Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
in a chart compare and contrast the different frameworks for HRD Evaluation frameworks: compare and contrast these frameworks in a chart Q uman Resource Development
in a chart compare and contrast the different frameworks for HRD Evaluation 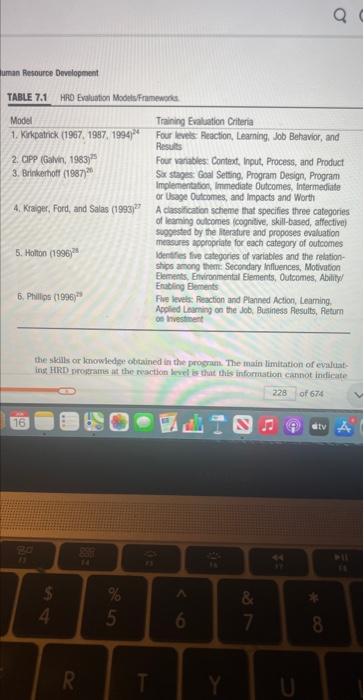
frameworks:

compare and contrast these frameworks in a chart 
Q uman Resource Development TABLE 7.1 HRD Evaluation Models/Frameworks Model Training Evaluation Criteria 1. Kirkpatrick (1967, 1987, 1994) Four levels: Reaction, Learning, Job Behavior, and Results 2. CIPP (Galvin, 1983) 3. Brinkerhoff (1987) Four variables: Context, Input, Process, and Product Six stages: Goal Setting, Program Design, Program Implementation, Immediate Outcomes, Intermediate or Usage Outcomes, and impacts and Worth 4. Kraiger, Ford, and Salas (1993) A classification scheme that specifies three categories of leaming outcomes (cognitive, skill-based, affective) suggested by the literature and proposes evaluation measures appropriate for each category of outcomes Identifies five categories of variables and the relation- ships among them: Secondary Influences, Motivation Elements, Environmental Elements, Outcomes, Ability/ Enabling Elements 5. Holton (1996) 6. Phillips (1996) Five levels: Reaction and Planned Action, Learning Applied Learning on the Job, Business Results, Return on Investment the skills or knowledge obtained in the program. The main limitation of evaluat- ing HRD programs at the reaction level is that this information cannot indicate 228 of 674 16 dtv A 11 $ 4 = 88 R % 5 0- T 6 Y & 7 44 U * 8 S uman Resource Development TABLE 7.1 HRD Evaluation Models/Frameworks. Model Training Evaluation Criteria 1. Kirkpatrick (1967, 1987, 1994)24 Four levels: Reaction, Learning, Job Behavior, and Results 2. CIPP (Galvin, 1983)25 3. Brinkerhoff (1987)26 Four variables: Context, Input, Process, and Product Six stages: Goal Setting, Program Design, Program Implementation, Immediate Outcomes, Intermediate or Usage Outcomes, and Impacts and Worth 4. Kraiger, Ford, and Salas (1993)27 A classification scheme that specifies three categories 5. Holton (1996)28 of learning outcomes (cognitive, skill-based, affective) suggested by the literature and proposes evaluation measures appropriate for each category of outcomes Identifies five categories of variables and the relation- ships among them: Secondary Influences, Motivation Elements, Environmental Elements, Outcomes, Ability/ Enabling Elements 6. Phillips (1996)29 Five levels: Reaction and Planned Action, Learning, Applied Learning on the Job, Business Results, Return on Investment the skills or knowledge obtained in the program. The main limitation of evaluat- ing HRD programs at the reaction level is that this information cannot indicate 228 of 674 AN 16 stv A 
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


