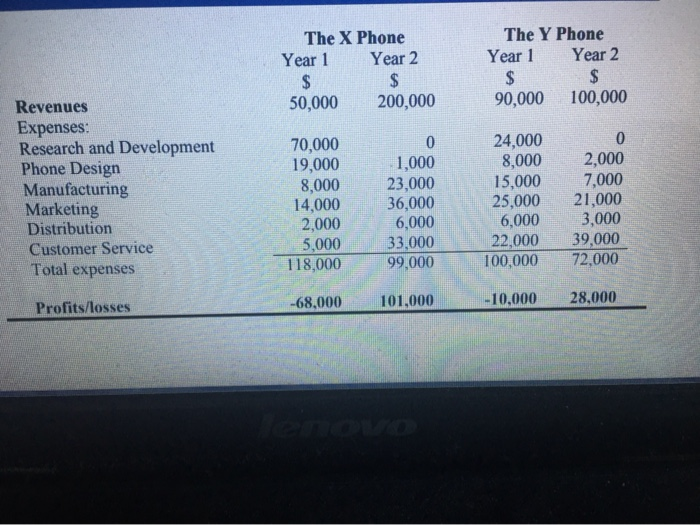
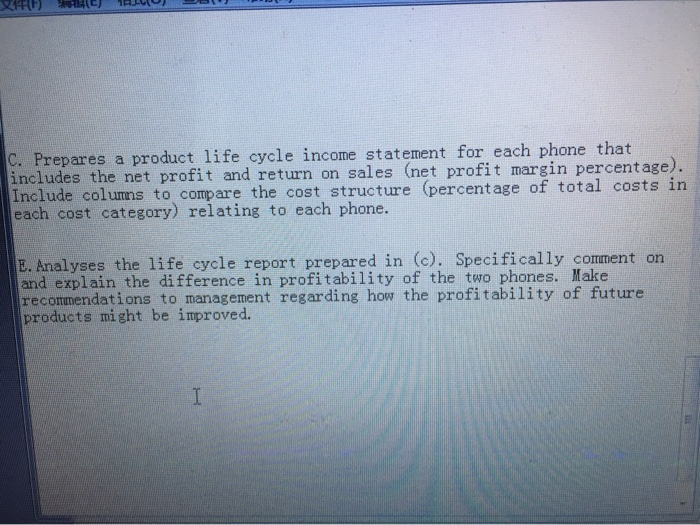
KiwiPhone Ltd designs and manufactures digital cordless phones, which are sold under the "Justaphone trademark direct to the public via the internet. KiwiPhone phones are basic handsets that do not incorporate any answer-phone or other fancy functions and they are marketed on the basis that they just do the job and are "value for money" as they are sold at rock bottom prices. KiwiPhone Ltd use internet and newspaper advertising to market their products and customers order the phones on-line and pay immediately by credit or debit card, for the phone and an additional delivery charge. Phones are despatched from stock within 2 working days of a customer order being placed and are delivered direct to the customer by New Zealand Couriers. You have recently joined KiwiPhone's small management accounting team and your new boss, Maria Manson, is keen that you pass on what you know about modern management accounting techniques. She has seen Shank and Govindarajan's Strategic Cost Management" described as a technique that improves the strategic position of a business organisation and reduces cost at the same time but is unsure how this is possible. Hence, she has asked you to prepare a brief report to explain what Strategic Cost Management is, how it might be used by KiwiPhone Ltd, and how it might be of benefit. KiwiPhone is concerned about recent increases in Research and Development (R&D) costs and the costs of designing new handsets. The marketing manager says: "We sell a basic handset and compete mainly on price and hence it is a waste of money spending so much on R&D." Your boss explains that the product life cycle of a handset has become shorter and is now only two years. In addition, records show that although handsets make losses in their first year they are profitable in their second year. She gives you data relating to two typical handsets that have just come to the end of their life eyele and asks you to produce an appropriate life cycle report and interpretit The X Phone Year 1 Year 2 $ $ 50,000 200,000 The Y Phone Year 1 Year 2 $ $ 90,000 100,000 Revenues Expenses: Research and Development Phone Design Manufacturing Marketing Distribution Customer Service Total expenses 70,000 19,000 8,000 14,000 2,000 5,000 118,000 0 1,000 23,000 36,000 6,000 33,000 99,000 24,000 8,000 15,000 25,000 6,000 22,000 100,000 0 2,000 7,000 21,000 3,000 39,000 72,000 Profits/losses -68,000 101,000 -10,000 28,000 C. Prepares a product life cycle income statement for each phone that includes the net profit and return on sales (net profit margin percentage). Include columns to compare the cost structure (percentage of total costs in each cost category) relating to each phone. E. Analyses the life cycle report prepared in (c). Specifically comment on and explain the difference in profitability of the two phones. Make recommendations to management regarding how the profitability of future products might be improved