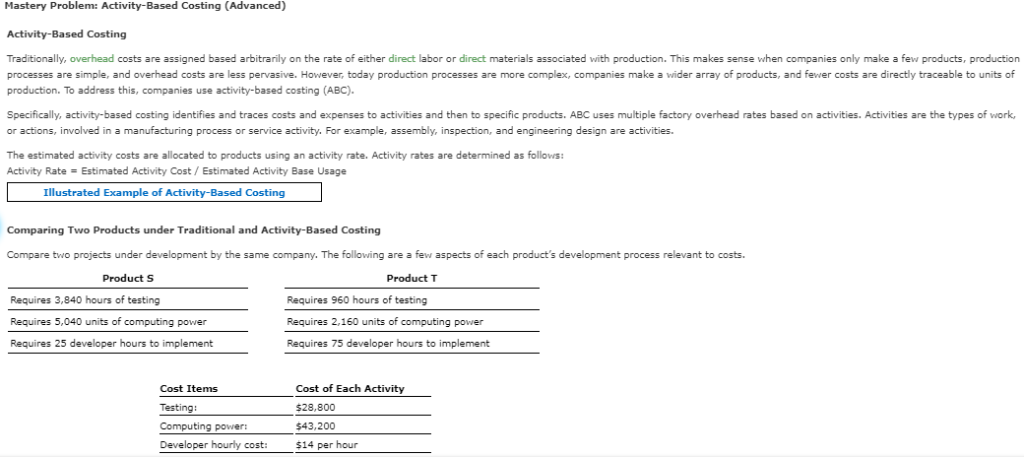
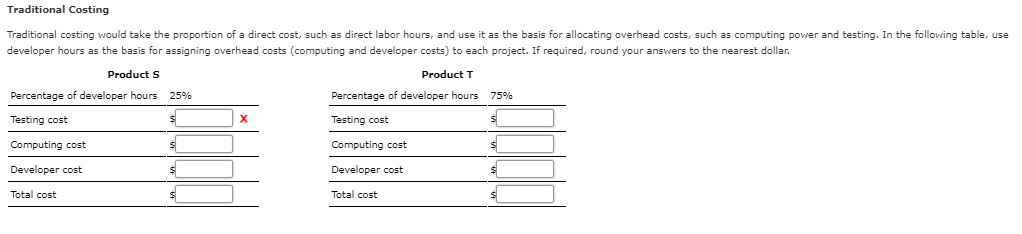
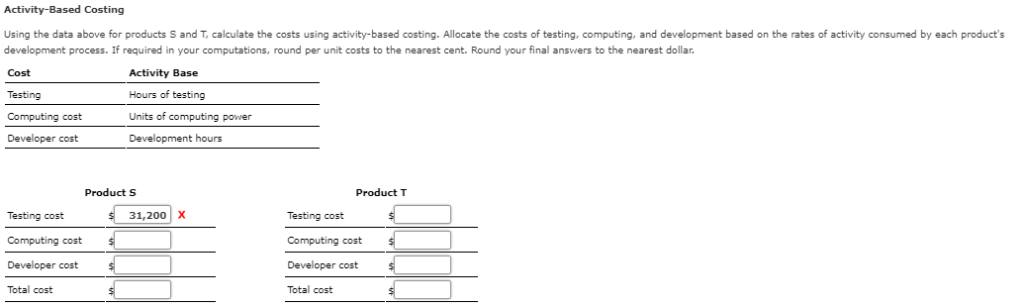

Mastery Problem: Activity-Based Costing (Advanced) Activity-Based Costing direct materials associated with production. This makes sense when companies only make a few products, production Traditionally, overhead costs are assigned based arbitrarily on the rate of either direct labor processes are simple, and overhead costs are less pervasive. However, today production processes are more complex, companies make a wider array of products, and fewer costs are directly traceable units of production. To address this, companies use activity-based costing (ABC). Specifically, activity-based costing identifies and traces costs and expenses to activities and then to specific products. ABC uses multiple factory overhead rates based on activities. Activities are the types of work, or actions, involved in a manufacturing process or service activity. For example, assembly, inspection, and engineering design are activities. The estimated activity costs are allocated to products using an activity rate. Activity rates are determined as follows: Activity Rate Estimated Activity Cost/ Estimated Activity Base Usage Illustrated Example of Activity-Based Costing Comparing Two Products under Traditional and Activity-Based Costing Compare two projects under development by the same company. The following are a few aspects each product's development process relevant to costs. Product S Product T Requires 3,840 hours of testing Requires 960 hours testing Requires 5,040 units of computing power Requires 2,160 units of computing power Requires 25 developer hours to implement Requires 75 developer hours to implement Cost of Each Activity Cost Items Testing: $28.800 Computing powers $43,200 Developer hourly cost $14 per hour Traditional Costing Traditional costing would take the proportion of a direct cost, such as direct labor hours, and use it as the basis for allocating overhead costs, such as computing power and testing. In the following table, use developer hours as the basis for assigning overhead costs (computing and developer costs) to each project. If required, round your answers t the nearest dollar Product S Product Percentage of developer hours Percentage of developer hours 25% 75% Testing cost X Testing cost Computing cost Computing cost Developer cost Developer cost Total cost Total cost Activity-Based Costing Using the data above for products S and T, calculate the costs using activity-based costing. Allocate the costs development process. If required i f testing, computing, and development based on the rates activity consumed by each product's your computations, round per unit costs to the nearest cent. Round your final answers the nearest dollar Cost Activity Base Hours of testing Testing Units of computing power Computing cost Developer cost Development hours Product S Product T X 31,200 Testing cost Testing cost Computing cost Computing cost Developer cost Developer cost Total cost Total cost Activity-based costing for varying batch production A manufacturing company has the following two activities associated with completion of products: machines for running batches of products 1. The setting up 2. The actual production of units produced The company has annual manufacturing overhead costs of $2.000,000, of which $200.000 is directly involved in setting up machines for batch runs. During the vear, the company expects to perform 400 machine setups, one setup per batch for a total of 400 batches f production. Assume that the batch sizes vary considerably, but the work involved in setting up the machines is not appreciably different from one job to the next. If the company estimates that the $200,000 costs associated with setups will yield 400 setups this year, the cost associated directly with each setup will be s per setup. Because each job will require its own setup, setup costs are viewed as batch costs. Because $200,000 f the $2,000,000 are costs associated with setups, this means that costs associated directly with the production of units equal s










