Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
need help plz asap for accounting Activity-Based Costing for a Service Company Crosswinds Hospital plans to use activity-based costing to assign hospital indirect costs to
need help plz asap for accounting 

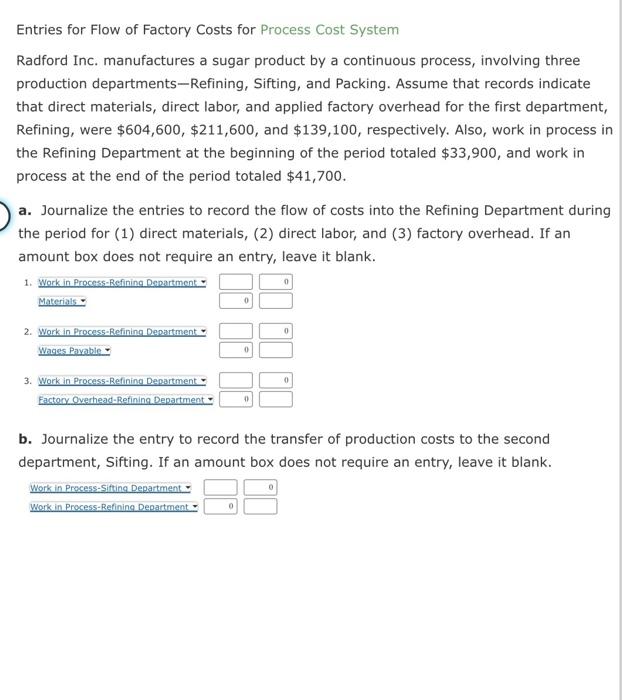

Activity-Based Costing for a Service Company Crosswinds Hospital plans to use activity-based costing to assign hospital indirect costs to the care of patients. The hospital has identified the following activities and activity rates for the hospital indirect costs: The activity usage information associated with the two patients is as follows: a. Determine the activity cost associated with each patient. Abel Putin $ Cheryl Umit b. Why is the total activity cost different for the two patients? apparently had a different condition that required more extensive treatment. Thus, the activity cost to is more than the activity cost of the other patient. Entries for Flow of Factory Costs for Process Cost System Radford Inc. manufactures a sugar product by a continuous process, involving three production departments-Refining, Sifting, and Packing. Assume that records indicate that direct materials, direct labor, and applied factory overhead for the first department, Refining, were $604,600,$211,600, and $139,100, respectively. Also, work in process in the Refining Department at the beginning of the period totaled $33,900, and work in process at the end of the period totaled $41,700. a. Journalize the entries to record the flow of costs into the Refining Department during the period for (1) direct materials, (2) direct labor, and (3) factory overhead. If an amount box does not require an entry, leave it blank. b. Journalize the entry to record the transfer of production costs to the second department, Sifting. If an amount box does not require an entry, leave it blank. Single Plantwide and Multiple Production Department Factory Overhead Rate Methods: and Product Cost Distortion The management of Nova Industries Inc. manufactures gasoline and diesel engines through two production departments, Fabrication and Assembly. Management needs accurate product cost information in order to guide product strategy. Presently, the company uses a single plantwide factory overhead rate for allocating factory overhead to the two products. However, management is considering the multiple production department factory overhead rate method. The following factory overhead was budgeted for Nova: Direct labor hours were estimated as follows: In addition, the direct labor hours (dih) used to produce a unit of each product in each department were determined from engineering records, as follows: a. Determine the per-unit factory overhead allocated to the gasoline and diesel engines under the single plantwide factory overhead rate method, using direct labor hours as the activity base. b. Determine the per-unit factory overhead allocated to the gasoline and diesel engines under the multiple production department factory overhead rate method, using direct labor hours as the activity base for each department. c. Recommend to management a product costing approach, based on your analyses in (a) and (b). Management should select the overhead costs. The products have the same factory overhead per unit. Each product uses the direct labor hours Thus, the accounting for the overhead factory overhead rate method of allocating factory overhead rate method indicates that both rate method avoids the cost distortions by Equivalent Units of Production and Related Costs The charges to Work in Process-Assembly Department for a period, together with information concerning production, are as follows. All direct materials are placed in process at the beginning of production. Determine the following: a. The number of units in work in process inventory at the end of the period. units b. Equivalent units of production for direct materials and conversion. If an amount is zero or a blank, enter in " 0 ". Work in Process-Assembly Department Equivalent Units of Production for Direct Materials and Conversion Costs c. Costs per equivalent unit for direct materials and conversion. If required, round your answers to the nearest cent. d. Cost of the units started and completed during the period. Activity-Based Costing for a Service Company Crosswinds Hospital plans to use activity-based costing to assign hospital indirect costs to the care of patients. The hospital has identified the following activities and activity rates for the hospital indirect costs: The activity usage information associated with the two patients is as follows: a. Determine the activity cost associated with each patient. Abel Putin $ Cheryl Umit b. Why is the total activity cost different for the two patients? apparently had a different condition that required more extensive treatment. Thus, the activity cost to is more than the activity cost of the other patient. Entries for Flow of Factory Costs for Process Cost System Radford Inc. manufactures a sugar product by a continuous process, involving three production departments-Refining, Sifting, and Packing. Assume that records indicate that direct materials, direct labor, and applied factory overhead for the first department, Refining, were $604,600,$211,600, and $139,100, respectively. Also, work in process in the Refining Department at the beginning of the period totaled $33,900, and work in process at the end of the period totaled $41,700. a. Journalize the entries to record the flow of costs into the Refining Department during the period for (1) direct materials, (2) direct labor, and (3) factory overhead. If an amount box does not require an entry, leave it blank. b. Journalize the entry to record the transfer of production costs to the second department, Sifting. If an amount box does not require an entry, leave it blank. Single Plantwide and Multiple Production Department Factory Overhead Rate Methods: and Product Cost Distortion The management of Nova Industries Inc. manufactures gasoline and diesel engines through two production departments, Fabrication and Assembly. Management needs accurate product cost information in order to guide product strategy. Presently, the company uses a single plantwide factory overhead rate for allocating factory overhead to the two products. However, management is considering the multiple production department factory overhead rate method. The following factory overhead was budgeted for Nova: Direct labor hours were estimated as follows: In addition, the direct labor hours (dih) used to produce a unit of each product in each department were determined from engineering records, as follows: a. Determine the per-unit factory overhead allocated to the gasoline and diesel engines under the single plantwide factory overhead rate method, using direct labor hours as the activity base. b. Determine the per-unit factory overhead allocated to the gasoline and diesel engines under the multiple production department factory overhead rate method, using direct labor hours as the activity base for each department. c. Recommend to management a product costing approach, based on your analyses in (a) and (b). Management should select the overhead costs. The products have the same factory overhead per unit. Each product uses the direct labor hours Thus, the accounting for the overhead factory overhead rate method of allocating factory overhead rate method indicates that both rate method avoids the cost distortions by Equivalent Units of Production and Related Costs The charges to Work in Process-Assembly Department for a period, together with information concerning production, are as follows. All direct materials are placed in process at the beginning of production. Determine the following: a. The number of units in work in process inventory at the end of the period. units b. Equivalent units of production for direct materials and conversion. If an amount is zero or a blank, enter in " 0 ". Work in Process-Assembly Department Equivalent Units of Production for Direct Materials and Conversion Costs c. Costs per equivalent unit for direct materials and conversion. If required, round your answers to the nearest cent. d. Cost of the units started and completed during the period 



Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


