Question
********************node1.h************** ******************node1.cpp*************** #include Node.h #include // Provides assert #include // Provides NULL and size_t using namespace std; namespace main_savitch_5{ size_t list_length( const node* head_ptr) //

********************node1.h**************
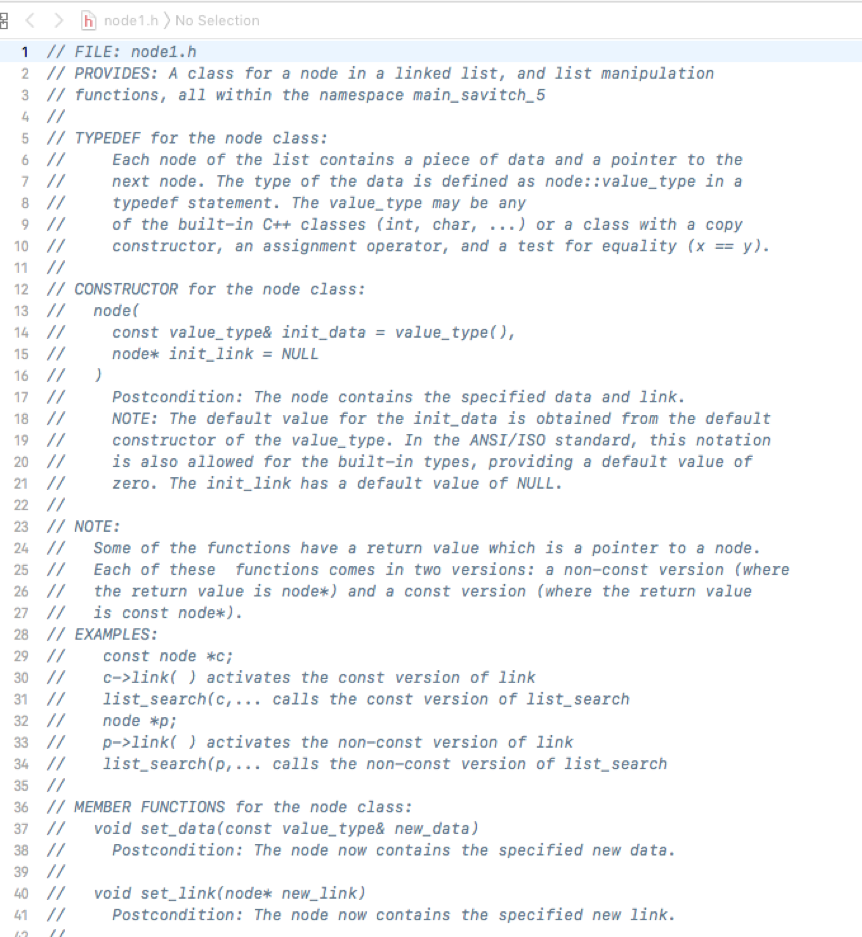

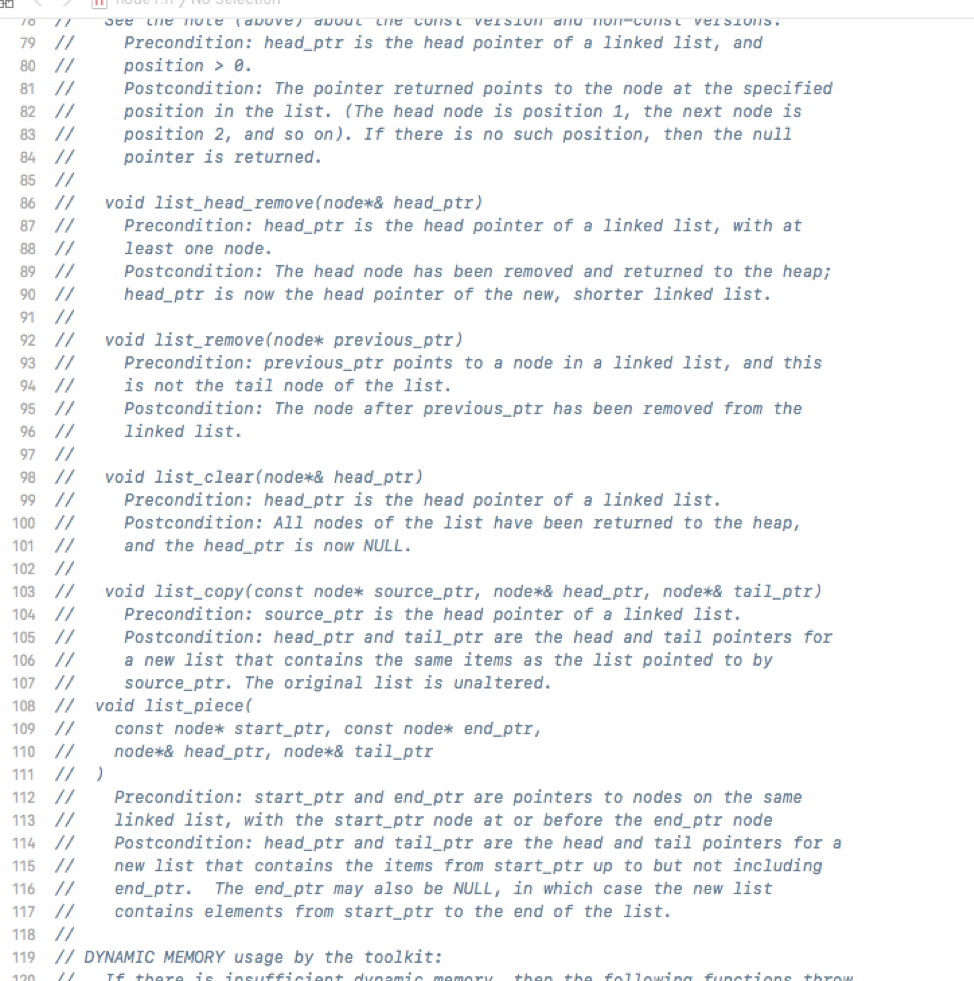
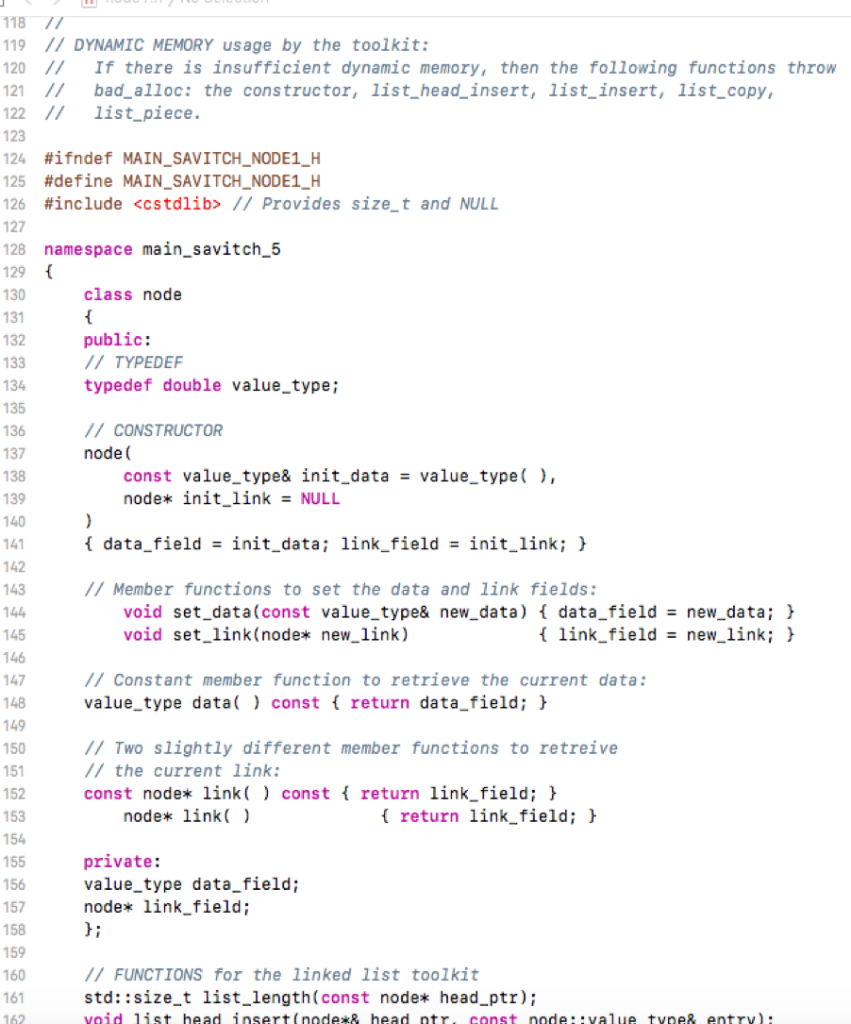
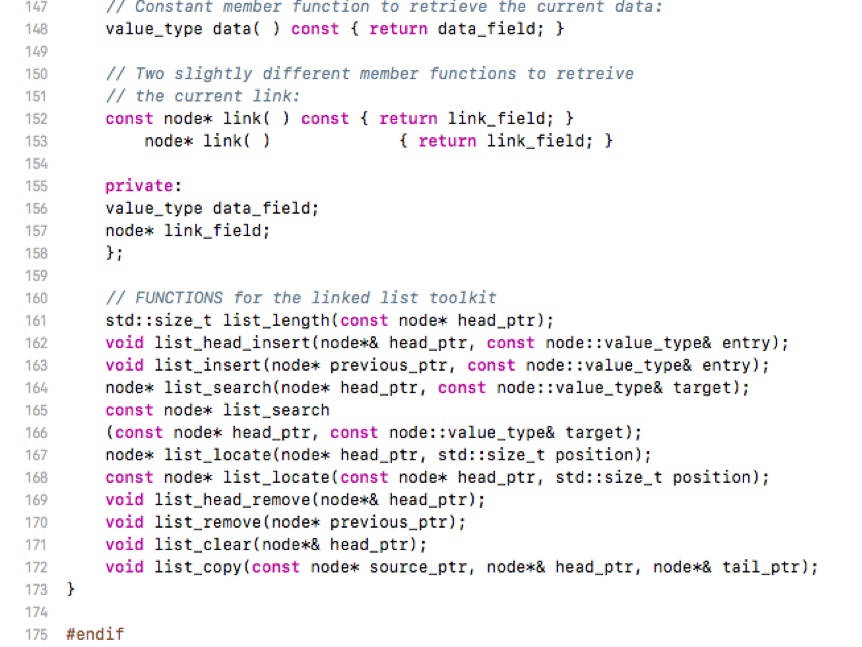
******************node1.cpp***************
#include "Node.h"
#include
#include
using namespace std;
namespace main_savitch_5{
size_t list_length(const node* head_ptr)
// Library facilities used: cstdlib {
const node *cursor;
size_t answer;
answer = 0;
for (cursor = head_ptr; cursor != NULL; cursor = cursor->link( ))
