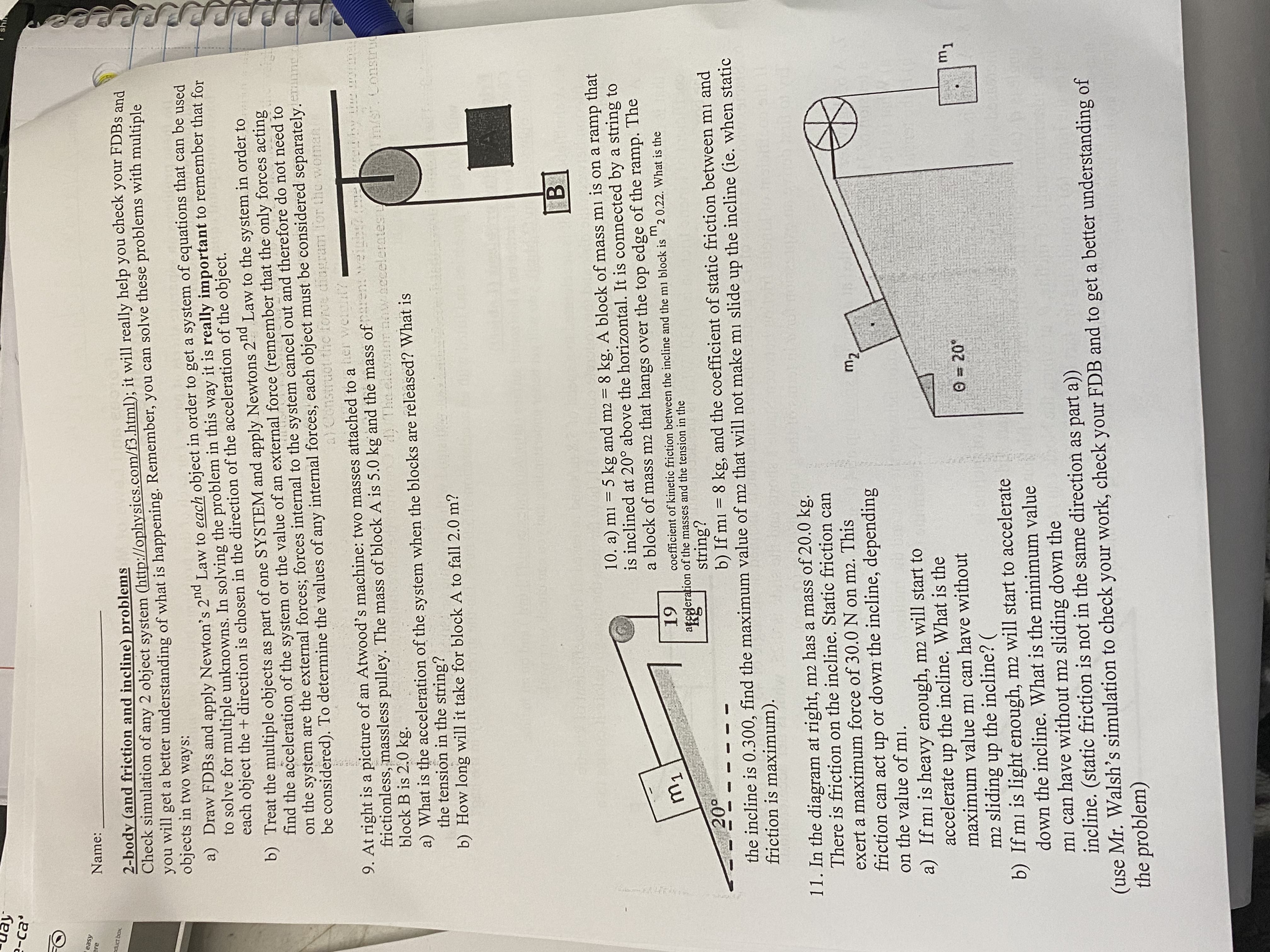
-ca Name: duct box 2-body (and friction and incline) problems Check simulation of any 2 object system (http://ophysics.com/f3.html); it will really help you check your FDBs and you will get a better understanding of what is happening. Remember, you can solve these problems with multiple objects in two ways: a) Draw FDBs and apply Newton's 2"d Law to each object in order to get a system of equations that can be used to solve for multiple unknowns. In solving the problem in this way it is really important to remember that for each object the + direction is chosen in the direction of the acceleration of the object. b) Treat the multiple objects as part of one SYSTEM and apply Newtons 2"" Law to the system in order to find the acceleration of the system or the value of an external force (remember that the only forces acting on the system are the external forces; forces internal to the system cancel out and therefore do not need to be considered). To determine the values of any internal forces, each object must be considered separately. eminnu chagram for the woman 9. At right is a picture of an Atwood's machine: two masses attached to a fer worth frictionless, massless pulley. The mass of block A is 5.0 kg and the mass of rent weight? (mal aret by the qoymal block B is 2.0 kg. how decelerates mist. Constru a) What is the acceleration of the system when the blocks are released? What is the tension in the string? b) How long will it take for block A to fall 2.0 m? 10. a) mi = 5 kg and m2 - 8 kg. A block of mass mi is on a ramp that is inclined at 20 above the horizontal. It is connected by a string to a block of mass m2 that hangs over the top edge of the ramp. The m1 19 coefficient of kinetic friction between the incline and the ml block is 2 0.22. What is the acceleration of the masses and the tension in the 20 string'? - - - - - - b) If mi = 8 kg, and the coefficient of static friction between mi and the incline is 0.300, find the maximum value of ma that will not make mi slide up the incline (ie. when static friction is maximum). 1 1. In the diagram at right, ma has a mass of 20.0 kg. There is friction on the incline. Static friction can exert a maximum force of 30.0 N on m2. This my friction can act up or down the incline, depending on the value of mi. a) If mi is heavy enough, m2 will start to accelerate up the incline. What is the maximum value mi can have without 0 = 20' m1 m2 sliding up the incline? ( b) If mi is light enough, ma will start to accelerate down the incline. What is the minimum value mi can have without m2 sliding down the incline. (static friction is not in the same direction as part a)) (use Mr. Walsh's simulation to check your work, check your FDB and to get a better understanding of the problem)Forces and Laws of Motion Friction, Inclines and Multi-Body