Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
LHSV = 6 Required: a) Draw a qualitative flow sheet showing the main and auxiliary units in the process b)The molar composition of the product
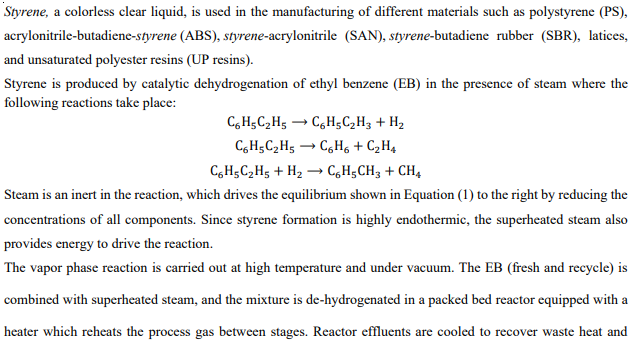

LHSV = 6
Required:
a) Draw a qualitative flow sheet showing the main and auxiliary units in the process
b)The molar composition of the product gas exit from the reactor and the selectivity of styrene for toluene and benzene production.
c) Calculate the flow rate of recycled ethylbenzene and state the function of the recycle stream and its effect on the process performance. d)The heat load on the reactor internal heaters.
e) The reactor volume
Styrene, a colorless clear liquid, is used in the manufacturing of different materials such as polystyrene (PS), acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene (ABS), styrene-acrylonitrile (SAN), styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR), latices, and unsaturated polyester resins (UP resins). Styrene is produced by catalytic dehydrogenation of ethyl benzene (EB) in the presence of steam where the following reactions take place: CHEC2Hs CHC2H3 + H2 CH3C2H5 CH + C2H4 CH5C,H3 + H2 CHCH3 + CH4 Steam is an inert in the reaction, which drives the equilibrium shown in Equation (1) to the right by reducing the concentrations of all components. Since styrene formation is highly endothermic, the superheated steam also provides energy to drive the reaction. The vapor phase reaction is carried out at high temperature and under vacuum. The EB (fresh and recycle) is combined with superheated steam, and the mixture is de-hydrogenated in a packed bed reactor equipped with a heater which reheats the process gas between stages. Reactor effluents are cooled to recover waste heat and condense the hydrocarbons and steam. Uncondensed off gas containing mostly hydrogen is compressed and is used as fuel or recovered as a valuable byproduct. Condensed hydrocarbons after being separated in an oil/water gravity separator are sent to the distillation section. A fractionation train (two towers) separates high-purity styrene product; unconverted EB, which is recycled. The mixture of EB, toluene and benzene are sent to a distillation tower where unreacted EB is separated as a bottom product and sent to the reactor. Benzene and toluene are separated in the next distillation tower. The following data are available: Feed rate of ethylbenzene = 500 kmol/h. The process achieves up to about 90% EB conversion per pass. The reaction yield is 80 %. The flow rate of toluene = 33 kmol/h and the recovery for all products is 90%. The specific heat of reaction is 125 kJ/mol. Density of ethylbenzene = 835 kg/m? Styrene, a colorless clear liquid, is used in the manufacturing of different materials such as polystyrene (PS), acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene (ABS), styrene-acrylonitrile (SAN), styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR), latices, and unsaturated polyester resins (UP resins). Styrene is produced by catalytic dehydrogenation of ethyl benzene (EB) in the presence of steam where the following reactions take place: CHEC2Hs CHC2H3 + H2 CH3C2H5 CH + C2H4 CH5C,H3 + H2 CHCH3 + CH4 Steam is an inert in the reaction, which drives the equilibrium shown in Equation (1) to the right by reducing the concentrations of all components. Since styrene formation is highly endothermic, the superheated steam also provides energy to drive the reaction. The vapor phase reaction is carried out at high temperature and under vacuum. The EB (fresh and recycle) is combined with superheated steam, and the mixture is de-hydrogenated in a packed bed reactor equipped with a heater which reheats the process gas between stages. Reactor effluents are cooled to recover waste heat and condense the hydrocarbons and steam. Uncondensed off gas containing mostly hydrogen is compressed and is used as fuel or recovered as a valuable byproduct. Condensed hydrocarbons after being separated in an oil/water gravity separator are sent to the distillation section. A fractionation train (two towers) separates high-purity styrene product; unconverted EB, which is recycled. The mixture of EB, toluene and benzene are sent to a distillation tower where unreacted EB is separated as a bottom product and sent to the reactor. Benzene and toluene are separated in the next distillation tower. The following data are available: Feed rate of ethylbenzene = 500 kmol/h. The process achieves up to about 90% EB conversion per pass. The reaction yield is 80 %. The flow rate of toluene = 33 kmol/h and the recovery for all products is 90%. The specific heat of reaction is 125 kJ/mol. Density of ethylbenzene = 835 kg/mStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


