in C++
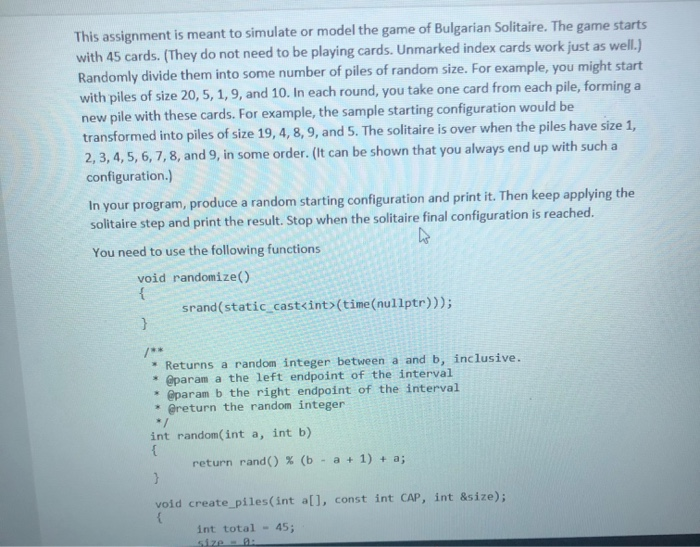
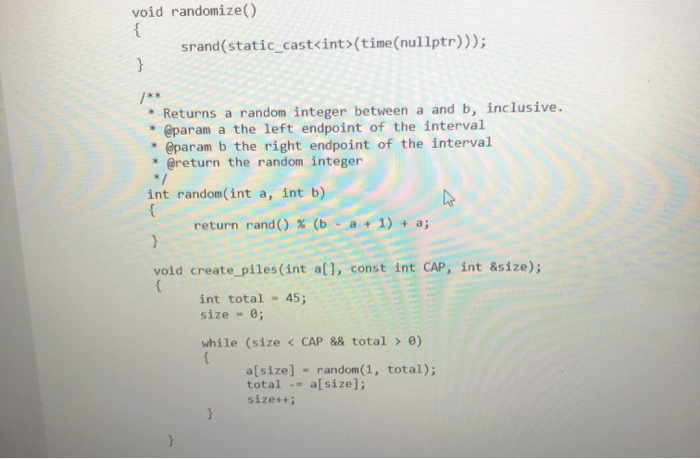
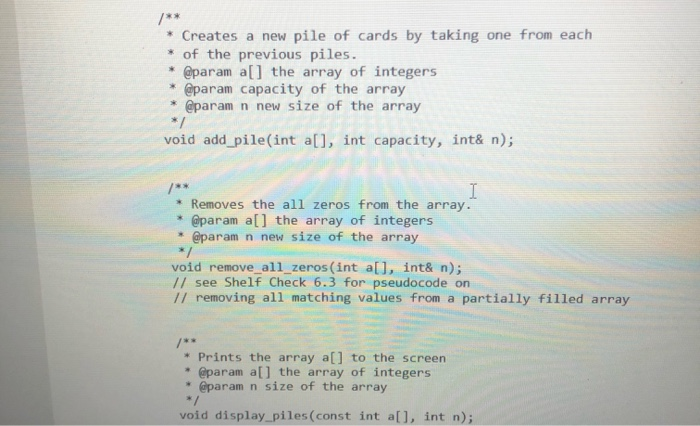
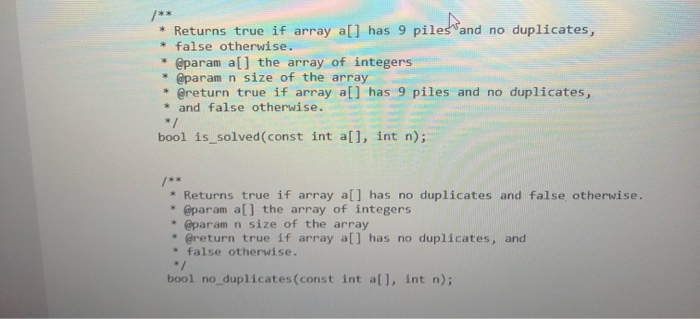
This assignment is meant to simulate or model the game of Bulgarian Solitaire. The game starts with 45 cards. (They do not need to be playing cards. Unmarked index cards work just as well.) Randomly divide them into some number of piles of random size. For example, you might start with piles of size 20,5, 1, 9, and 10. In each round, you take one card from each pile, forming a new pile with these cards. For example, the sample starting configuration would be transformed into piles of size 19, 4, 8, 9, and 5. The solitaire is over when the piles have size 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9, in some order. (It can be shown that you always end up with such a configuration.) In your program, produce a random starting configuration and print it. Then keep applying the You need to use the following functions void randomize() srand(static cast int>(time(nullptr))); Returns a random integer between a and b, inclusive. * @param a the left endpoint of the interval * @param b the right endpoint of the interval * @return the random integer / int random(int a, int b) return rand() % (b - a + 1) + a; void create_piles(int all, const int CAP, int &size); int total - 45; void randomize() srand(static_cast int>(time(nullptr))); Returns a random integer between a and b, inclusive. @param a the left endpoint of the interval @param b the right endpoint of the interval * @return the random integer int random(int a, int b) return rand() % (b void create_piles(int a[], const int CAP, int &size); int total - 45; size - ; while (size 0) a[size] - random(1, total); total -= a[size] size++; /** * Creates a new pile of cards by taking one from each * of the previous piles. * @param all the array of integers * @param capacity of the array * @param n new size of the array void add_pile(int a[], int capacity, int& n); * Removes the all zeros from the array. * @param all the array of integers * @param n new size of the array void remove_all_zeros(int a[], int& n); // see Shelf Check 6.3 for pseudocode on // removing all matching values from a partially filled array * Prints the array a[] to the screen * @param a[] the array of integers * @param n size of the array */ void display_piles (const int a[], int n); Returns true if array a[] has 9 piles and no duplicates, false otherwise. * @param a[] the array of integers * @param n size of the array * @return true if array all has 9 piles and no duplicates, * and false otherwise. * bool is_solved(const int a[], int n); * Returns true if array all has no duplicates and false otherwise. * @param all the array of integers * @param n size of the array * @return true if array all has no duplicates, and * false otherwise. bool no_duplicates (const int all, int n)










