I NEED HELP WITH NUMBER 4 (PARTIALLY COMPLETE) AND NUMBER 5. ALL INFORMATION IS BELOW TO HELP.
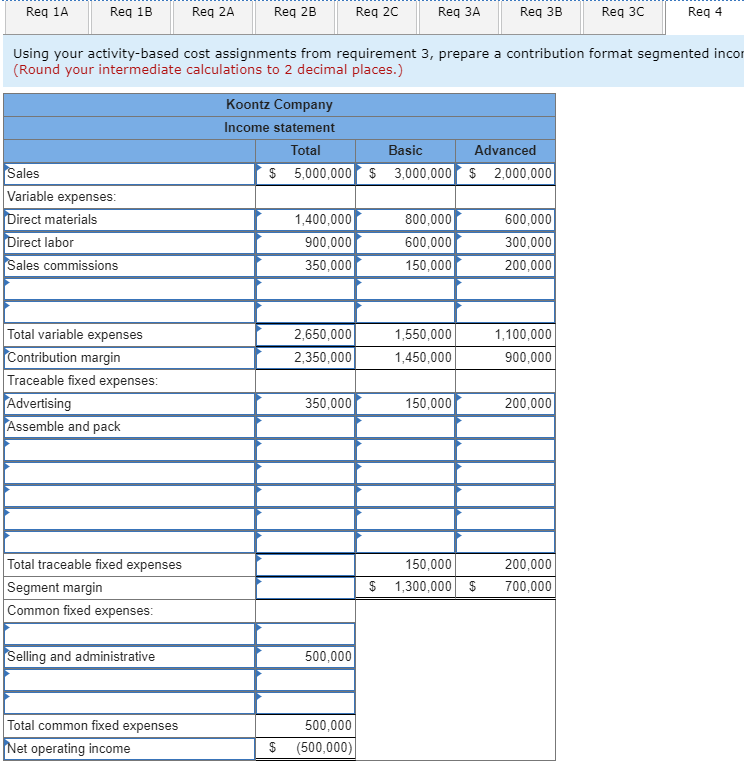
NOI is auto-calculated, so its incorrect. I need help with Assemble and Pack and any additional traceables and then common fixed expenses.
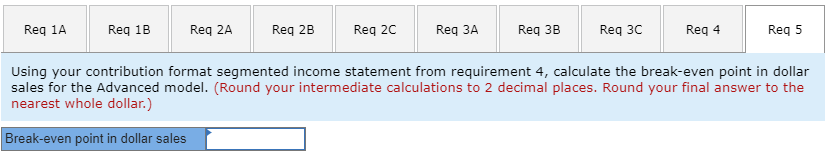
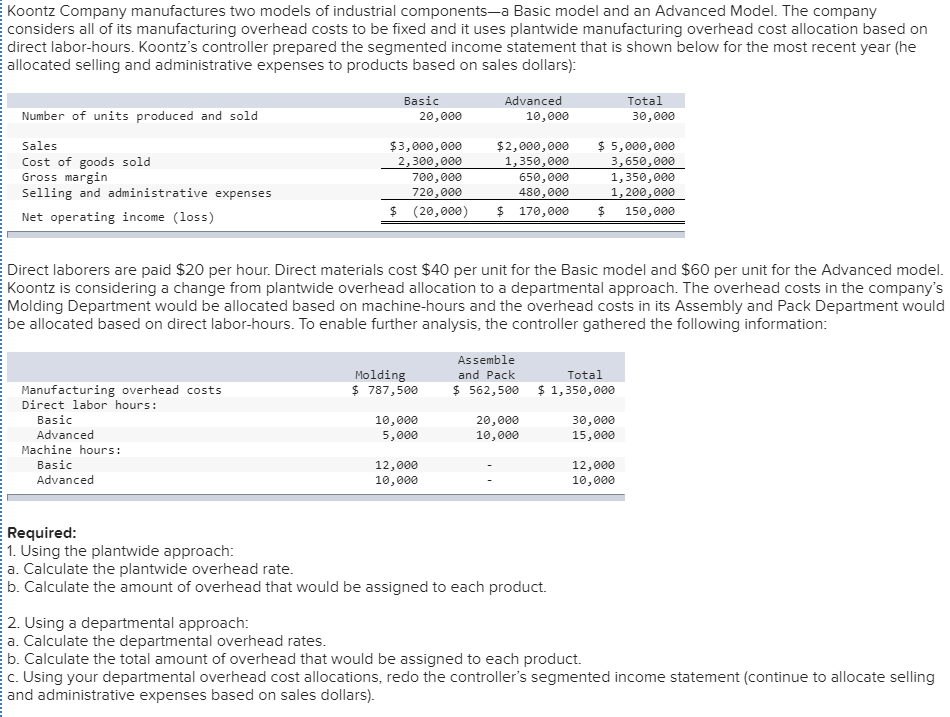
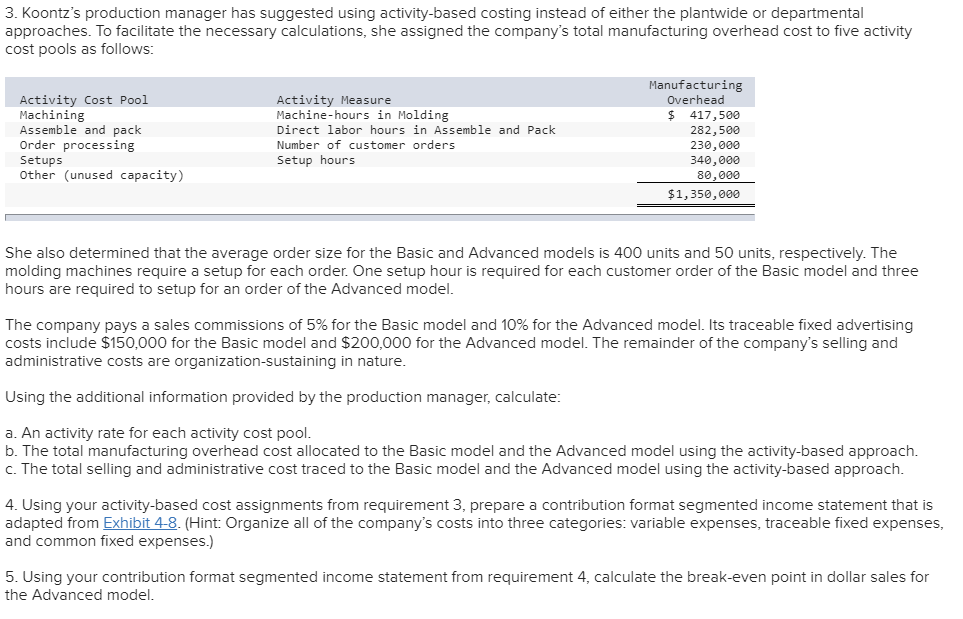
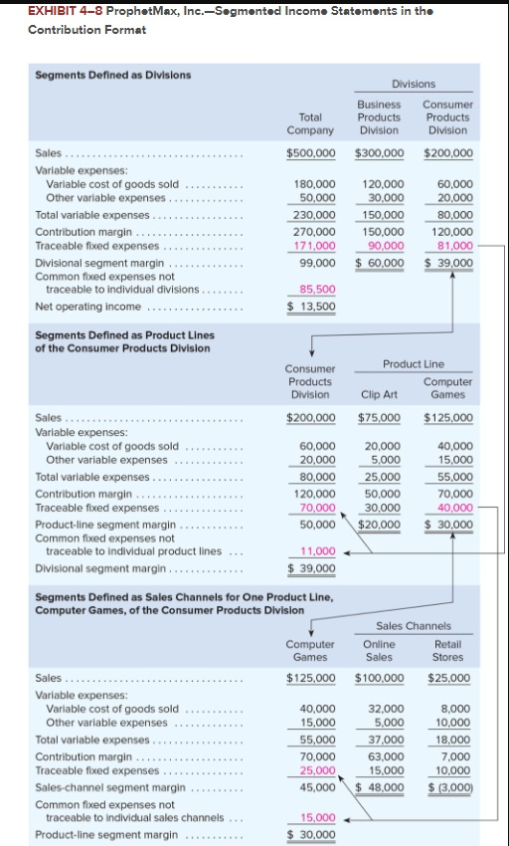
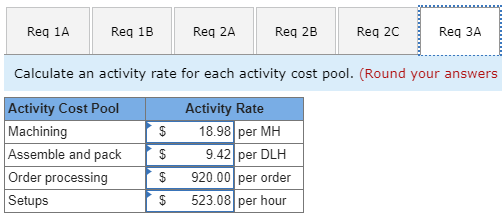
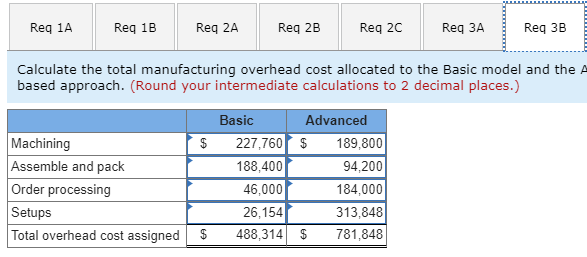
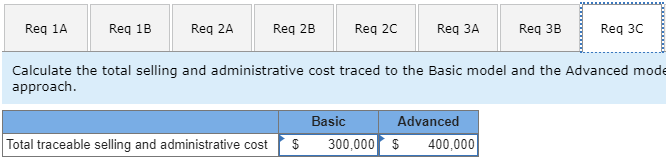
Koontz Company manufactures two models of industrial components-a Basic model and an Advanced Model. The company considers all of its manufacturing overhead costs to be fixed and it uses plantwide manufacturing overhead cost allocation based on direct labor-hours. Koontz's controller prepared the segmented income statement that is shown below for the most recent year (he E allocated selling and administrative expenses to products based on sales dollars): Basic 20,000 Advanced 10,000 Number of units produced and sold Total 30,000 Sales Cost of goods sold Gross margin Selling and administrative expenses Net operating income (loss) $3,000,000 2,300,000 700,000 720,000 $ (20,000) $2,000,000 1,350,000 650,000 480,000 $ 170,000 $5,000,000 3,650,000 1,350,000 1,200,000 $ 150,000 Direct laborers are paid $20 per hour. Direct materials cost $40 per unit for the Basic model and $60 per unit for the Advanced model. Koontz is considering a change from plantwide overhead allocation to a departmental approach. The overhead costs in the company's E Molding Department would be allocated based on machine-hours and the overhead costs in its Assembly and Pack Department would be allocated based on direct labor-hours. To enable further analysis, the controller gathered the following information: Molding $ 787,500 Assemble and Pack $ 562,500 Total $ 1,350,000 Manufacturing overhead costs Direct labor hours: Basic Advanced Machine hours: Basic Advanced 10,000 5,000 20,000 10,000 30,000 15,000 12,000 10,000 12,000 10,000 Required: 1. Using the plantwide approach: a. Calculate the plantwide overhead rate. b. Calculate the amount of overhead that would be assigned to each product. 