Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
If the question is too long, I can split it into parts and post each part separately. Just solve all of them please, if you
If the question is too long, I can split it into parts and post each part separately. Just solve all of them please, if you want me to post the rest of the question as a new question just comment down.
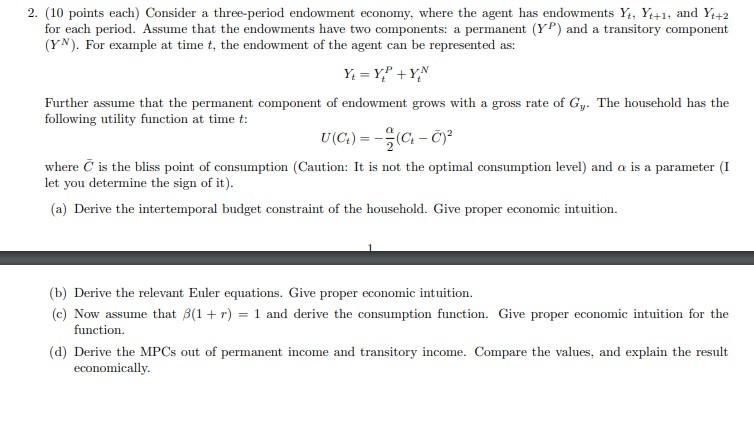
2. (10 points each) Consider a three-period endowment economy, where the agent has endowments Y, Y4+1, and Y4+2 for each period. Assume that the endowments have two components: a permanent (Y) and a transitory component (YN). For example at time t, the endowment of the agent can be represented as: Y = Y;!! + YN Further assume that the permanent component of endowment grows with a gross rate of Gy. The household has the following utility function at time t: U(C:) = C. - )? where is the bliss point of consumption (Caution: It is not the optimal consumption level) and a is a parameter (I let you determine the sign of it). (a) Derive the intertemporal budget constraint of the household. Give proper economic intuition. (b) Derive the relevant Euler equations. Give proper economic intuition. (c) Now assume that B(1 + r) = 1 and derive the consumption function. Give proper economic intuition for the function. (d) Derive the MPCs out of permanent income and transitory income. Compare the values, and explain the result economically. 2. (10 points each) Consider a three-period endowment economy, where the agent has endowments Y, Y4+1, and Y4+2 for each period. Assume that the endowments have two components: a permanent (Y) and a transitory component (YN). For example at time t, the endowment of the agent can be represented as: Y = Y;!! + YN Further assume that the permanent component of endowment grows with a gross rate of Gy. The household has the following utility function at time t: U(C:) = C. - )? where is the bliss point of consumption (Caution: It is not the optimal consumption level) and a is a parameter (I let you determine the sign of it). (a) Derive the intertemporal budget constraint of the household. Give proper economic intuition. (b) Derive the relevant Euler equations. Give proper economic intuition. (c) Now assume that B(1 + r) = 1 and derive the consumption function. Give proper economic intuition for the function. (d) Derive the MPCs out of permanent income and transitory income. Compare the values, and explain the result economicallyStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


