N.B: Coding for this task must be done by using the software 'Vivado'
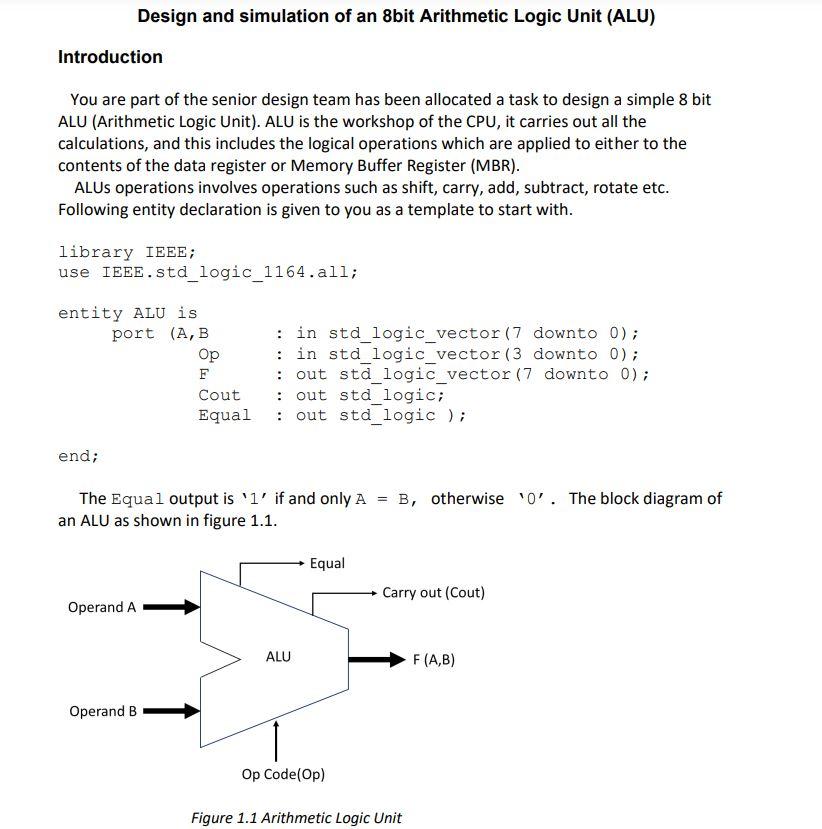
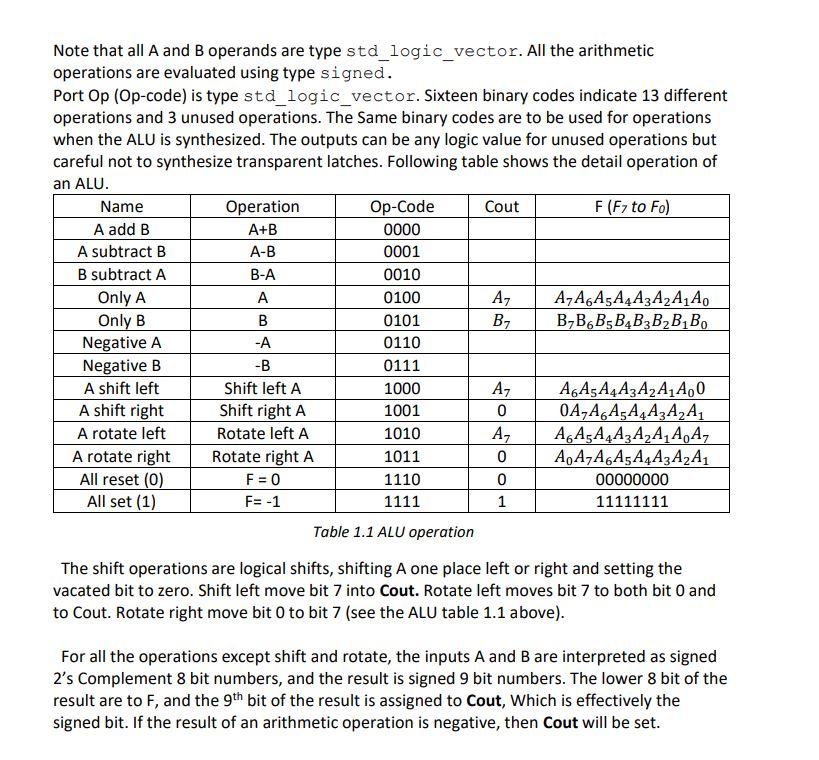
Design and simulation of an 8bit Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) Introduction You are part of the senior design team has been allocated a task to design a simple 8 bit ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit). ALU is the workshop of the CPU, it carries out all the calculations, and this includes the logical operations which are applied to either to the contents of the data register or Memory Buffer Register (MBR). ALUs operations involves operations such as shift, carry, add, subtract, rotate etc. Following entity declaration is given to you as a template to start with. library IEEE; use IEEE.std_logic_1164.all; entity ALU is port (A,B : in std_logic_vector (7 downto 0); Op : in std_logic_vector (3 downto 0); F : out std_logic_vector (7 downto 0); Cout : out std_logic; Equal : out std_logic ); end; B, otherwise '0'. The block diagram of The Equal output is 'l' if and only A an ALU as shown in figure 1.1. Equal Carry out (Cout) Operand A ALU F(A,B) Operand B Op Code(Op) Figure 1.1 Arithmetic Logic Unit Note that all A and B operands are type std_logic_vector. All the arithmetic operations are evaluated using type signed. Port Op (Op-code) is type std_logic_vector. Sixteen binary codes indicate 13 different operations and 3 unused operations. The Same binary codes are to be used for operations when the ALU is synthesized. The outputs can be any logic value for unused operations but careful not to synthesize transparent latches. Following table shows the detail operation of an ALU. Name Operation Op-Code Cout F (Fy to Fo) A add B A+B 0000 A subtract B A-B 0001 B subtract A B-A 0010 Only A A 0100 A7A6A5A4A3A2A1A0 Only B B 0101 B2 B B B5B4B3B2BB. Negative A -A 0110 Negative B -B 0111 A shift left Shift left A 1000 Az AGASA4A3A2A1A00 A shift right Shift right A 1001 0 0AAGA5A4A2A2A1 A rotate left Rotate left A 1010 A7 A6A5A4A2A,A,A,A, A rotate right Rotate right A 1011 0 A0A7A6A5A4A3A2A1 All reset (0) F = 0 1110 0 00000000 All set (1) F= -1 1111 1 11111111 Table 1.1 ALU operation Az 6 The shift operations are logical shifts, shifting A one place left or right and setting the vacated bit to zero. Shift left move bit 7 into Cout. Rotate left moves bit 7 to both bit 0 and to Cout. Rotate right move bit O to bit 7 (see the ALU table 1.1 above). For all the operations except shift and rotate, the inputs A and B are interpreted as signed 2's Complement 8 bit numbers, and the result is signed 9 bit numbers. The lower 8 bit of the result are to F, and the 9th bit of the result is assigned to Cout, Which is effectively the signed bit. If the result of an arithmetic operation is negative, then Cout will be set








