Question
I have written the code but cannot complete the assignment please help me to complete. Please don't just copy other s answers as your own.
I have written the code but cannot complete the assignment please help me to complete. Please don't just copy other s answers as your own.
// Insertion sort
/*
#include
#include
using namespace std;
void insertionSort(int arr[], int n) {
int i, key, j;
for (i = 1; i
key = arr[i];
j = i - 1;
// Move elements of arr[0..i-1], that are greater than key, to one position ahead of their current position
while (j >= 0 && arr[j] > key) {
arr[j + 1] = arr[j];
j = j - 1;
}
arr[j + 1] = key;
}
}
int main() {
int n;
cout
cin >> n;
int arr[n];
cout
for (int i = 0; i
cin >> arr[i];
}
int num = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
clock_t start, end;
double timetaken;
start = clock();
insertionSort(arr, num);
end = clock();
cout
for (int i = 0; i
cout
cout
timetaken = ((double) (end - start)) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
cout
return 0;
}
*/
// Shell Sort
/*
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int shellSort(int arr[], int n) {
for (int gap = n/2; gap > 0; gap /= 2) {
for (int i = gap; i
int temp = arr[i];
int j;
for (j = i; j >= gap && arr[j - gap] > temp; j -= gap)
arr[j] = arr[j - gap];
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
return 0;
}
void printArray(int arr[], int n) {
for (int i=0; i cout } int main() { int n; cout cin >> n; int arr[n]; cout for (int i = 0; i cin >> arr[i]; } int num = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]); clock_t start, end; double timetaken; start = clock(); shellSort(arr, num); end = clock(); cout printArray(arr, n); cout timetaken = (double)(end - start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC; cout return 0; } */ // MergeSort /* #include #include using namespace std; void merge(int arr[], int l, int m, int r) { int i, j, k; int n1 = m - l + 1; int n2 = r - m; int L[n1], R[n2]; for (i = 0; i L[i] = arr[l + i]; for (j = 0; j R[j] = arr[m + 1 + j]; i = 0; j = 0; k = l; while (i if (L[i] arr[k] = L[i]; i++; } else { arr[k] = R[j]; j++; } k++; } while (i arr[k] = L[i]; i++; k++; } while (j arr[k] = R[j]; j++; k++; } } void mergeSort(int arr[], int l, int r) { if (l int m = l + (r - l) / 2; mergeSort(arr, l, m); mergeSort(arr, m + 1, r); merge(arr, l, m, r); } } int main() { int n; cout cin >> n; int arr[n]; cout for (int i = 0; i cin >> arr[i]; } int arr_size = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]); clock_t start; clock_t end; double timetaken; start = clock(); mergeSort(arr, 0, arr_size - 1); end = clock(); timetaken = (double)(end - start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC; cout for (int i = 0; i cout cout cout return 0; } */ // Radix Sort /* #include #include #include #include using namespace std; void countingSort(vector { int n = arr.size(); vector vector for (int i = 0; i count[(arr[i] / exp) % 10]++; for (int i = 1; i count[i] += count[i - 1]; for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) { output[count[(arr[i] / exp) % 10] - 1] = arr[i]; count[(arr[i] / exp) % 10]--; } for (int i = 0; i arr[i] = output[i]; } void radixSort(vector { int n = arr.size(); int max_val = *max_element(arr.begin(), arr.end()); for (int exp = 1; max_val / exp > 0; exp *= 10) countingSort(arr, exp); } int main() { int n; cout cin >> n; vector cout for (int i = 0; i cin >> arr[i]; } clock_t start; clock_t end; double timetaken; start = clock(); radixSort(arr); end = clock(); timetaken = (end - start) / (double)CLOCKS_PER_SEC; cout for (int x : arr) cout cout cout return 0; } */ // std::sort /* #include #include #include #include using namespace std; int main() { int n; cout cin >> n; vector cout for (int i = 0; i cin >> arr[i]; } clock_t start = clock(); sort(arr.begin(), arr.end()); clock_t end = clock(); double timetaken = double(end - start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC; cout for (int x : arr) { cout } cout cout return 0; } */ #include #include #include #include using namespace std; int main() { int n; cout cin >> n; vector cout for (int i = 0; i cin >> arr[i]; } clock_t start; clock_t end; double timetaken; // pre-sorted start = clock(); sort(arr.begin(), arr.end()); end = clock(); timetaken = (end - start) / (double)CLOCKS_PER_SEC; cout for (int x : arr) { cout } cout cout // reverse-sorted reverse(arr.begin(), arr.end()); start = clock(); sort(arr.begin(), arr.end()); end = clock(); timetaken = (end - start) / (double)CLOCKS_PER_SEC; cout for (int x : arr) { cout } cout cout // rand%N random_shuffle(arr.begin(), arr.end()); start = clock(); sort(arr.begin(), arr.end()); end = clock(); timetaken = (end - start) / (double)CLOCKS_PER_SEC; cout for (int x : arr) { cout } cout cout // rand%10 for (int i = 0; i arr[i] = rand() % 10; } start = clock(); sort(arr.begin(), arr.end()); end = clock(); timetaken = (end - start) / (double)CLOCKS_PER_SEC; cout for (int x : arr) { cout } cout cout // zeros for (int i = 0; i arr[i] = 0; } start = clock(); sort(arr.begin(), arr.end()); end = clock(); timetaken = (end - start) / (double)CLOCKS_PER_SEC; cout for (int x : arr) { cout } cout cout return 0; } 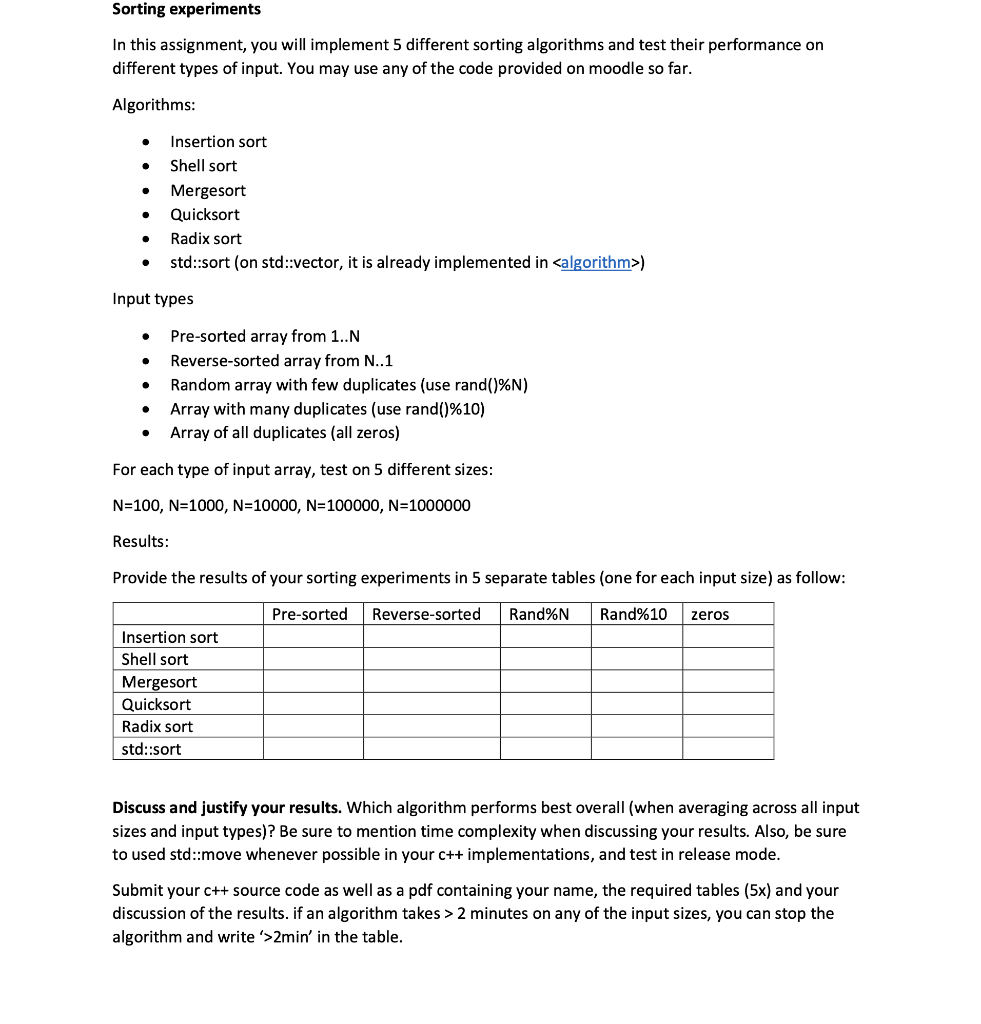

Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


