Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
MAE 241 - Spring 2023 - Homework 2 Administered 01/20/2023 - Due Sunday 01/29/2023, 11:59 PM to Gradescope Problem 1 (20 points) As you



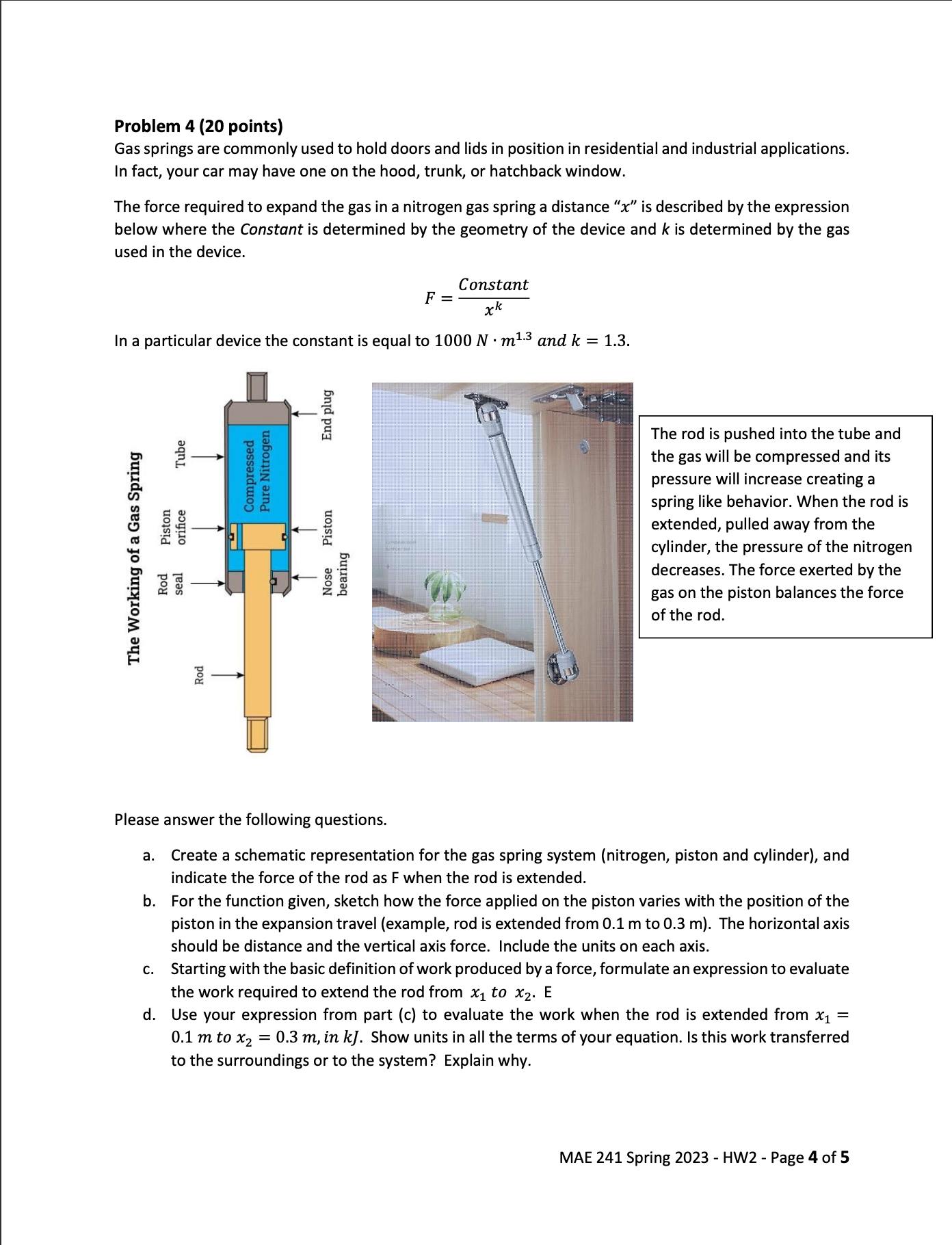

MAE 241 - Spring 2023 - Homework 2 Administered 01/20/2023 - Due Sunday 01/29/2023, 11:59 PM to Gradescope Problem 1 (20 points) As you may recall from lectures in chapter 2, there are different types of transport of energy by work, one of them related to the change in volume in a closed system, referred to as "boundary work." The assembly shown in the figure below represents a conventional frictionless piston cylinder- device, initially in thermodynamic equilibrium. The atmospheric pressure and ambient temperature are 100 kPa and 27C, respectively. Consider that the inside diameter of the cylinder is "D," and the assembly is filled with an inert gas. Also, the seal between the piston and the cylinder walls is very good such that there are no gas leaks and the friction between the piston and the cylinder walls is very small (negligible). a. For the initial condition, what would be the temperature of the gas? Justify and explain your answer. P atm = 100 kPa T = 27C amb Piston Inert Gas D Cylinder Heating Element Electrical Wires b. Next, a heating element of negligible thickness and volume, placed inside the cylinder is turned on for 15 minutes, and delivers heat continuously at a rate of 250 Joules every second. Of that energy, 80% is taken by gas and 20% is exchanged with the surroundings. Create a schematic representation for the system that includes the gas and the energy interactions between the system and its surroundings. Please identify all the directions of energy transport across a boundary and explain why or how you chose the direction. C. For the situation in part (b), is the system in thermodynamic equilibrium? Why? Which forms of equilibrium are present? d. During the 15 minutes when heat is applied to the device, the cylinder moves slowly such that the changes of state can be considered in quasi-equilibrium process. Indicate the direction of motion of the piston. e. After 15 minutes, the heating element is turned off and you notice that the volume occupied by the gas increased by 15%. Determine the energy released by the heating element in kJ. f. Based on temperature measurements you conclude that the internal energy of the gas has increased by 100 kJ. Using the First Law of Thermodynamics, determine the work done by the gas, in kJ, and the direction of energy transport. MAE 241 Spring 2023 - HW2 - Page 1 of 5 Problem 2 (20 points) Fans are mechanical devices used to move air in industrial ventilation applications. In this situation you have an electrical motor that steadily powers a fan, see illustration below. The shaft of the motor is coupled to the fan shaft such that both rotate at an angular speed equal to 600 RPM; a torque equal to 8 N-m is transferred from the motor shaft to the compressor shaft. Please answer the following questions. a. Estimate the shaft power for the motor, in Watt and in hp. b. As the air passes through the fan blades, it experiences an increase in pressure equal to 2 kPa. The inlet and exit diameters for the fan are such that the inlet and exit velocities for the air are approximately equal; also, the inlet and exit are at the same elevation. Because of the small pressure difference for the air between the inlet and exit, it is reasonably justified from ideal gas law to assume that the densities at both places are approximately equal to 1.20 kg/m. Using symbols defined by you in which subscript 1 denotes the inlet and subscript 2 the exit of the air, write in literal form a general expression that can be used to compute the mass flow rate of air. For terms in your equation that can be neglected or canceled, include the justification. Hint: use the rate of change of mechanical energy for the air and relate it to mechanical work. C. If the efficiency of the fan is 75%. Determine the maximum air mass flow rate that can be transported by the fan, in kg/min. d. Determine the minimum efficiency for a 0.75 hp electrical motor that could be used to move the mass flow rate of air computed in part (c). e. Compute the combined efficiency for the assembly of motor and fan. Shaft Air Motor Fan MAE 241 Spring 2023 - HW2 - Page 2 of 5 Problem 3 (20 points) The wall of a storage shed is made with a 1 in thick layer