Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
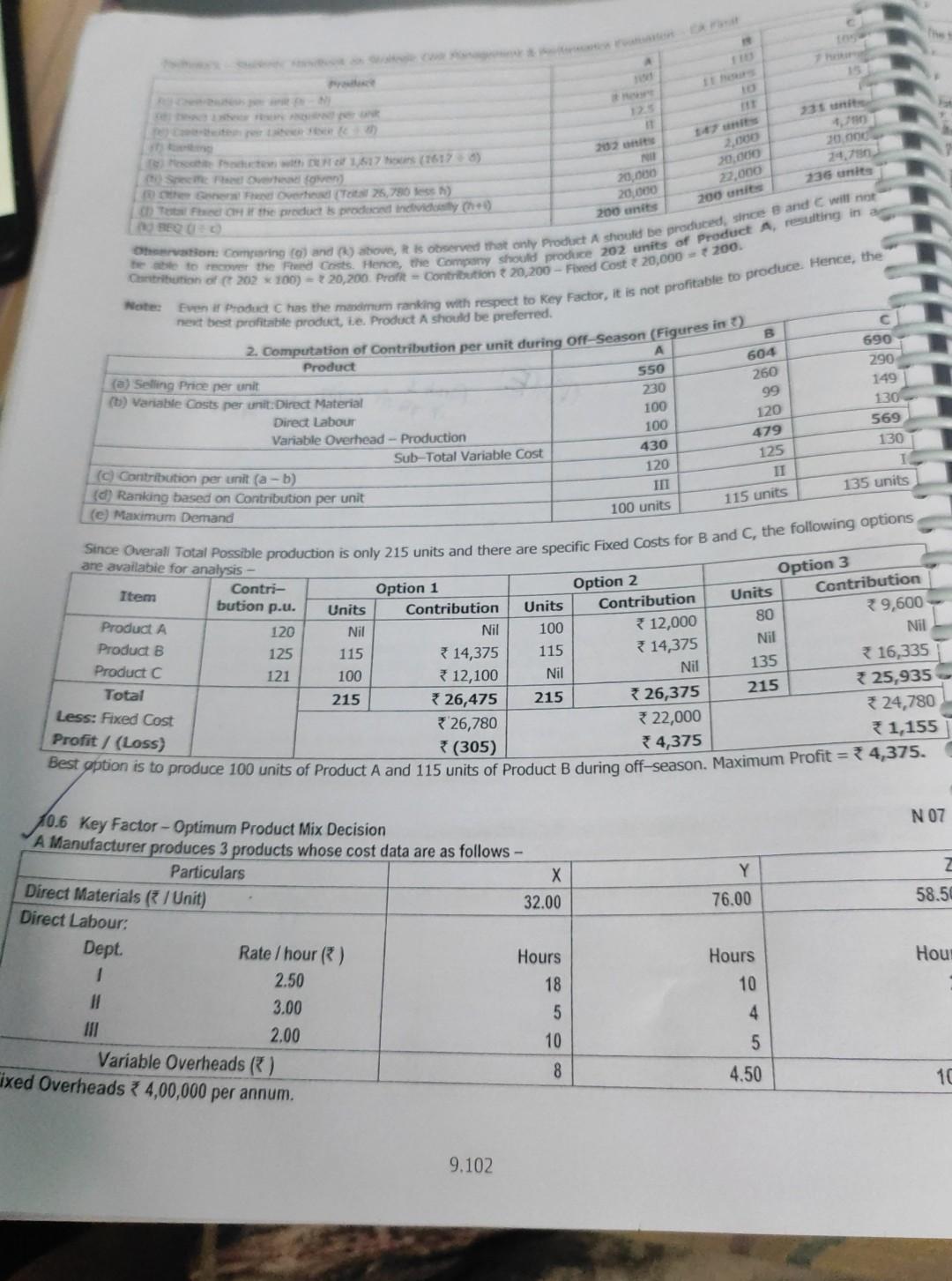
Notes and project report on a 202 30.0 24,790 236 units 20.000 22.000 200 units 20.000 20.000 