Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
i. 1's complement and 2's complement of a 32 bit number in location 'X' and store the result in memory. ii. 1's complement and 2's

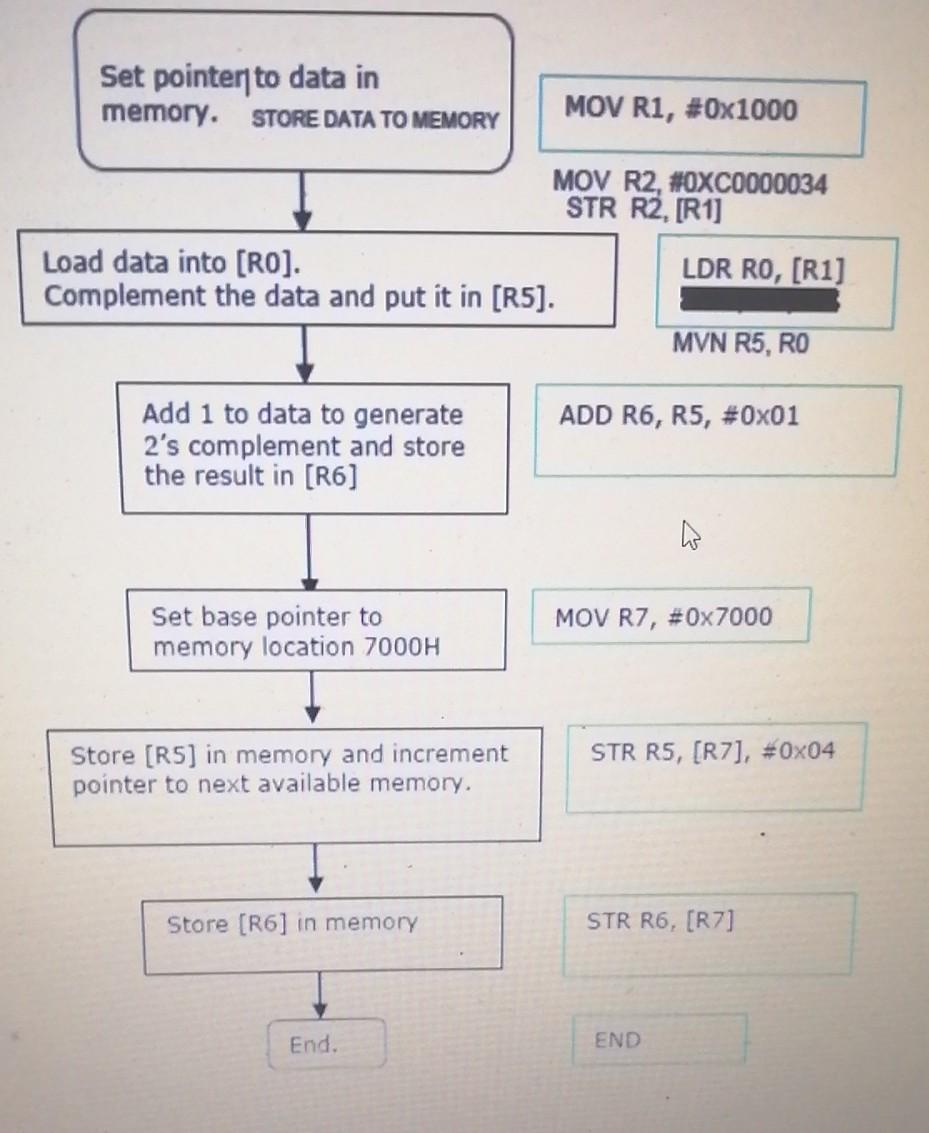



i. 1's complement and 2's complement of a 32 bit number in location 'X' and store the result in memory. ii. 1's complement and 2's complement of a 64-bit number in locations 'X' and 'X+1' (lower order first followed by higher order) and store the result in consecutive memory locations. i. 1's complement and 2's complement (32-bit) a) assume the location X is 1000, and operand is C0000034H. b) assume the output locations for 1's complement and 2's complement of a 32 bit number are 7000 and 7004. MOV R1, #0x1000 Set pointer to data in memory STORE DATA TO MEMORY MOV R2, #0XC0000034 STR R2, (RV) IDRO Ril Set pointer to data in memory. STORE DATA TO MEMORY MOV R1, #0x1000 MOV R2, #OXC0000034 STR R2, [R1] Load data into [RO]. LDR RO, [R1] Complement the data and put it in (R5). MVN R5, RO ADD R6, R5, #0x01 Add 1 to data to generate 2's complement and store the result in (R6) MOV R7, #0x7000 Set base pointer to memory location 7000H Store (R5) in memory and increment pointer to next available memory. STR R5, (R7], #Ox04 Store (R6) in memory STR R6, (R7] End. END ii. 1's complement and 2's complement (64-bit) Assume that X = 6300H Input to program: If we want to find the 2's complement of the 64-bit number FF00 0000 C000 0034H, then (6300H) = 0xC0000034 (lower order of the 64-bit number) (6304H) = 0xFF000000 (higher order of the 64-bit number) Output of program: Assume result is stored in 6400H and 6408H (lower order followed by higher order) (6400H) = 0x3FFFFFCB (6404H) = 0x00FFFFFF (6408H) = 0x3FFFFFCC (640CH) = 0x00FFFFFF 2. Perform the following BCD addition operation (one digit of BCD code add with another one digit of BCD code) by writing a program in ARM Assembly Language: a) Operand 1 is stored in memory location 6000H and Operand 2 is stored in memory location 6004H. b) Place the result in two consecutive memory locations if the result exceeds the value 10nco: 7000H and 7004H 3. Perform the following Multiplication and Division by 2 operation by writing a program in ARM Assembly Language: a) The Operand (assume the operand is one decimal bit, less than or equal to 810 and must be in even number) is stored in memory location 5000H b) Perform a Multiplication by 2 by performing a logical shift to the left and store the result in memory location 5004H. c) Perform a Division by 2 by performing a logical shift to the right and store the result in memory location 5008H. 4. Within the processor, there is a set of registers that is located above the main memory and the cache in the memory hierarchy. Based on the role of the registers, list and describe the TWO major groups of the registers. 5. List out the basic addressing modes of the Intel 8086 microprocessor. 6. Assume that Word 10 contains 20, Word 20 contains 30, Word 30 contains 40, and Word 40 contains 50. Given the above memory values and a one-address machine with an accumulator, what values do the following instructions load into the accumulator? i) LOAD IMMEDIATE 30 ii) LOAD DIRECT 30 iii) LOAD INDIRECT 30 iv) LOAD IMMEDIATE 10 v) LOAD DIRECT 40 vi) LOAD INDIRECT 10 7. Contemporary computer designs are based on concepts referred to as a von Neumann architecture. What are those THREE key concepts? 