++answer;
return answer; }
void list_head_insert(node*& head_ptr, const node::value_type& entry){
head_ptr = new node(entry, head_ptr); }
void list_insert(node* previous_ptr, const node::value_type& entry){
node *insert_ptr;
insert_ptr = new node(entry, previous_ptr->link( ));
previous_ptr->set_link(insert_ptr); }
node* list_search(node* head_ptr, const node::value_type& target)
// Library facilities used: cstdlib {
node *cursor;
for (cursor = head_ptr; cursor != NULL; cursor = cursor->link( ))
if (target == cursor->data( ))
return cursor;
return NULL; }
const node* list_search(const node* head_ptr, const node::value_type& target)
// Library facilities used: cstdlib {
const node *cursor;
for (cursor = head_ptr; cursor != NULL; cursor = cursor->link( ))
if (target == cursor->data( ))
return cursor;
return NULL;}
node* list_locate(node* head_ptr, size_t position)
// Library facilities used: cassert, cstdlib{
node *cursor;
size_t i;
assert (0
cursor = head_ptr;
for (i = 1; (i NULL); i++)
cursor = cursor->link( );
return cursor;}
const node* list_locate(const node* head_ptr, size_t position)
// Library facilities used: cassert, cstdlib {
const node *cursor;
size_t i;
assert (0
cursor = head_ptr;
for (i = 1; (i NULL); i++)
cursor = cursor->link( );
return cursor;}
void list_head_remove(node*& head_ptr){
node *remove_ptr;
remove_ptr = head_ptr;
head_ptr = head_ptr->link( );
delete remove_ptr; }
void list_remove(node* previous_ptr){
node *remove_ptr;
remove_ptr = previous_ptr->link( );
