Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Inputs Regular price Quality discount structure $30.00 At least Unit cost Leftover price $10.00 0 $24.00 1000 $23.00 Decision variable 2000 $22.25 Order quantity
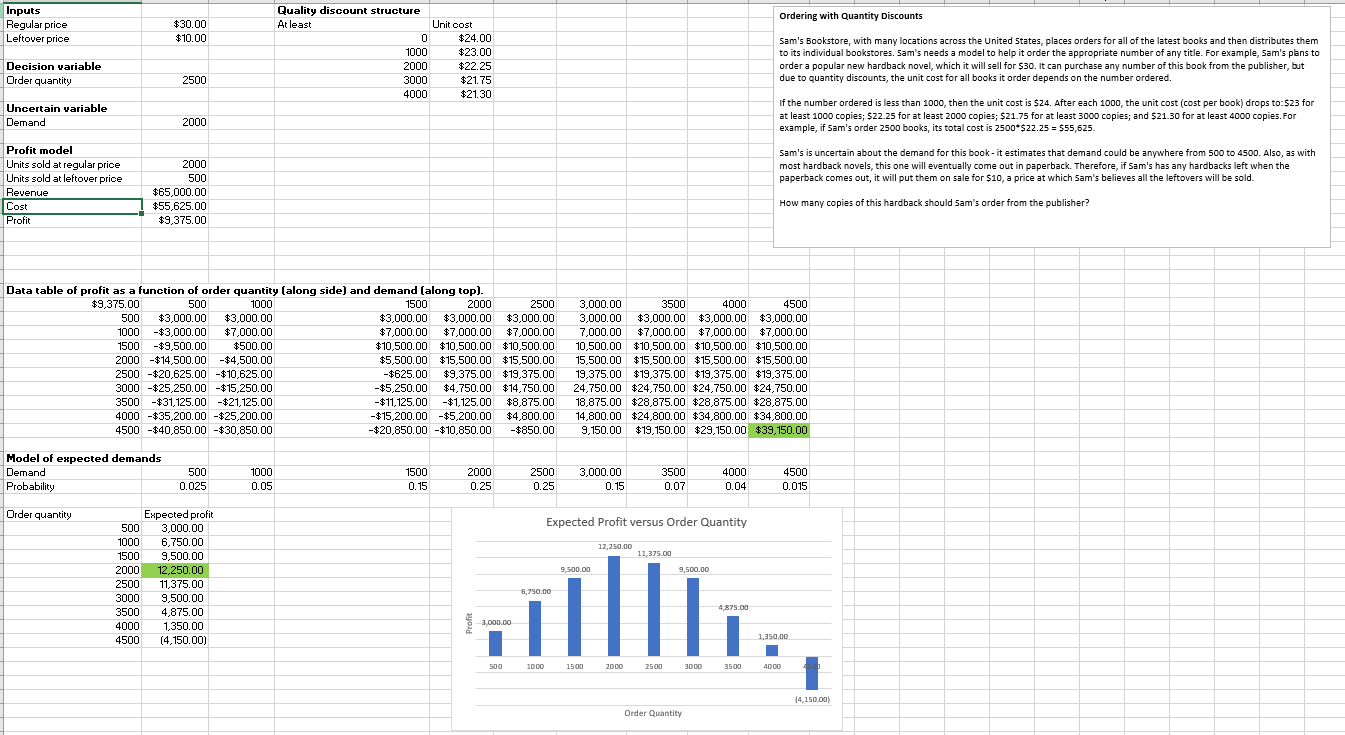
Inputs Regular price Quality discount structure $30.00 At least Unit cost Leftover price $10.00 0 $24.00 1000 $23.00 Decision variable 2000 $22.25 Order quantity 2500 3000 $21.75 4000 $21.30 Uncertain variable Demand 2000 Profit model Units sold at regular price Units sold at leftover price Revenue Cost Profit 2000 500 $65,000.00 $55,625.00 $9,375.00 Ordering with Quantity Discounts Sam's Bookstore, with many locations across the United States, places orders for all of the latest books and then distributes them to its individual bookstores. Sam's needs a model to help it order the appropriate number of any title. For example, Sam's plans to order a popular new hardback novel, which it will sell for $30. It can purchase any number of this book from the publisher, but due to quantity discounts, the unit cost for all books it order depends on the number ordered. If the number ordered is less than 1000, then the unit cost is $24. After each 1000, the unit cost (cost per book) drops to: $23 for at least 1000 copies; $22.25 for at least 2000 copies; $21.75 for at least 3000 copies; and $21.30 for at least 4000 copies. For example, if Sam's order 2500 books, its total cost is 2500*$22.25 = $55,625. Sam's is uncertain about the demand for this book-it estimates that demand could be anywhere from 500 to 4500. Also, as with most hardback novels, this one will eventually come out in paperback. Therefore, if Sam's has any hardbacks left when the paperback comes out, it will put them on sale for $10, a price at which Sam's believes all the leftovers will be sold. How many copies of this hardback should Sam's order from the publisher? Data table of profit as a function of order quantity (along side) and demand (along top). $9,375.00 500 500 $3,000.00 1000 -$3,000.00 1500 -$9,500.00 1000 $3,000.00 $7,000.00 $500.00 2000 -$14,500.00 - $4,500.00 2500 -$20,625.00 - $10,625.00 3000 -$25,250.00 - $15,250.00 3500 -$31,125.00 -$21,125.00 4000 -$35,200.00 - $25,200.00 4500 -$40,850.00 - $30,850.00 1500 2000 2500 $3,000.00 $3,000.00 $3,000.00 $7,000.00 $7,000.00 $7,000.00 $10,500.00 $10,500.00 $10,500.00 $5,500.00 $15,500.00 $15,500.00 -$625.00 $9,375.00 $19,375.00 -$5,250.00 $4,750.00 $14,750.00 -$11,125.00 -$1,125.00 $8,875.00 -$15,200.00 -$5,200.00 $4,800.00 -$20,850.00 - $10,850.00 -$850.00 3,000.00 3500 4000 4500 3,000.00 $3,000.00 $3,000.00 $3,000.00 7,000.00 $7,000.00 $7,000.00 $7,000.00 10,500.00 $10,500.00 $10,500.00 $10,500.00 15,500.00 $15,500.00 $15,500.00 $15,500.00 19,375.00 $19,375.00 $19,375.00 $19,375.00 24,750.00 $24,750.00 $24,750.00 $24,750.00 18,875.00 $28,875.00 $28,875.00 $28,875.00 14,800.00 $24,800.00 $34,800.00 $34,800.00 9,150.00 $19,150.00 $29,150.00 $39,150.00 Model of expected demands Demand 500 Probability 0.025 1000 0.05 Order quantity Expected profit 500 3,000.00 1000 6,750.00 1500 0.15 2000 0.25 2500 0.25 3,000.00 0.15 3500 0.07 4000 0.04 4500 0.015 1500 9,500.00 2000 12,250.00 2500 11,375.00 3000 9,500.00 3500 4,875.00 4000 1,350.00 1 4500 (4,150.00) 3,000.00 6,750.00 Expected Profit versus Order Quantity 9,500.00 12,250.00 11,375.00 9,500.00 4,875.00 1,350.00 500 1000 1500 2000 2500 3000 3500 4000 Order Quantity (4,150.00)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


