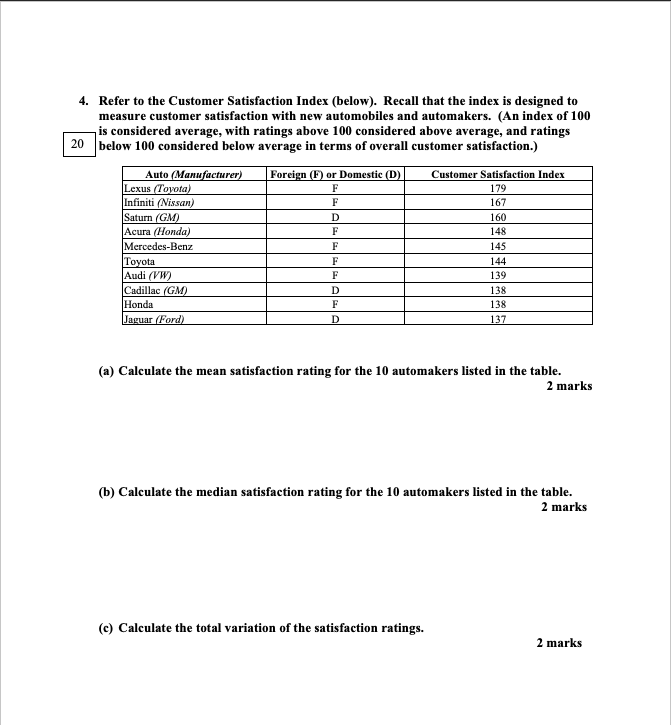
II. Refer to the Customer Satisfaction [n-da: [below]. Recall that the index is designed to measure customer satisfaction with new automobiles and automakers. {An index of 1111] is considered average, with ratings above lll'llI eonaivdered above average, and ratings below 1111] coasidered belvtlr'IIIIr average in terms of overall customer satisfaction.) For .- H "mm - CmtaaterSatiel'actioandu {a} Calculate the meal satisfaction rating for the II] automakers listed in the table. 1 marks [b] Calculate the medial satisiaction rating for the It] automakers listed in the table. 1 marks [1:]: Calculate the total variation of the satisfaction ratings. 1 marlcs (d) Calculate the standard deviation and variance of the satisfaction ratings. 4 marks (e) Find the 90th percentile of the satisfaction ratings. 2 marks (f) Find the z score for Cadillac. Interpret this value. 4 marks (g) Calculate the mean satisfaction rating of the seven foreign automakers in the sample. Compare this value to the mean for the three domestic automakers. Does it appear that customers are more satisfied with foreign than with domestic automakers? Discuss. 4 marks5. The notion of using the Empirical Rule and the interval X" + 2s to detect outliers is well documented in business and industry. In the 1960s, a beverage company was one of the first to apply the procedure to determine whether to conduct a search for specific causes of consumer complaints. (Consumer complaints were primarily concerned with chipped bottles that looked dangerous.) For one of the firm's brands, the complaint rate was known to have a mound-shaped distribution with a mean of 26.01 per 10,000 bottles sold and a standard deviation of 11.28 when the bottling process was operating properly (Journal of Marketing Research, Aug. 1964). The complaint rate observed during a later 2-week period was 93.12 complaints per 10,000 bottles sold. (a) Compute the z score for the observed rate of 93.12. 3 marks (b) Give a general interpretation of the z value computed in part (a). 3 marks (c) Use the Empirical Rule to determine whether the observed rate is due to chance or whether it is due to some specific cause. (In actuality, a search for a possible problem in the bottling process led to a discovery of rough handing of the bottled beverage in the warehouse by newly hired workers. As a result, a training program for new workers was instituted.) 3 marks6. Foresters "cruising" British Columbia's boreal forest have determined that the diameter at breast height of white spruce trees in a particular community is approximately normal, with mean 17 meters and standard deviation 6 meters. 26 (a) Find the probability that the breast height diameter of a randomly selected white spruce in the forest community is less than 12 meters. 8 marks (b) Suppose you observe a white spruce with a breast height diameter of 12 meters. Is this an unusual event? Explain 2 marks (c) Find the probability that the breast height diameter of a randomly selected white spruce in the forest community will exceed 37 meters. 8 marks (d) Suppose you observe a tree in the forest community with a breast height diameter of 38 meters. Is this tree likely to be a white spruce? Explain. 8 marks