previous_ptr->set_link( remove_ptr->link( ) );
delete remove_ptr; }
void list_clear(node*& head_ptr)
// Library facilities used: cstdlib{
while (head_ptr != NULL)
list_head_remove(head_ptr);}
void list_copy(const node* source_ptr, node*& head_ptr, node*& tail_ptr)
// Library facilities used: cstdlib {
head_ptr = NULL;
tail_ptr = NULL;
// Handle the case of the empty list.
if (source_ptr == NULL)
return;
// Make the head node for the newly created list, and put data in it.
list_head_insert(head_ptr, source_ptr->data( ));
tail_ptr = head_ptr;
// Copy the rest of the nodes one at a time, adding at the tail of new list.
source_ptr = source_ptr->link( );
while (source_ptr != NULL){
list_insert(tail_ptr, source_ptr->data( ));
tail_ptr = tail_ptr->link( );
source_ptr = source_ptr->link( );}
}
}
***********************sequence3.h******************
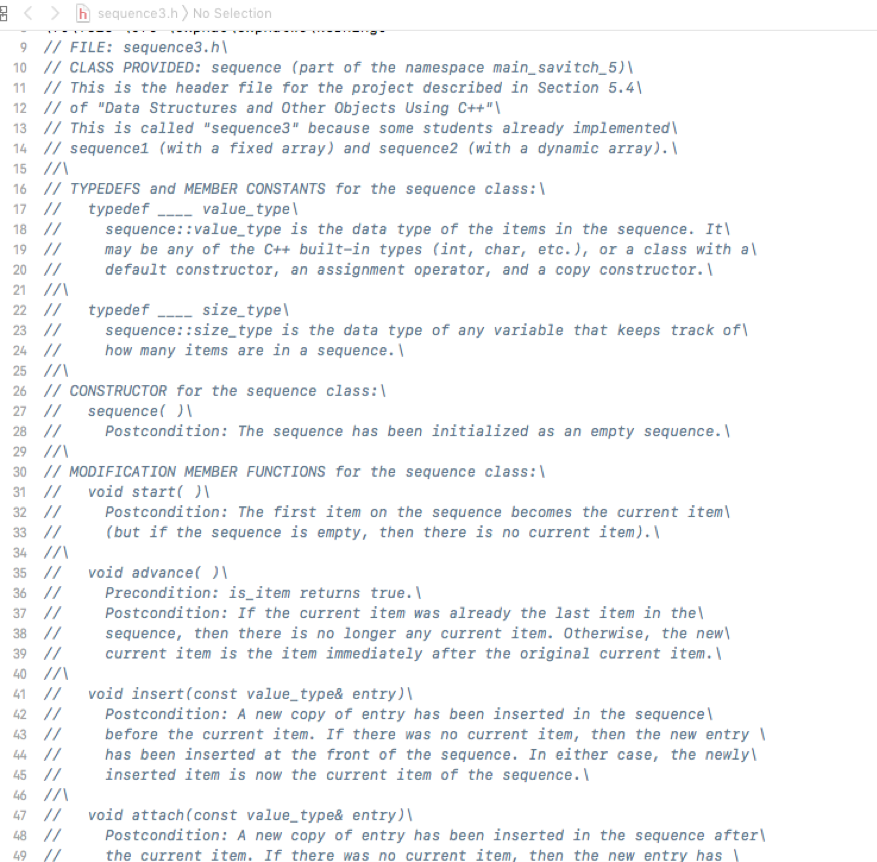

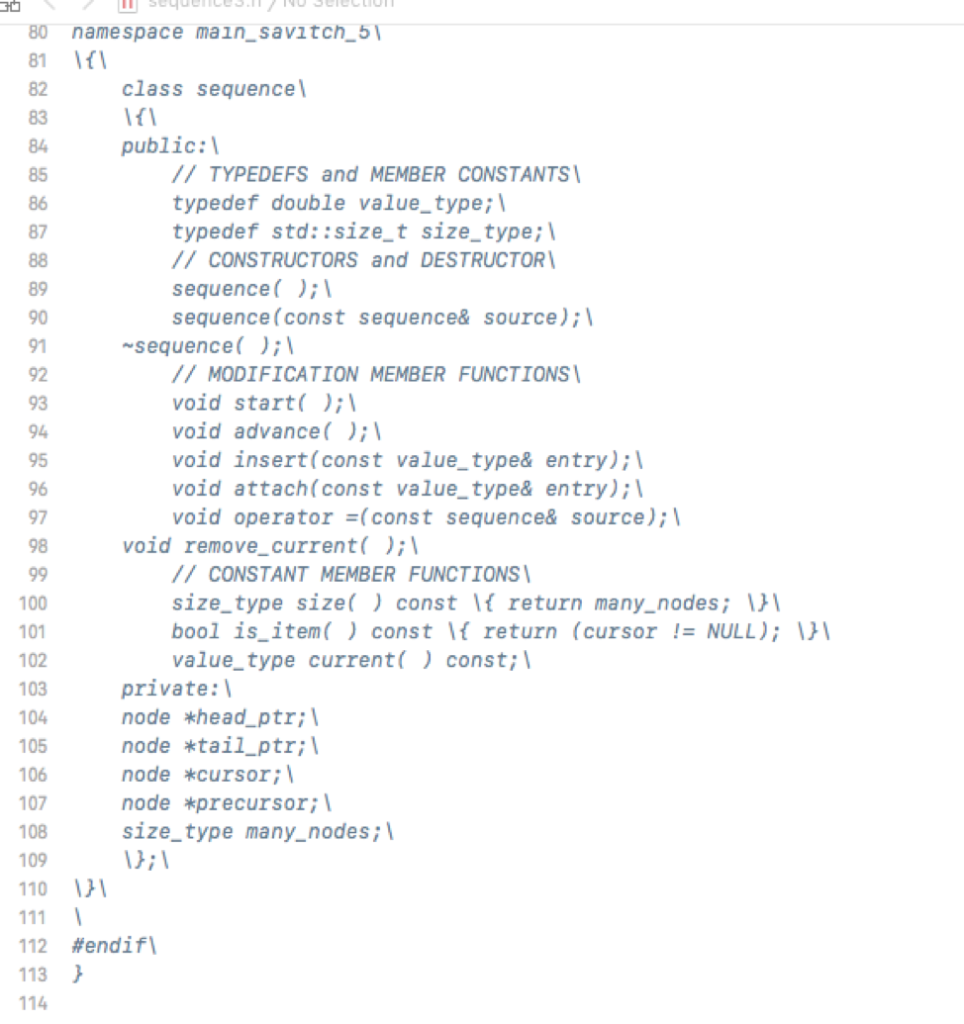
*******************sequence3.cpp*******************(partially implemented file)----should implement the listed functions on the question at the beginning
#include
#include "sequence3.h"
namespace main_savitch_5{
sequence::sequence(){
head_ptr = NULL;
tail_ptr = NULL;
precursor = NULL;
cursor = head_ptr;
many_nodes = 0;}
sequence::sequence(const sequence& source){
// Implement this function
/*** use list copy to copy the node values from source to
* current sequence * setting the cursor and pre-cursor: * you need to traverse the source sequence to see* which node the cursor for source is pointing to.
