

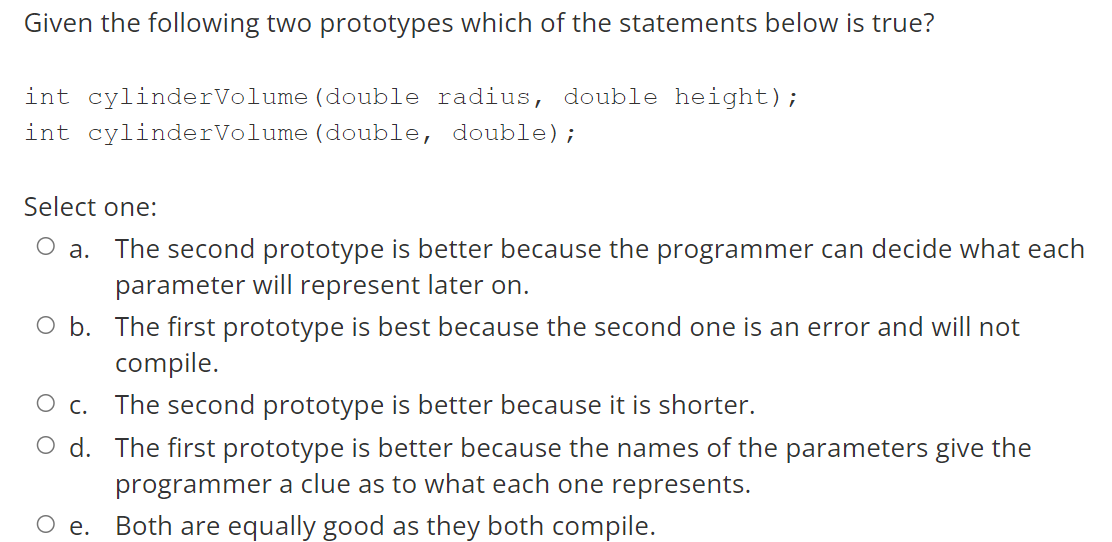


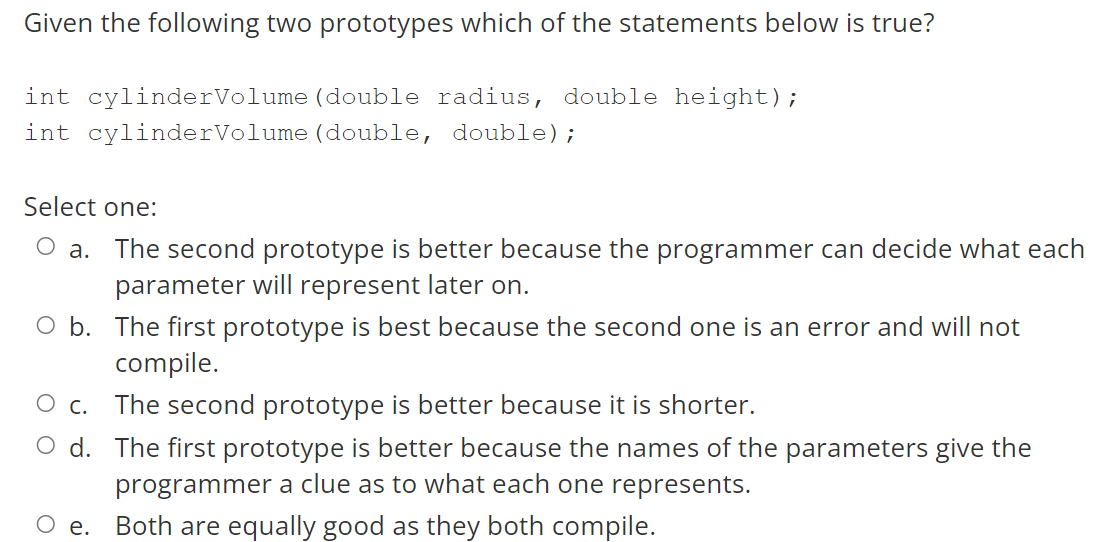














In ANSI standard C a variable can be declared: Select one: O Anywhere in the program. o Only before "main" o Only in the main function O After a curly bracket "{" or outside any function. o Only at the beginning of the program a To define a preprocessor constant called MAX that will be replace with the value 100anywhereit is found in the code you place the following near the top of your program: Select one: const MAX = 100; O #define MAX = 100; = O #define MAX = 100 const int MAX = = 100; O #define MAX 100 Given the following two prototypes which of the statements below is true? int cylindervolume (double radius, double height); int cylindervolume (double, double); Select one: O a. The second prototype is better because the programmer can decide what each parameter will represent later on. O b. The first prototype is best because the second one is an error and will not compile. O C. The second prototype is better because it is shorter. O d. The first prototype is better because the names of the parameters give the programmer a clue as to what each one represents. e. Both are equally good as they both compile. O What is stored into d after the following line of code executes: d = 5 != 10; Select one: O a. false O b. 0 O C. random number less than 0 O d. true e. 1. The difference between a while loop and a do while loop is: Select one: O a. A do-while loop will always exectute the code in the loop once and a while loop might never execute it. O b. A while loop will always exectute the code in the loop once and a do-while loop might never execute it. O C. A while loop is faster. d. A do-while loop is just an upside-down while loop but works the same. Given the following two prototypes which of the statements below is true? int cylindervolume (double radius, double height); int cylindervolume (double, double); Select one: O a. The second prototype is better because the programmer can decide what each parameter will represent later on. O b. The first prototype is best because the second one is an error and will not compile. O C. The second prototype is better because it is shorter. O d. The first prototype is better because the names of the