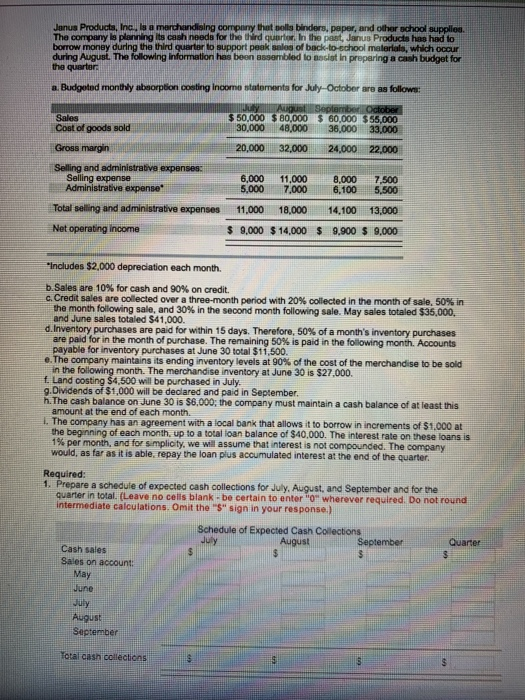
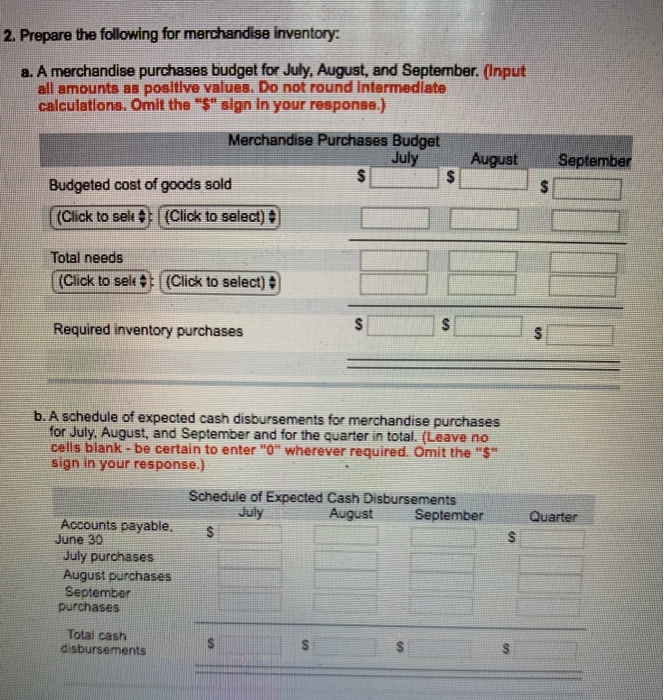
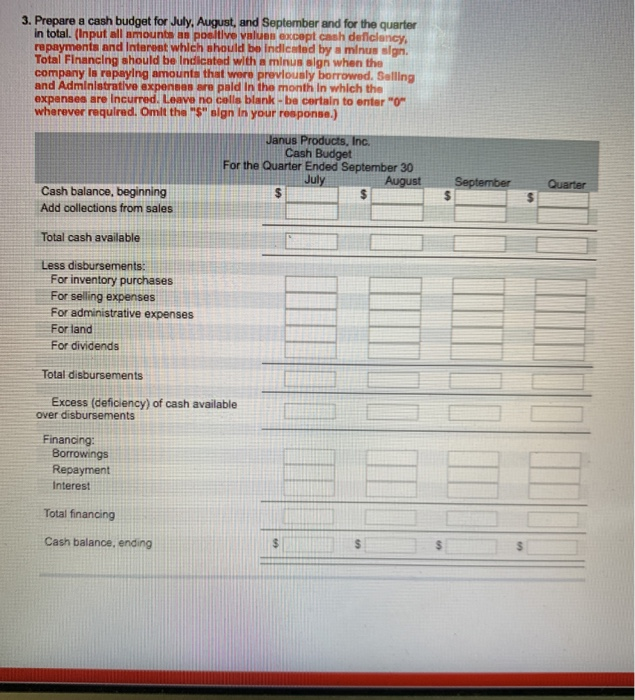
Janus Products, Inc., is a merchandising compuny thet nolls binders, peper, and other school suppliea. The company is planing its cash needs for the third quarter. In the past, Janus Products has had to borrow money during the third quarter to support peak sales of back-to-school malerials, which occur during August. The following information hes been Bssembled to Besist in prepering a cash budget for the quarter a Budgetnd monthly absorption costing incomo ntatements for July October are as follow Sales $ 50,000 $ 80,000 60,000 $55,000 30,000 48,000 36,000 33,000 20,000 32,000 24,000 22,000 Cost of goods sold Gross margin Selling and administrative expenses: Selling expense Administrative expense 6,000 11,000 8000 7,500 5,000 7,000 6,100 5,500 Total selling and administrative expenses 11,000 18,000 14,100 13,000 $ 9,000 $ 14,000 $ 9,900 $ 9,000 Net operating income Includes $2,000 depreciation each month Sales are 10% for cash and 90% on credit. C. Credit sales are colected over a three-month period with 20% collected in the month of sale, 50% in the month follow ng sale, and 30% in the second month following sale. May sales totaled S35,0 and June sales totaled $41,000. d Inventory purchases are paid for within15 days. Therefore, 50% of a month's inventory purchases are paid for in the month of purchase. The rema ning 50% is paid in the following month. Acounts payable for inventory purchases at June 30 total $11,500 e The company maintains its ending inventory levels at 90% ofthe cost of the merchandise to be sold in the month. The merchandise inventory at June 30 is $27,000 f Land costing $4,500 will be purchased in July. g.Dividends of $1,000 will be declared and paid in September. h. The cash balance on June 30 is $8,000; the company must maintain a cash balance of at least this amount at the end of each month. . The company has an agreement with a local bank that allows it to borrow in increments of $1.000 at the beginning of each month, up to a total loan balance of $40.000. The interest rate on these loans is 1% per month, and for smploty. we wla assume that interest is not compounded. The