Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
m/staticb/ui/evo/index.html?deploymentid=5953162386137714123236765163&ISBN=9780357114582&snapshotid= MINDTAP Q Search this cours Assessment where they experience different growth rates during different parts of the cycle. For valuing these firms, the generalized
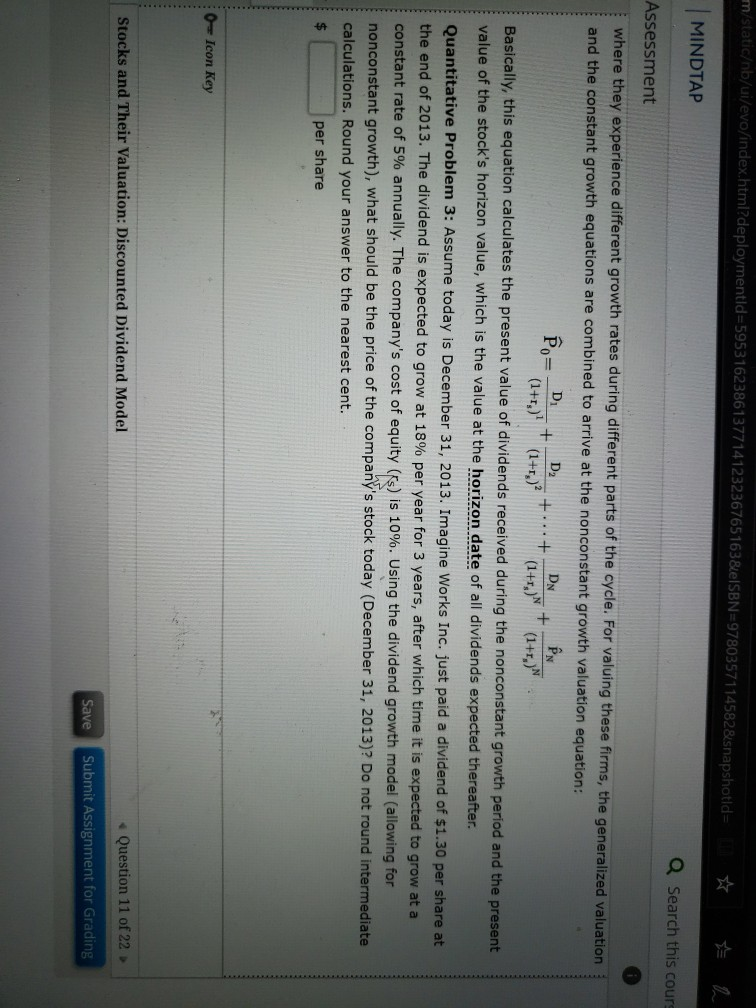
m/staticb/ui/evo/index.html?deploymentid=5953162386137714123236765163&ISBN=9780357114582&snapshotid= MINDTAP Q Search this cours Assessment where they experience different growth rates during different parts of the cycle. For valuing these firms, the generalized valuation and the constant growth equations are combined to arrive at the nonconstant growth valuation equation: D for D2 DN N + +...+ + (1+1) (1+r)? (1+r) (1+r,)N. Basically, this equation calculates the present value of dividends received during the nonconstant growth period and the present value of the stock's horizon value, which is the value at the horizon date of all dividends expected thereafter. Quantitative Problem 3: Assume today is December 31, 2013. Imagine Works Inc. just paid a dividend of $1.30 per share at the end of 2013. The dividend is expected to grow at 18% per year for 3 years, after which time it is expected to grow at a constant rate of 5% annually. The company's cost of equity (ks) is 10%. Using the dividend growth model (allowing for nonconstant growth), what should be the price of the company's stock today (December 31, 2013)? Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to the nearest cent. $ per share 0 Icon Key Stocks and Their Valuation: Discounted Dividend Model Question 11 of 22 Save Submit Assignment for Grading
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