* then use list_locate to get the same(number) node and* have the cursor point to it in the current sequence* use similar process to get the previous node to the cursor
* and have precursor point to it* set many_nodes = source.many nodes ****/
}
sequence::~sequence(){
many_nodes = 0;
list_clear(head_ptr);}
void sequence::start(){
cursor = head_ptr;}
void sequence::advance(){
assert(is_item());
precursor = cursor;
cursor = cursor -> link();}
void sequence::insert(const value_type &entry){
/****** if the sequence is empty, insert the head node * using list_head_insert. Then set the cursor to * point to the new node
* precursor should be NULL * check to see if cursor is at the head node * or if it is NULL. insert at the head of the list
* cursor is = head_ptr and precursor should be NULL *else, insert the new node* before the cursor and after the precursor calling
* list_insert. recgnize which pointer points to the * previous node* set cusor to the new node
* precursor will not need to be moved * * increment many_node * *******/
}
void sequence::attach(const value_type &entry){
//Implement this function
/**** You need to check 3 mutually exclusive conditions for attach*****/ /**** check if head_ptr == NULL (empty list) **** call list_head_insert(head_ptr, entry)
**** set tail_ptr and cursor = head_ptr**** set precursor to NULL as precursor always points to the previous node to cursor
**** increment the many_nodes counter*****/ /**** else check is if cursor == NULL or if cursor== tail_ptr the attach will happen at the end of the list
**** call list_insert(tail_ptr, entry)**** set precursor to tail ptr**** set move tail_ptr to the next node**** set cursor to tail_ptr
**** increment many_node****//*** if neither of the above conditions are true then the attach needs to happen in the middle of the list
**** call list_insert(cursor, entry)**** set precursor = cursor **** move cursor to the next node**** increment many_nodes
****/
}
void sequence:: operator =(const sequence &source)
{
if (this == &source) {
return;}
list_clear(head_ptr);
many_nodes = 0;
int index = 1;
for(cursor = source.head_ptr; cursor != source.cursor; cursor = cursor -> link()){
index++; }
list_copy(source.head_ptr, head_ptr, tail_ptr);
cursor = list_locate(head_ptr, (size_t) index);
if(index == 1){
precursor = NULL; }
else{
precursor = list_locate(head_ptr, (size_t) index - 1);}
many_nodes = source.many_nodes;}
void sequence::remove_current(){
//Implement this function
/*** if empty list i.e. head_ptr == NULL then return ***//*** if cursor points to the head node (cursor == head_ptr)**** move head_ptr to next node
**** call list_head_remove(cursor)**** set cursor = head_ptr****decrement many_nodes****/
/**** else call list_remove(precursor) - this causes the current node pointed to by cursor to be deleted***** make cursor point to the node = precursor->link()
****decrement many-nodes***/
}
sequence::value_type sequence::current() const{
assert(is_item());
return cursor -> data();}
}
The purpose of this lab is to help reinforce linked list concepts in C++ Specifically, the lab to repeat the "sequence" lab except to use a linked list. Note that there is no upper bound on the size of the sequence. You need to use author's header file and test file. sequence3.h and sequence exam3.cpp and the nodel.h and nodel.cpp files. You will be provided with a partially implemented sequence3.cpp. Your assignment includes: 1. Implement copy constructor, insert, attach and remove_current functions. 2. understand the implementation of the other functions for this sequence class. 