Question
import networkx as nx def Question5(): #create a directed graph G = nx.DiGraph() #adding an edge also adds the node G.add_edge('Spider', 'A', weight=1.0) G.add_edge('Spider', 'H',

import networkx as nx
def Question5(): #create a directed graph G = nx.DiGraph() #adding an edge also adds the node G.add_edge('Spider', 'A', weight=1.0) G.add_edge('Spider', 'H', weight=1.0) G.add_edge('Spider', 'J', weight=1.0) G.add_edge('H', 'G', weight=1.0) G.add_edge('H', 'K', weight=1.0) G.add_edge('G', 'L', weight=1.0) G.add_edge('G', 'F', weight=1.0) G.add_edge('F', 'E', weight=1.0) G.add_edge('E', 'Fly', weight=1.0) G.add_edge('J', 'S', weight=1.0) G.add_edge('J', 'K', weight=1.0) G.add_edge('K', 'L', weight=1.0) G.add_edge('L', 'M', weight=1.0) G.add_edge('M', 'N', weight=1.0) G.add_edge('M', 'F', weight=1.0) G.add_edge('N', 'O', weight=1.0) G.add_edge('N', 'E', weight=1.0) G.add_edge('O', 'Fly', weight=1.0) G.add_edge('A', 'S', weight=1.0) G.add_edge('A', 'B', weight=1.0) G.add_edge('B', 'R', weight=1.0) G.add_edge('B', 'C', weight=1.0) G.add_edge('S', 'R', weight=1.0) G.add_edge('R', 'Q', weight=1.0) G.add_edge('Q', 'C', weight=1.0) G.add_edge('Q', 'P', weight=1.0) G.add_edge('C', 'D', weight=1.0) G.add_edge('D', 'Fly', weight=1.0) G.add_edge('P', 'D', weight=1.0) G.add_edge('P', 'O', weight=1.0) G.add_edge('O', 'Fly', weight=1.0) G.add_edge('T', 'Q', weight=1.0) G.add_edge('T', 'P', weight=1.0) G.add_edge('T', 'O', weight=1.0) G.add_edge('T', 'N', weight=1.0) G.add_edge('T', 'M', weight=1.0) G.add_edge('R', 'T', weight=1.0) G.add_edge('S', 'T', weight=1.0) G.add_edge('J', 'T', weight=1.0) G.add_edge('K', 'T', weight=1.0) G.add_edge('L', 'T', weight=1.0) #each edge has a weight of 1. The shortest path is the fewest edges. #Use this to verify that your graph built correctly. t = nx.shortest_path(G, 'Spider', 'Fly', weight='weight') print(t)
def main(): Question3() Question5()
if __name__ == "__main__": main()
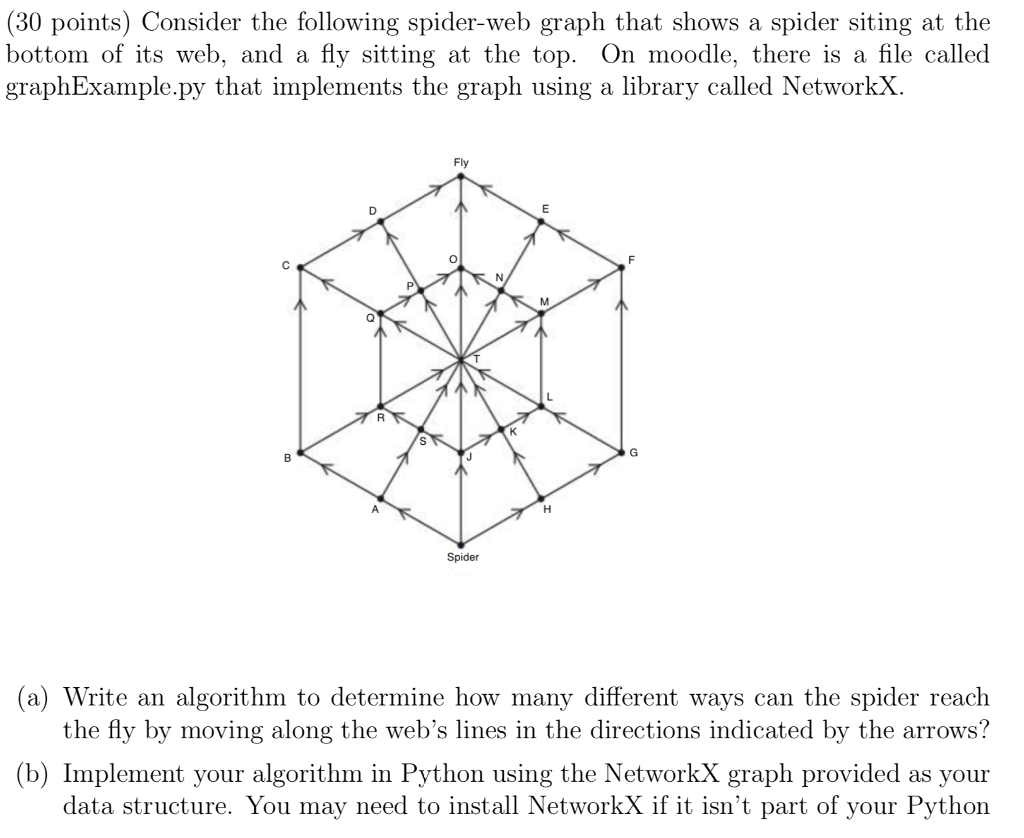
(30 points) Consider the following spider-web graph that shows a spider siting at the bottom of its web, and a fly sitting at the top. On moodle, there is a file called graphExample.py that implements the graph using a library called NetworkX (a) Write an algorithm to determine how many different ways can the spider reach the fly by moving along the web's lines in the directions indicated by the arrows? (b) Implement your algorithm in Python using the NetworkX graph provided as your data structure. You may need to install NetworkX if it isn't part of your Python (30 points) Consider the following spider-web graph that shows a spider siting at the bottom of its web, and a fly sitting at the top. On moodle, there is a file called graphExample.py that implements the graph using a library called NetworkX (a) Write an algorithm to determine how many different ways can the spider reach the fly by moving along the web's lines in the directions indicated by the arrows? (b) Implement your algorithm in Python using the NetworkX graph provided as your data structure. You may need to install NetworkX if it isn't part of your PythonStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