2. Using a departmental approach: Ea. Calculate the departmental overhead rates. b. Calculate the total amount of overhead that would be assigned to each product. c. Using your departmental overhead cost allocations, redo the controller's segmented income statement (continue to allocate selling and administrative expenses based on sales dollars). 3. Koontz's production manager has suggested using activity-based costing instead of either the plantwide or departmental approaches. To facilitate the necessary calculations, she assigned the company's total manufacturing overhead cost to five activity cost pools as follows: Activity Cost Pool Machining Assemble and pack Order processing Setups Other (unused capacity) Activity Measure Machine-hours in Molding Direct labor hours in Assemble and Pack Number of customer orders Setup hours Manufacturing Overhead $ 417,500 282,500 230,000 340,000 80,000 $1,350,000 She also determined that the average order size for the Basic and Advanced models is 400 units and 50 units, respectively. The molding machines require a setup for each order. One setup hour is required for each customer order of the Basic model and three hours are required to setup for an order of the Advanced model. The company pays a sales commissions of 5% for the Basic model and 10% for the Advanced model. Its traceable fixed advertising costs include $150,000 for the Basic model and $200,000 for the Advanced model. The remainder of the company's selling and administrative costs are organization-sustaining in nature. Using the additional information provided by the production manager, calculate: a. An activity rate for each activity cost pool. b. The total manufacturing overhead cost allocated to the Basic model and the Advanced model using the activity-based approach. c. The total selling and administrative cost traced to the Basic model and the Advanced model using the activity-based approach. 4. Using your activity-based cost assignments from requirement 3, prepare a contribution format segmented income statement that is adapted from Exhibit 4-8. (Hint: Organize all of the company's costs into three categories: variable expenses, traceable fixed expenses, and common fixed expenses.) 