Problems Do these problems on separate sheets of paper. For each of the problems below, you must begin your solution with a clear, accurate free body diagram. Show your solutions step by step starting with the basic conceptual equation (Newton's 2"d Law). Compute the size of the initial upward acceleration of a rocket of mass 1.30 x 10" kg if the initial upward thrust of its engine is 2.60 x 10" N. Do not neglect the weight of the rocket. Construct the force diagram 2. A 60 kg woman stands in an elevator that is accelerating downward at 3.10 m/s2. a) Construct the force diagram for the woman b) What is her weight? c) What is her apparent weight? (measured by the normal force acting on her) d) The elevator now accelerates up at 3.10 m/s . Construct the force diagram and determine the woman's apparent weight. 3. The maximum force that a grocery bag can withstand without ripping is 250 N. Suppose that bag is filled with 20.0 kg of groceries and lifted with an acceleration of 5.0 m/s . Do the groceries stay in the bag? Friction Practice problems (1 object) Check simulations of friction on a horizontal surface (http://ophysics.com/f1.html ) and on an incline (http://ophysics.com/f2.html); you will get better understanding and you can check your work. 4. A shuffleboard disk is accelerated to a speed of 5.8 m/s and released. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the disk and the concrete court is 0.31, how far does the disk go before it comes to a stop? The courts are 15.8 m long. F ensio 5. A 15.0 kg box is being pulled along level ground by a 75.0 N force pull that is directed at an angle of 20 above the horizontal. The 20 coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.330. What is the acceleration of the box? 6. Stacie, who has a mass of 45 kg, starts down a slide that is inclined at an angle of 450 with the horizontal. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between Stacie's shorts and the slide is 0.25, what is her acceleration? Try to first derive an expression for a in terms of the given variables (q, k, g). 7. A 63-kg water skier is pulled at a constant speed up a 14.0 incline by a rope parallel to the incline with a tension of 31 1 N. a) What is the coefficient of kinetic friction between the skis and the incline? b) If the tension in the rope were increased to 511 N, determine the acceleration of the skier. 8. A block is set on an adjustable ramp and the angle of incline is increased slowly until the block is observed to start sliding when the angle is q. (a) Determine the coefficient of static friction, us, in terms of the maximum angle of incline, 0, at which the block can remain at rest on the ramp. (b) Considering the fact that us is almost always less than or equal to one, at what amount of incline would there be too o little friction to prevent virtually anything from sliding