8 h node1.h No Selection 1 //FILE: node1.h 2 II PROVIDES:A class for a node in a linked list, and list manipulation 3 I/ functions, all within the namespace main savitch5 4 5 ITYPEDEF for the node class: Each node of the list contains a piece of data and a pointer to the next node. The type of the data is defined as node::value_type in a typedef statement. The value type may be any 9IIof the built-in C++ classes (int, char, ...) or a class with a copy constructor, an assignment operator, and a test for equality (x y) 12 CONSTRUCTOR for the node class: 13node( const value_type& init datavalue_type) node* init linkNULL 15 / 16 II) Postcondition: The node contains the specified data and link. NOTE: The default value for the init data is obtained from the default constructor of the value_type. In the ANSI/ISO standard, this notation is also allowed for the built-in types, providing a default value of zero. The init link has a default value of NULL 21 / 22 II 23 /I NOTE 24 IISome of the functions have a return value which is a pointer to a node. 25 I/Each of these functions comes in two versions: a non-const version (where 26 I/the return value is nodex) and a const version (where the return value 27 I/is const node*). 28 II EXAMPLES: 9 IIconst node *c 30 // ->link( ) activates the const version of link 31 IIlist search(c,... calls the const version of list search 32 node *p 33 p->link) activates the non-const version of link 34 IIlist search p,... cal1s the non-const version of list search 36 /MEMBER FUNCTIONS for the node class: 37 IIvoid set data(const value_type& new data) Postcondition: The node now contains the specified new data 40 IIvoid set_link(node* new link) 41 Postcondition: The node now contains the specified new link. h node1.h No Selection Postcondition: The node now contains the specified new data. 39 / 40 IIvoid set link(node* new link) Postcondition: The node now contains the specified new link. 42 / 43 IIvalue type datal const 4 I 45 / 46 I1const node link const e. Postcondition: The pointer returned points to the node at the specified position in the list. (The head node is position 1, the next node is position 2, and so on). If there is no such position, then the null pointer is returned. 86 IIvoid list head_remove(node*& head ptr) Precondition: head_ptr is the head pointer of a linked list, with at least one node. Postcondition: The head node has been removed and returned to the heapi head ptr is now the head pointer of the new, shorter linked list. 92 IIvoid list_remove(node* previous_ptr) Precondition: previous ptr points to a node in a linked list, and this is not the tail node of the list. Postcondition: The node after previous ptr has been removed from the linked list. 98 IIvoid list clear(node*&head ptr) 99 II Precondition: head ptr is the head pointer of a linked list. Postcondition: Al1 nodes of the list have been returned to the heap, and the head_ptr is now NULL 103 Ivoid list_copy(const node* source_ptr, nodex& head_ptr, nodex& tail_ptr) 04// 105/1 106 /1 Precondition: source_ptr is the head pointer of a linked list. Postcondition: head ptr and tail ptr are the head and tail pointers for a new list that contains the same items as the list pointed to by source_ptr. The original list is unaltered. 08void list piece 109 IIconst nodex start_ptr, const node* end ptr, 110 IInode*& head ptr, nodex& tail ptr 112 IIPrecondition: start_ptr and end_ptr are pointers to nodes on the same 113 IIinked list, with the start_ptr node at or before the end ptr node 114 IIPostcondition: head ptr and tail ptr are the head and tail pointers for a 115 IInew list that contains the items from start_ptr up to but not including 116 IIend ptr. The end ptr may also be NULL,in which case the new list 117 IIcontains elements from start_ptr to the end of the list. 119 I/ DYNAMIC MEMORY Usage by the toolkit: 19 // DYNAMIC MEMORY Usage by the toolkit: 20IIf there is insufficient dynamic memory, then the following functions throw 21 IIbad_alloc: the constructor, list head insert, list insert, list_copy, 22 IIlist piece. 123 124 #ifndef MAIN-SAV ITCH-NODE1_A 125 #define MAIN-SAVITCH NODE1_A 126 #includeStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