5. Using your contribution format segmented income statement from requirement 4, calculate the break-even point in dollar sales for the Advanced model. EXHIBIT 4-8 ProphotMax, Inc.-Segmented Income Statements in the Contribution Format Segments Defined as Divisions Divisions Total Company Business Products Division Consumer Products Division $500,000 $300,000 $200,000 Sales ...... Variable expenses: Variable cost of goods sold ........... Other variable expenses. Total variable expenses........... Contribution margin...... Traceable fixed expenses Divisional segment margin... Common fixed expenses not traceable to individual divisions...... Net operating income .... 180,000 50,000 230,000 270,000 171.000 99,000 120,000 30,000 150,000 150,000 90.000 $ 60,000 60,000 20,000 80,000 120,000 81.000 $39,000 85,500 $ 13,500 Segments Defined as Product Lines of the Consumer Products Division Consumer Products Division Product Line Computer Clip Art Games $75,000 $125,000 $200,000 Sales. Variable expenses: Variable cost of goods sold ...... Other variable expenses. .. Total variable expenses..... Contribution margin Traceable fixed expenses............. Product line segment margin Common fixed expenses not traceable to individual product lines Divisional segment margin... 60,000 20,000 80,000 120,000 70,000 50,000 20,000 5,000 25,000 50,000 30,000 $20,000 40,000 15,000 55,000 70,000 40,000 $ 30,000 11,000 $ 39,000 Segments Defined as Sales Channels for One Product Line, Computer Games, of the Consumer Products Division Computer Games $125,000 Sales Channels Online Retail Sales Stores $100,000 $25,000 Sales ..... Variable expenses: Variable cost of goods sold .......... Other variable expenses Total variable expenses. Contribution margin .... . Traceable fixed expenses.... Sales-channel segment margin.... Common fixed expenses not traceable to individual sales channels... Product-line segment margin ... 