Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
It must be done with python. Question 1 80 points 85 mins In this question, you will implement a binary tree according to the following


It must be done with python.
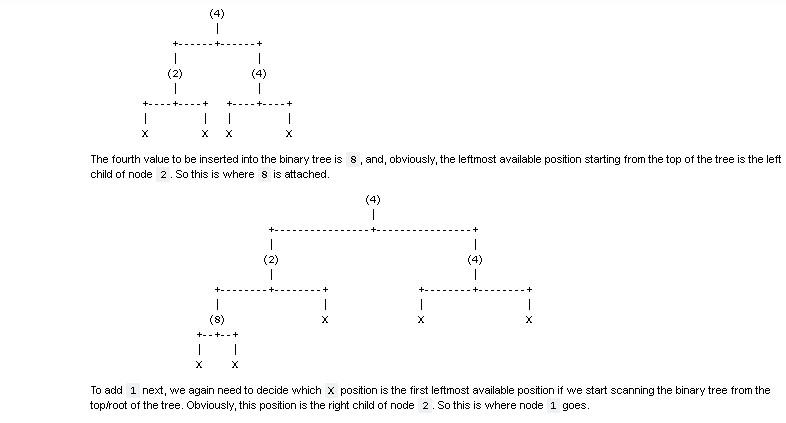
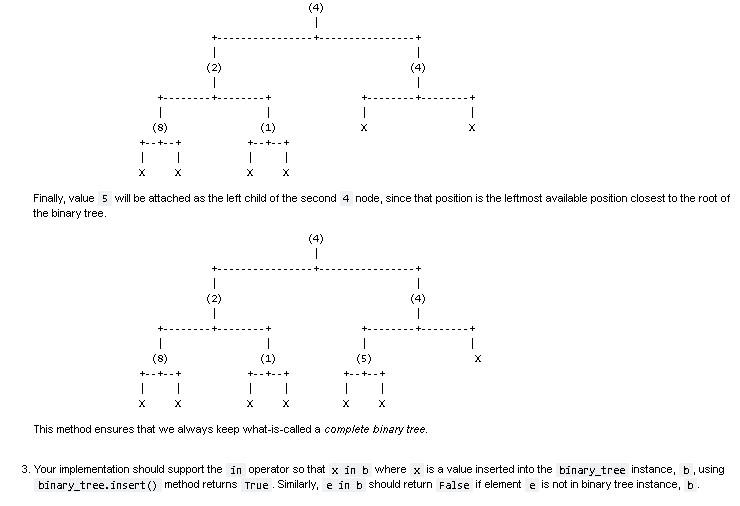
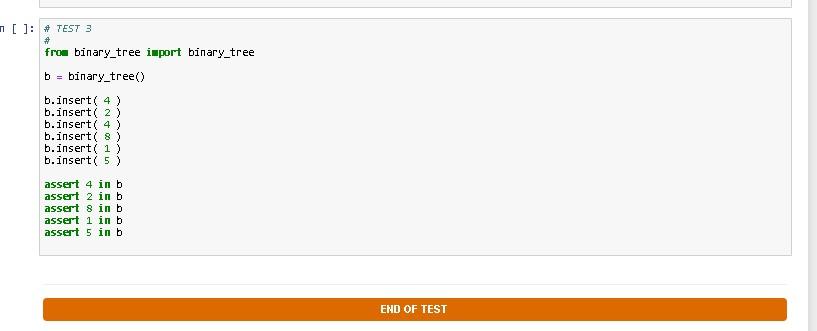
Question 1 80 points 85 mins In this question, you will implement a binary tree according to the following specifications: Implement a Python class named binary_tree that provides the following APls: 1. binary_tree() creates and returns an empty binary tree. Each node of the binary tree should be created as an instance of the bt_node class, whose (partial incomplete) implementation has been provided to you below. The root of the binary must be stored in an instance variable named root. When the tree is empty, the root value must be None. In addition, the bt_node class must support the == operation. 2. binary_tree.insert( self, item ) should unconditionally insert the provided item in the binary tree. This function should insert the new item into the first leftmost position available that is closest to the root of tree. Hint: Consider using iteration/looping to implement this functionality! Example: Consider the following code snippet that adds some values to the binary tree, b: binary_tree() for v in [4, 2, 4, 8, 1, 5]: # b.insert(v) b = Once the root node with value 4 is inserted into the binary tree, we have both of root's children empty. Empty child node positions will be indicated with X characters in the figures below. One node 4 becomes the root of the binary tree being built, we will have the following structure: (4) + 1 1 X Since we need to insert 2 next, we need to attach a new bt_node with value 2 as the left child of 4, since that position is the first available leftmost position with respect to the root of the tree. So now the binary tree will look as follows: 1 1 1 (2) | To add the second 4 value, we need to determine to which x position this value will have to be attached according to the provided specifications. Going from the top to the bottom of the tree, the leftmost available position is the right child of the first 4 node. So we attach the second 4 there: 4) + 1 (2) 1 (4) -+----+ | X 1 X The fourth value to be inserted into the binary tree is 8, and, obviously, the leftmost available position starting from the top of the tree is the left child of node 2. So this is where 8 is attached. 1 1 (2) 1 1 1 +--- 1 (8) +--+--+ | 1 To add 1 next, we again need to decide which x position is the first leftmost available position if we start scanning the binary tree from the top/root of the tree. Obviously, this position is the right child of node 2. So this is where node 1 goes. 1 | (2) 1 1 (1) +--+- 1 X (8) X +--+--+ 1 1 Finally, value 5 will be attached as the left child of the second 4 node, since that position is the leftmost available position closest to the root of the binary tree. 1 +- 1 (2) 1 1 + (8) 1 (1) 1 (5) +--+--+ 1 1 +--+--+ +--+--+ | | 1 X This method ensures that we always keep what-is-called a complete binary tree. 3. Your implementation should support the in operator so that x in b where x is a value inserted into the binary_tree instance, b, using binary_tree.insert() method returns True . Similarly, e in b should return false if element e is not in binary tree instance, b. [ ]: # TEST 3 # from binary_tree import binary_tree binary_tree() b.insert( 4 ) b.insert( 2 ) b.insert( 4 ) b.insert( 8 ) b.insert( 1 ) b.insert( 5 ) assert 4 in b assert 2 in b assert 8 in b assert 1 in b assert 5 in b END OF TESTStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


