Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
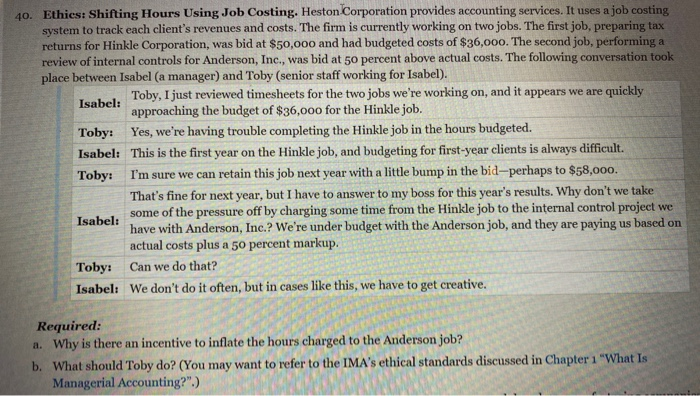
i need to answer the parts if the question in excel for this class. 40. Ethics: Shifting Hours Using Job Costing. Heston Corporation provides accounting


i need to answer the parts if the question in excel for this class.
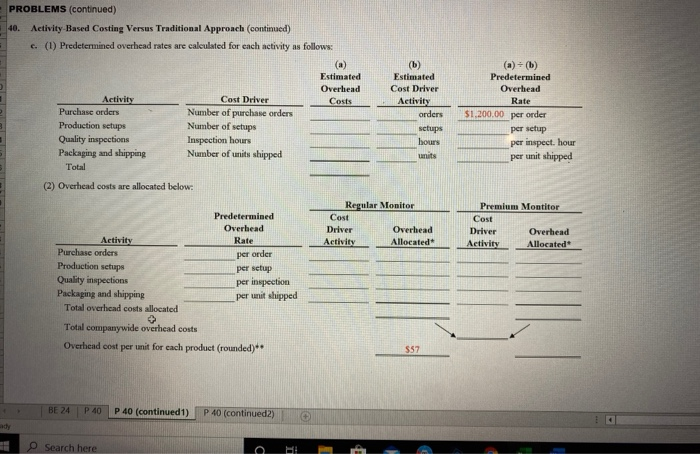
40. Ethics: Shifting Hours Using Job Costing. Heston Corporation provides accounting services. It uses a job costing system to track each client's revenues and costs. The firm is currently working on two jobs. The first job, preparing tax returns for Hinkle Corporation, was bid at $50,000 and had budgeted costs of $36,000. The second job, performing a review of internal controls for Anderson, Inc., was bid at 50 percent above actual costs. The following conversation took place between Isabel (a manager) and Toby (senior staff working for Isabel). Toby, I just reviewed timesheets for the two jobs we're working on, and it appears we are quickly Isabel: approaching the budget of $36,000 for the Hinkle job. Toby: Yes, we're having trouble completing the Hinkle job in the hours budgeted. Isabel: This is the first year on the Hinkle job, and budgeting for first-year clients is always difficult. Toby: I'm sure we can retain this job next year with a little bump in the bid-perhaps to $58,000. That's fine for next year, but I have to answer to my boss for this year's results. Why don't we take Isabel: some of the pressure off by charging some time from the Hinkle job to the internal control project we have with Anderson, Inc.? We're under budget with the Anderson job, and they are paying us based on actual costs plus a 50 percent markup. Toby: Can we do that? Isabel: We don't do it often, but in cases like this, we have to get creative. Required: a. Why is there an incentive to inflate the hours charged to the Anderson job? b. What should Toby do? (You may want to refer to the IMA's ethical standards discussed in Chapter 1 "What Is Managerial Accounting?".) 12 X A B C D E G H K per unit 6 7 per unit PROBLEMS 40. Activity-Based Costing Versus Traditional Approach a. The cost per unit for direct materials is calculated as follows: Regular Premium Monitor Monitor Total direct material costs (a) $1,908,000 Units produced (b) 36,000 units units Direct material cost per unit (a) (b) $53_per unit The cost per unit for direct labor is calculated as follows: Regular Premium Monitor Monitor 3 Total direct labor costs (c) 9 Units produced (d) units units 0 Direct labor cost per unit (c) (d) $48 per unit 1 2 b. (1) The plantwide allocation used by the company is based on 24 The rate is calculated as: 26 Estimated overhead cost Estimated activity in allocation base hours 29 per direct labor hour 31 Calculate the overhead cost per unit for each product here: 33 34 35 36 37 (2) Per unit product costs are calculated as follows: 39 Regular Premium 40 Monitor Monitor 41 Direct materials (from part a) 42 Direct labor (from parta) 43 Overhead 61.25 44 Total product cost per unit 45 per unit per unit 49 50 BE 24 P40 P 40 (continued) P 40 (continued) Ready PROBLEMS (continued) 40. Activity-Based Costing Versus Traditional Approach (continued) c. (1) Predetermined overhead rates are calculated for each activity as follows: (a) Estimated Overhead Activity Cost Driver Costs Purchase orders Number of purchase orders Production setups Number of setups Quality inspections Inspection hours Packaging and shipping Number of units shipped Total (b) Estimated Cost Driver Activity orders setups hours units (a) = (b) Predetermined Overhead Rate $1.200.00 per order per setup per inspect. hour per unit shipped (2) Overhead costs are allocated below: Predetermined Overhead Rate Regular Monitor Cost Driver Overhead Activity Allocated Premium Montiter Cost Driver Overhead Activity Allocated per order Activity Purchase orders Production setups Quality inspections Packaging and shipping Total overhead costs allocated per setup per inspection per unit shipped Total company wide overhead costs Overhead cost per unit for each product (rounded)** $57 BE 24 P 40 P 40 (continued 1) P 40 (continued) Search here ABC DE PROBLEMS (continued) 40. Activity Based Costing Versus Traditional Approach (continued) c. (3) Per unit product costs are: Regular Monitor Direct materials (from parta) Direct labor (from part a) Overhead (from parte) Total product cost per unit Premium Monitor Premium Monitor d. Traditional Costing (Direct labor hours as the allocation base) Regular Monitor Direct materials Direct labor Overhead Total product cost per unit(a) $162 25 Sales price () Profit (b)-(a) Activity-Based Costing (Several different allocation bases) Regular Monitor Direct materials Direct labor Overhead Total product cost per unit (c) $158.00 Sales price (d) Profit (loss)-(d)-() Premium Monitor 3 4 5 6 e. 8 Enter your answer for parte here: 10 12 45 16 47 BE24 Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