40,000 15,000 55,000 70,000 25,000 45,000 32,000 5,000 37,000 63,000 15,000 $ 48,000 8,000 10,000 18.000 7,000 10,000 $ (3,000) 15,000 $ 30,000 Req 1A Reg 1B Req 2A Reg 2B Reg 20 Req Calculate an activity rate for each activity cost pool. (Round your answers Activity Cost Pool Machining Assemble and pack Order processing Setups $ $ $ $ Activity Rate 18.98 per MH 9.42 per DLH 920.00 per order 523.08 per hour Req 1A Reg 1B Req 2A Req 2B Req 2c Req 3A Req 3B Calculate the total manufacturing overhead cost allocated to the Basic model and the based approach. (Round your intermediate calculations to 2 decimal places.) Machining | $ Assemble and pack Order processing Setups Total overhead cost assigned $ Basic 227,760 188,400 46,000 26,154 488,314 Advanced $ 189,800 94,200 184,000 313,848 $ 781.848 Req 1A Req 1B Req 2A Req 2B Req 2C Req 3A Req 3B Req 30 Calculate the total selling and administrative cost traced to the Basic model and the Advanced mode approach. Basic 300,000 Advanced $ 400,000 Total traceable selling and administrative cost $ Req 1A Req 1B Reg 2A Reg 2B Req 20 Req 3A Req 3B Req 3C Reg 4 Using your activity-based cost assignments from requirement 3, prepare a contribution format segmented incon (Round your intermediate calculations to 2 decimal places.) Koontz Company Income statement Total $ 5,000,000 Basic 3,000,000 Advanced $ 2,000,000 $ Sales Variable expenses: Direct materials Direct labor Sales commissions I 1,400,000 900,000 350,000 800,000 600,000 150,000 600,000 300,000 200,000 2,650,000 2,350,000 1,550,000 1,450,000 1,100,000 900,000 Total variable expenses Contribution margin Traceable fixed expenses: Advertising Assemble and pack 350,000 150,000 200,000 Total traceable fixed expenses Segment margin Common fixed expenses: 150,000 1,300,000 200,000 700,000 | $ $ Selling and administrative 500,000 Total common fixed expenses Net operating income 500,000 (500,000) $ Req 1A Req 1B Req 2A Req 2B Req 2c Req Req 3B Req 30 Req 4 Req 5 Using your contribution format segmented income statement from requirement 4, calculate the break-even point in dollar sales for the Advanced model. (Round your intermediate calculations to 2 decimal places. Round your final answer to the nearest whole dollar.) Break-even point in dollar sales