8. In order to understand the organization of the processor (CPU), certain requirements placed on the processor are considered. What are these processor requirements? i. 1's complement and 2's complement of a 32 bit number in location 'X' and store the result in memory. ii. 1's complement and 2's complement of a 64-bit number in locations 'X' and 'X+1' (lower order first followed by higher order) and store the result in consecutive memory locations. i. 1's complement and 2's complement (32-bit) a) assume the location X is 1000, and operand is C0000034H. b) assume the output locations for 1's complement and 2's complement of a 32 bit number are 7000 and 7004. MOV R1, #0x1000 Set pointer to data in memory STORE DATA TO MEMORY MOV R2, #0XC0000034 STR R2, (RV) IDRO Ril Set pointer to data in memory. STORE DATA TO MEMORY MOV R1, #0x1000 MOV R2, #OXC0000034 STR R2, [R1] Load data into [RO]. LDR RO, [R1] Complement the data and put it in (R5). MVN R5, RO ADD R6, R5, #0x01 Add 1 to data to generate 2's complement and store the result in (R6) MOV R7, #0x7000 Set base pointer to memory location 7000H Store (R5) in memory and increment pointer to next available memory. STR R5, (R7], #Ox04 Store (R6) in memory STR R6, (R7] End. END ii. 1's complement and 2's complement (64-bit) Assume that X = 6300H Input to program: If we want to find the 2's complement of the 64-bit number FF00 0000 C000 0034H, then (6300H) = 0xC0000034 (lower order of the 64-bit number) (6304H) = 0xFF000000 (higher order of the 64-bit number) Output of program: Assume result is stored in 6400H and 6408H (lower order followed by higher order) (6400H) = 0x3FFFFFCB (6404H) = 0x00FFFFFF (6408H) = 0x3FFFFFCC (640CH) = 0x00FFFFFF 2. Perform the following BCD addition operation (one digit of BCD code add with another one digit of BCD code) by writing a program in ARM Assembly Language: a) Operand 1 is stored in memory location 6000H and Operand 2 is stored in memory location 6004H. b) Place the result in two consecutive memory locations if the result exceeds the value 10nco: 7000H and 7004H 3. Perform the following Multiplication and Division by 2 operation by writing a program in ARM Assembly Language: a) The Operand (assume the operand is one decimal bit, less than or equal to 810 and must be in even number) is stored in memory location 5000H b) Perform a Multiplication by 2 by performing a logical shift to the left and store the result in memory location 5004H. c) Perform a Division by 2 by performing a logical shift to the right and store the result in memory location 5008H. 4. Within the processor, there is a set of registers that is located above the main memory and the cache in the memory hierarchy. Based on the role of the registers, list and describe the TWO major groups of the registers. 5. List out the basic addressing modes of the Intel 8086 microprocessor. 6. Assume that Word 10 contains 20, Word 20 contains 30, Word 30 contains 40, and Word 40 contains 50. Given the above memory values and a one-address machine with an accumulator, what values do the following instructions load into the accumulator? i) LOAD IMMEDIATE 30 ii) LOAD DIRECT 30 iii) LOAD INDIRECT 30 iv) LOAD IMMEDIATE 10 v) LOAD DIRECT 40 vi) LOAD INDIRECT 10 7. Contemporary computer designs are based on concepts referred to as a von Neumann architecture. What are those THREE key concepts? 8. In order to understand the organization of the processor (CPU), certain requirements placed on the processor are considered. What are these processor requirements
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


