Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
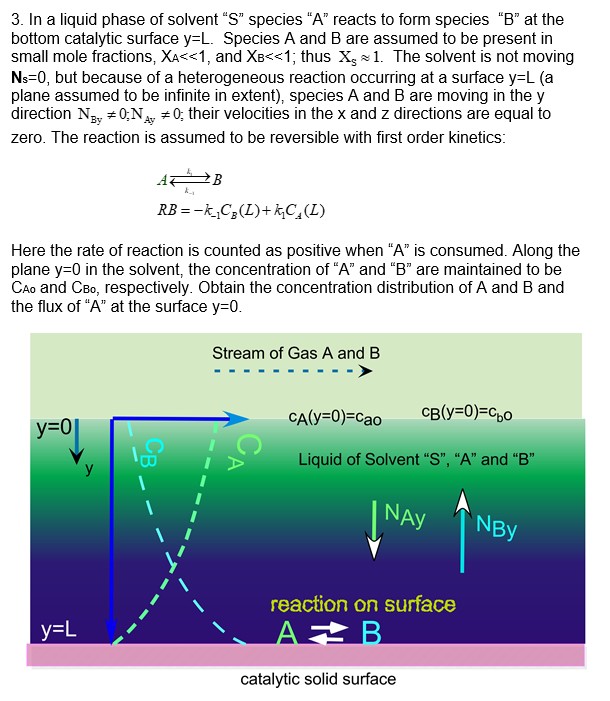
In a liquid phase of solvent S species A reacts to form species B at the bottom catalytic surface
In a liquid phase of solvent species reacts to form species at the
bottom catalytic surface Species A and are assumed to be present in
small mole fractions, and ; thus ~~ The solvent is not moving
but because of a heterogeneous reaction occurring at a surface a
plane assumed to be infinite in extent species A and are moving in the
direction ;; their velocities in the and directions are equal to
zero. The reaction is assumed to be reversible with first order kinetics:
Here the rate of reaction is counted as positive when is consumed. Along the
plane in the solvent, the concentration of and are maintained to be
and respectively. Obtain the concentration distribution of A and and
the flux of at the surface
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