of plywood facing the outdoors and another layer of asbestos-cement board 5 mm thick, separated by a layer of air equal to 50 mm. The outside temperature of the air is To = 40C during a night in which the inside temperature of the air inside the shed is T = 70C, and the inside surface of the wall temperature is Tiw = 60C. The heat transfer coefficient by convection for the air in contact with the external surface of the wall is assumed equal to h = 5; and the thermal conductivity values for the materials used to build the W m.C, , wall are: kplywood 0.12; W m.ockair = 0.030 , kasb-cem = 0.58 W m.C Assume steady-state conditions W m.C for the situation presented. Please answer the following. a. Show a schematic representation of the composite wall with its layers for the different materials. Indicate the thickness for each material and the direction of transport of heat. Explain why heat gets transported in the direction you chose. b. For the conditions given in this scenario, estimate the heat transfer rate per unit of surface of wall, in W/m. Hint: for steady-state, the rate of heat transfer across each layer is equal and constant. Start by writing the heat transfer rate equation for each layer whether heat convection or heat conduction. MAE 241 Spring 2023 - HW2 - Page 3 of 5 The Working of a Gas Spring Problem 4 (20 points) Gas springs are commonly used to hold doors and lids in position in residential and industrial applications. In fact, your car may have one on the hood, trunk, or hatchback window. The force required to expand the gas in a nitrogen gas spring a distance "x" is described by the expression below where the Constant is determined by the geometry of the device and k is determined by the gas used in the device. In a particular device the constant is equal to 1000 N m.3 and k = 1.3. Compressed Pure Nitrogen Rod seal Piston orifice Tube Rod Nose Piston End plug bearing F = Constant xk The rod is pushed into the tube and the gas will be compressed and its pressure will increase creating a spring like behavior. When the rod is extended, pulled away from the cylinder, the pressure of the nitrogen decreases. The force exerted by the gas on the piston balances the force of the rod. Please answer the following questions. a. Create a schematic representation for the gas spring system (nitrogen, piston and cylinder), and indicate the force of the rod as F when the rod is extended. b. For the function given, sketch how the force applied on the piston varies with the position of the piston in the expansion travel (example, rod is extended from 0.1 m to 0.3 m). The horizontal axis should be distance and the vertical axis force. Include the units on each axis. c. Starting with the basic definition of work produced by a force, formulate an expression to evaluate the work required to extend the rod from x to x2. E d. Use your expression from part (c) to evaluate the work when the rod is extended from x = 0.1 m to x2 = 0.3 m, in kJ. Show units in all the terms of your equation. Is this work transferred to the surroundings or to the system? Explain why. MAE 241 Spring 2023 - HW2 - Page 4 of 5 Problem 5 (20 points) - Self-Assessment Conduct a self-assessment of Problem 4 from Written Homework 1. Please refer to the Self-Assessment Rubric and the Self-Assessment Example documents on Canvas for guidance on how to perform the self- assessment. Here is a brief overview of the self-assessment procedure: 1. Consult the Written Homework 1 solution (posted on Canvas) and use the provided rubric (Self- Assessment Rubric document on Canvas) to give yourself a score (1-5) in each of the 3 major rubric categories. For each score you give, provide justification/reasoning for the score. 2. Rework OR extend your solution, depending on your self-assessment score. a. If you score yourself below a 13/15 on the self-assessment, you must rework your previous solution, correcting the areas of improvement you identified. b. If you score yourself at 13/15 or better on the self-assessment, you must extend the problem of interest in some meaningful way. There are many ways to extend problems in a meaningful way, but here are some examples of things that are not considered meaningful: i. Simply changing the numbers. ii. Changing the physical system so that it looks different but leads to identical analysis. MAE 241 Spring 2023 - HW2 - Page 5 of 5
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