parameters give the programmer a clue as to what each one represents. e. Both are equally good as they both compile. O When you see the * operator in front of a variable name e.g. *p,this should be read as: Select one: O a. the contents of p. O b. the address of p. O c. the thing pointed to by p. O d. pointer p. O e. the value in p. We should always initialise a pointer because: a. Select one: It is an error not to and the code will not compile. O b. If you mistakenly use an unitiialised pointer it can produce bugs that are difficult to find. O c. You have to give it an address at the start and can't change it later in the code. d. We were told to. The name of a structure refers to: Select one: O a. the address of the first member of the structure. O b. the template of the structure. O c. the first member of the structure. O d. the structure itself. The number 3 in C has the type: Select one: : O a. int O b. double O c. float O d. char O e. long int What gets stored in x as a result of the following code? unsigned char y = 0x55; unsigned char x; X = ~y; Select one: O a. true O b. 0 O c. 1 O d. Ox35 O e. false O f. Ox33 O g OxAA The function call that matches the following prototype is: int myFunction(int x, double y); Select one: int ans = myFunction(2, 3.0); O b. int ans = myFunction(2, 3.0); O c. ans = myFunction(2, 3.0); O d. int ans = myFunction(int a, double b); O e. ans = myFunction(); O f. myFunction(2, 3.0) = ans; = What does the following code do? = = int x = 2, y = 3; int *p &x, *q *q = &y; = = *p = = *q; Select one: a. Puts 2 into p. O b. Puts 2 into y. Puts 3 into x. . O d. Puts 3 into q. Puts 2 into q. Of. Puts 3 into p. O c. O. What does the following code do? struct Complex cl; Select one: O a. creates a structure called "Complex" with a member called "c1". O b. creates a structure template (blueprint) that tells the compiler what a structre of this type will look like. O c. creates to structure variables called "Complex" and "c1". O d.creates a variable called "c1" that is of type struct Complex. The number 3000L in C has the type: Select one: o long int O double o hexadecimal O int O float What is the value of the variable i after the following code runs? int i, j = 10, k = 28; i = ( (j > 5) && (k


























