Question
Morton Companys budgeted variable manufacturing overhead is $2.50 per direct labor-hour and its budgeted fixed manufacturing overhead is $180,000 per year. The company manufactures a
Morton Companys budgeted variable manufacturing overhead is $2.50 per direct labor-hour and its budgeted fixed manufacturing overhead is $180,000 per year.
The company manufactures a single product whose standard direct labor-hours per unit is 2.5 hours. The standard direct labor wage rate is $10 per hour. The standards also allow 3 feet of raw material per unit at a standard cost of $7 per foot.
Although normal activity is 60,000 direct labor-hours each year, the company expects to operate at a 50,000-hour level of activity this year.
4. Assume that the company actually produces 21,200 units and works 54,000 direct labor-hours during the year. Actual manufacturing overhead costs for the year are:
| Variable manufacturing overhead cost | $ | 136,000 |
| Fixed manufacturing overhead cost | 181,500 | |
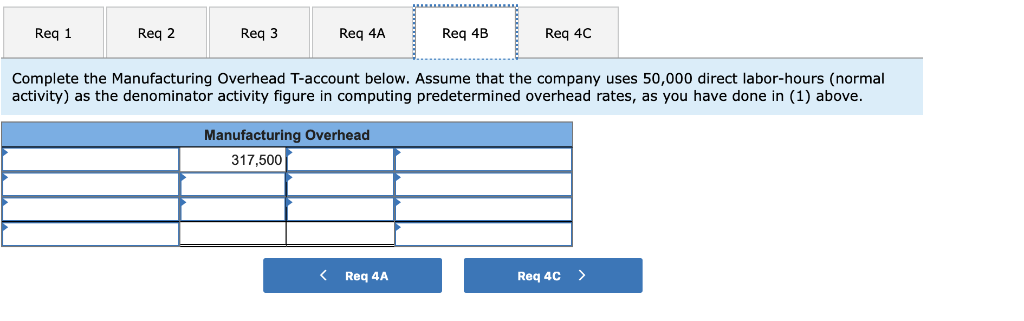
| Total manufacturing overhead cost | $ | 317,500 |
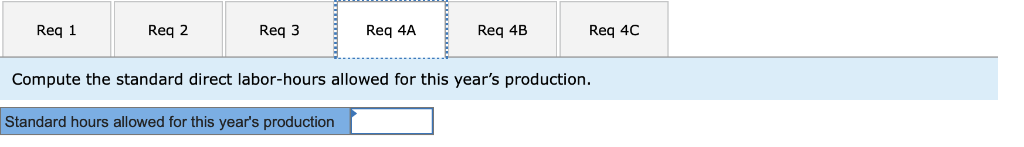
a. Compute the standard direct labor-hours allowed for this years production.
b. Complete the Manufacturing Overhead T-account below. Assume that the company uses 50,000 direct labor-hours (normal activity) as the denominator activity figure in computing predetermined overhead rates, as you have done in (1) above.
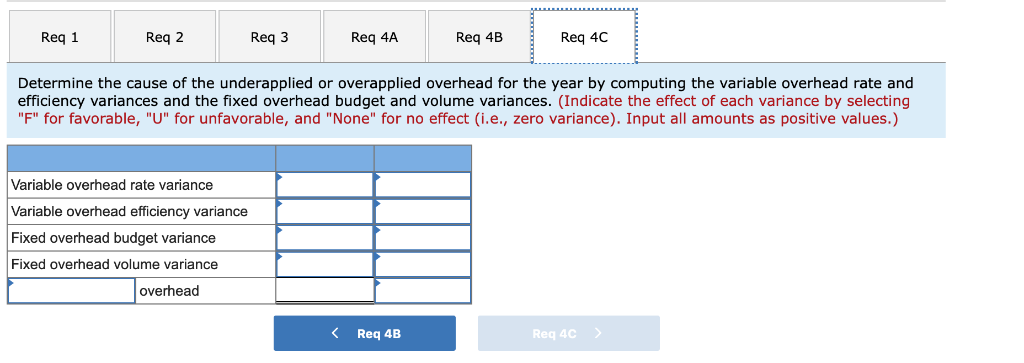
c. Determine the cause of the underapplied or overapplied overhead for the year by computing the variable overhead rate and efficiency variances and the fixed overhead budget and volume variances.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