200 units A 550 230 100 100 Power
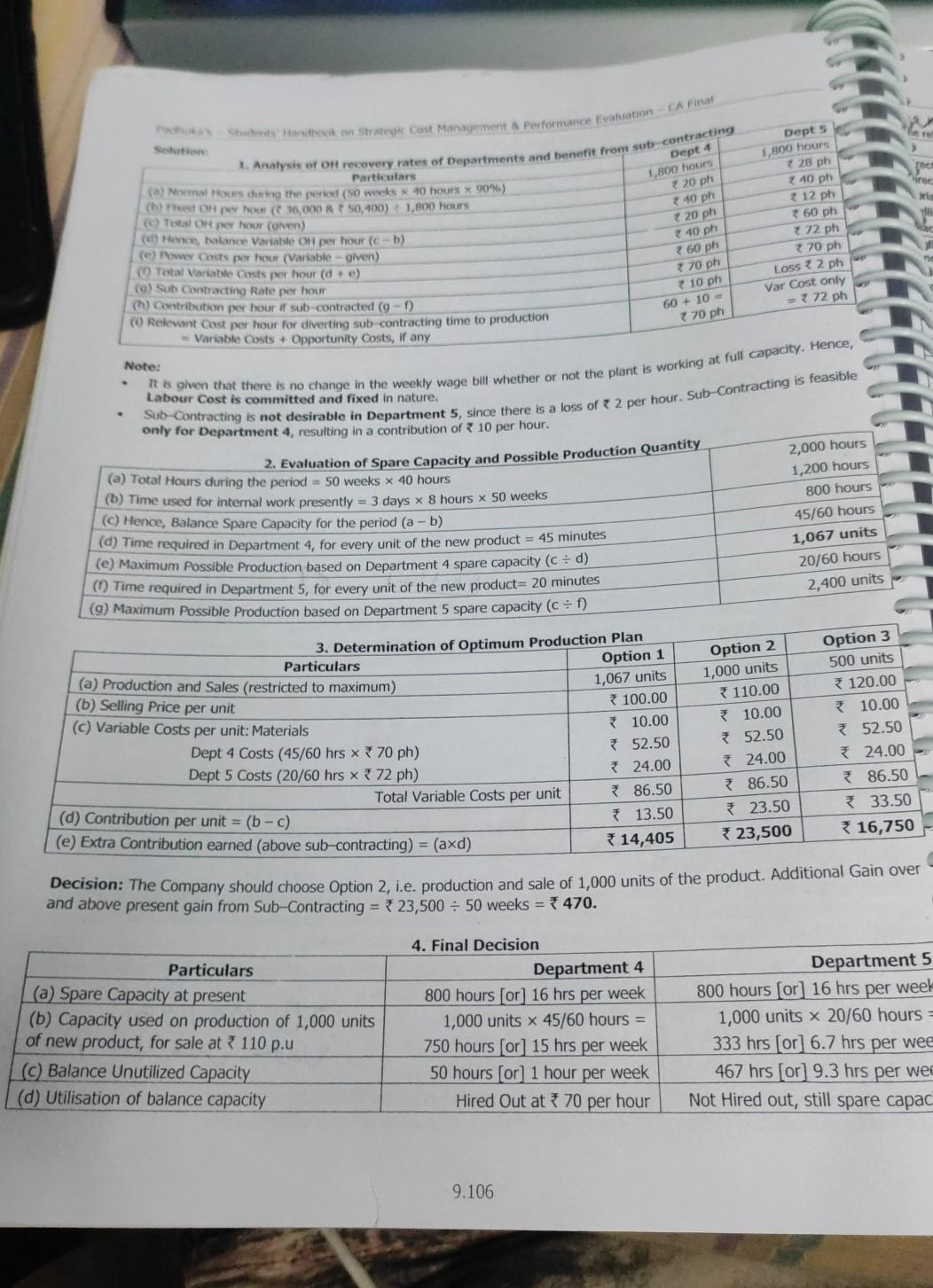
Notes and project report on a
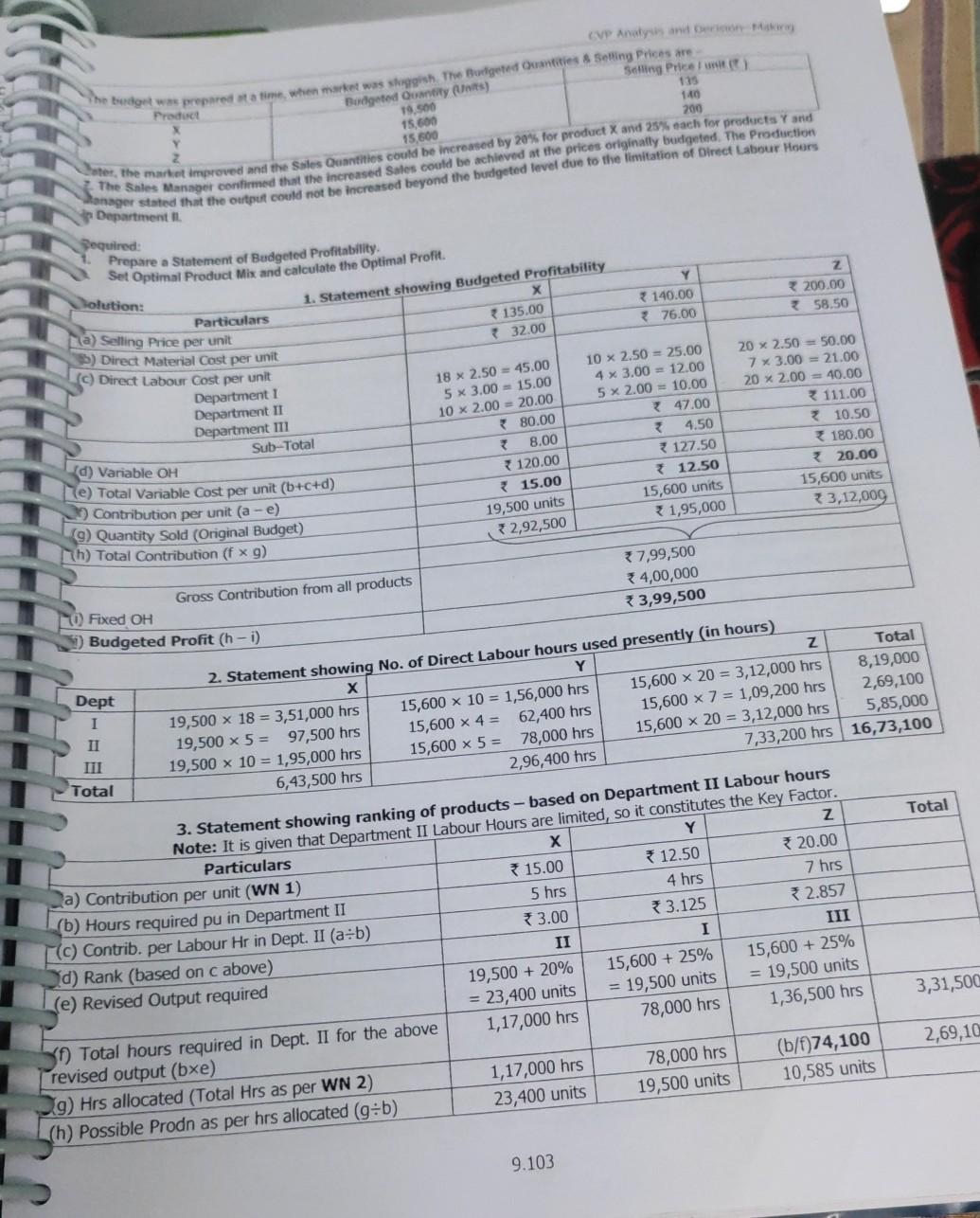
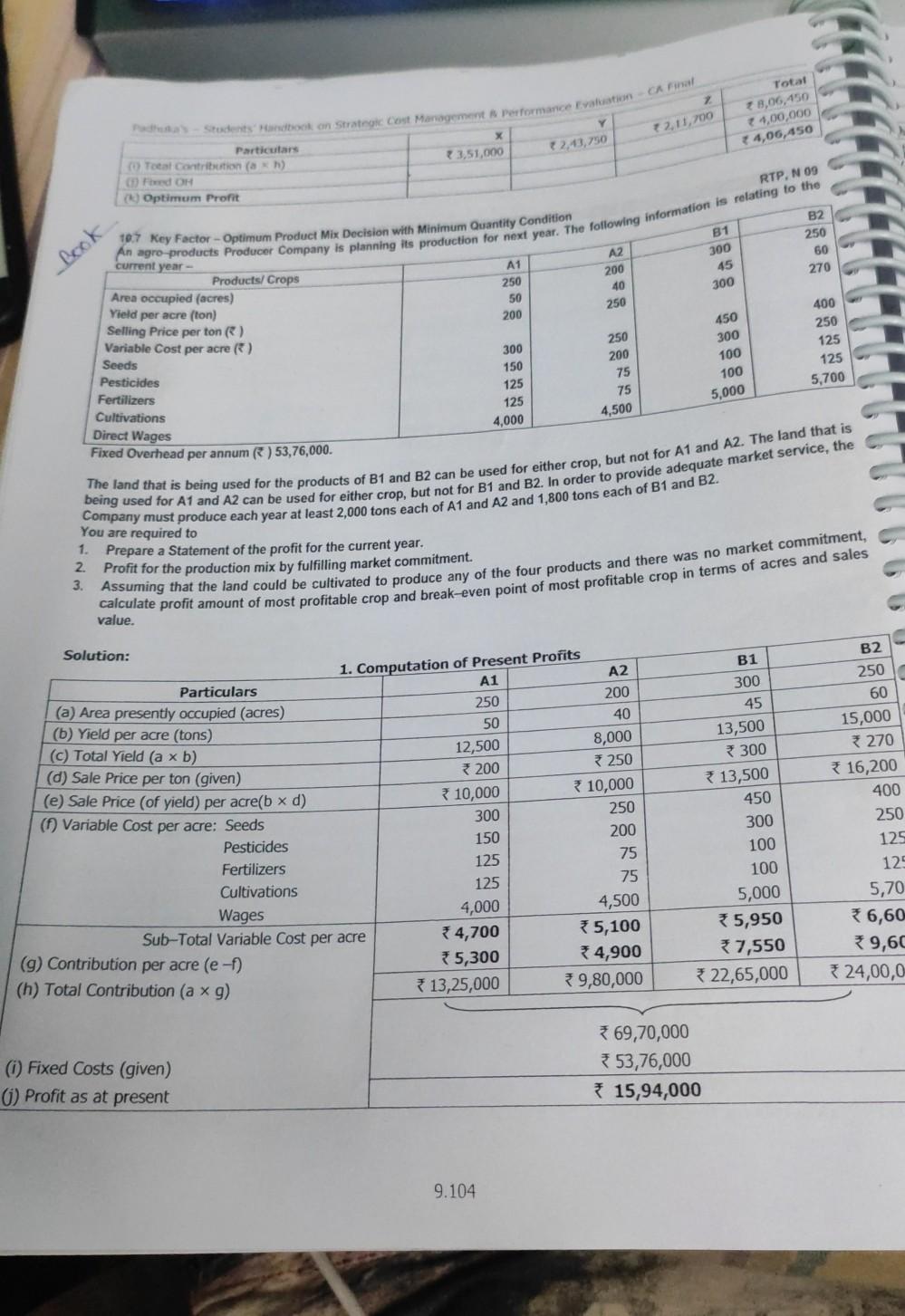
