I need help in solving these.
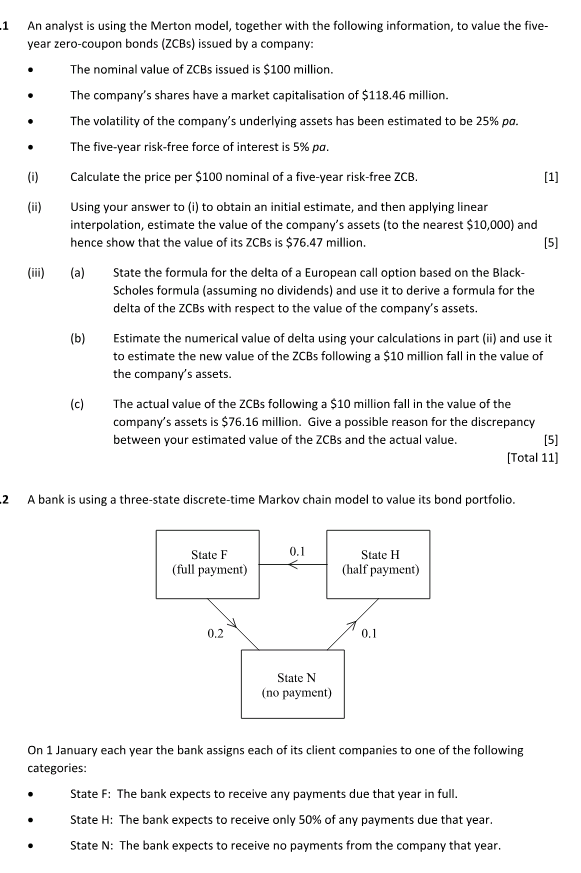
.1 An analyst is using the lvlerton modeL together with the following information, to value the ve year zero-coupon bonds {Elms} issued by a company: [ii [ii] [iii] The nominal value of 3235 issued is $10!] million. The company's shares have a market capitalisation of $115.55 million. The volatility of the company's underlying assets has been estimated to be 25% pa. The ve-vyear risioiree force of interest is 596 pa. Calculate the price per 510:] nominal of a five-year risk-free 2:3. [1] Using your ansvver to {ll to obtain an initial estimate} and then applying linear interpolation, estimate the value of the company's assets Ito the nearest $1y} and hence show that the value of its IL'Bs is SSE.\" million. [5] [a] State the formula for the delta of a European call option based on the Black. Scholes formula [assuming no dividends] and use it to derive a formula for the delta of the ECBs with respect to the value of the company's assets. [bi Estimate the numerical value of delta using your calculations in part [ii] and use it to estimate the new value of the ECE-s following a SID million fall in the value of the company's assets. [c] The actual value ofte EEBs following a 5'10 million fall in the value of the company's assets is STEJE million. Give a possible reason for the discrepancy between your estimated value of the IEBs and the actual value. [5] [Total 11] .1 A bank is using a three-state discrete-time Markov chain model to value its bond portfolio. Slate F ' Slate H [full payment} {half payment} State N [no payment} Dn 1 January each year the bank assigns each of its client companies to one of the following categories: State F: The bani: expects to receive any payments due that year in full. State H: The bank expects to receive only sass of any payments due that year. State H: The bank expects to receive no payments from the company that year. The diagram shows the risk-neutral probabilities that each company will move from its current rating level to another level at the time of each review. These probabilities are independent of the company's previous ratings and the behaviour of other companies. Let p;(0,t) denote the probability that a company initially in State i will be in State / t years later. (i) Calculate p;;(0,t) for j=F,H and t = 1,2,3. [3] The bank is considering purchasing at par a 3-year bond issued by a company currently rated as F. Under the terms of the bond, interest of 10% of the face value of the bond will be paid at the end of each year, and the bond will be redeemed at par at the end of the 3 years. The annual effective yields on 1-year, 2-year and 3-year government bonds are all 5%. (ii) (a) Calculate the risk-neutral expected present value of the payments from the bond per $100 face value. (b) Comment on your answer in (ii)(a). [3] After negotiations, the bank agrees to purchase the bonds at a price of 695.20. (iii) Calculate the credit spread for this bond. [3] [Total 9] 3 In the Vasicek model, the spot rate of interest is governed by the stochastic differential equation: dre = a(b-r )dt + adB where 8, is a standard Brownian motion and a, b > 0 are constants. (1) A stochastic process (U, : t 2 0) is defined by Up =ectr . (a) Derive an equation for dur (b) Hence solve the equation to find Up . (c) Hence show that: It = b+ ( ro-b)e-at + a fells -") dB, [5] (ii) Determine the probability distribution of r and the limiting distribution for large t. [4] (iii) Derive, in the case where s