company would, as far as it is able, repay the loan plus accumulated interest at the end of the quarter. Required 1. Prepare a schedule of expected cash collections for July, August, and September and for the quarter in total. (Leave no celis blank - be certain to enter "o" wherever required. Do not round intermediate calculations. Omit the "S" sign in your response.) Schedule of Expected Cash Collections July August September Quarter Cash sales Sales on account May June July August otal cash collecticns 2. Prepare the following for merchandise inventory a. A merchandise purchases budget for July, August, and September. (Input all amounts as positive values. Do not round infermediate calculations. Omlt the " sign in your response.) Merchandise Purchases Budget Jul August September Budgeted cost of goods sold [ (Click to sel (Click to select Total needs (Click to see #1 (Click to select) #] Required inventory purchases b. A schedule of expected cash disbursements for merchandise purchases for July. August, and September and for the quarter in total. (Leave no cells blank -be certain to enter "O" wherever required. Omit the "$" sign in your response.) Schedule of Expected Cash Disbursements July August SeptemberQuarter Accounts payable.s June 30 July purchases August purchases September purchases Total cash disbursements 3. Prepare a cash budget for July, August, and September and for the quarter in total. (Input all amounte as poeltive values except cash deficlancy repayments and Interest which should be Indicated by a minus sign. Total Financing should be Indicated with a minus sign when the company is repaying amounts that were prevlously borrowed. Selling and Administrative expenses ere pald In the month In which the expenses are incurred. Leave no cells blank- be certain to enter O wherever required. Omlt the "S Bign In your response. Cash Budget For the Quarter Ended September 30 July Cash balance, beginning Add collections from sales Total cash available Less disbursements: For inventory purchases For selling expenses For administrative expenses For land For dividends Total disbursements Excess (deficlency) of cash available over disbursements Financing Borrowings Interest Total financing Cash balance, ending