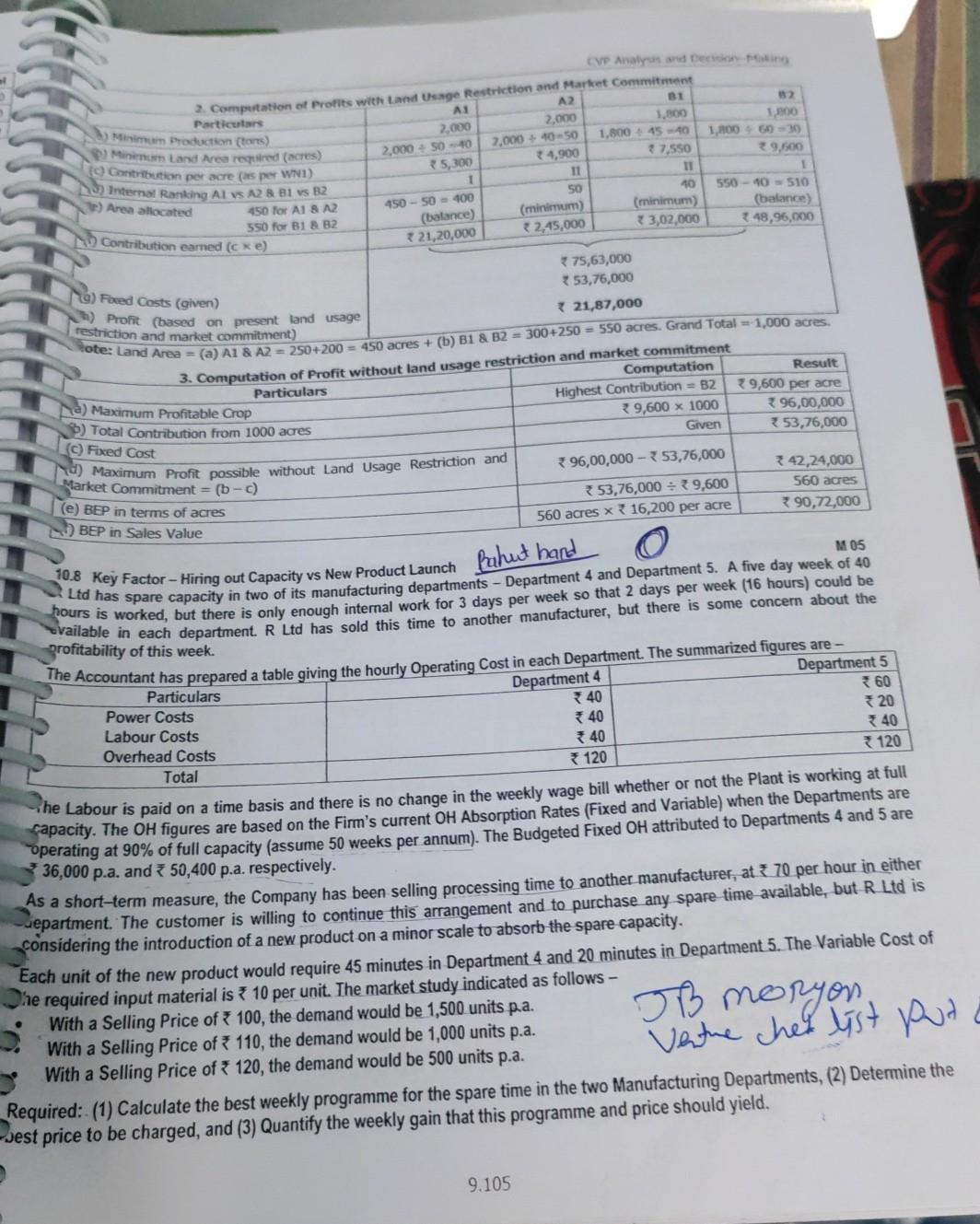
202 30.0 24,790 236 units 20.000 22.000 200 units 20.000 20.000 200 units A 550 230 100 100 Power 1617 hours (1617) Specie de cover) Seren Overhead ( T25,790 ess) The Cat the product is produd individ(+6) Oto: Coming (0) and above, is observed that only Product A should be produced, since and will not Contribution of 202 100) 20,200. Profit - Contribution 20,200 - Fixed Cost 20.000 200. hehe to cover the red Costs. Hence, the Company should produce 202 units of Product A, resulting in a Note Even if Product C has the maximum ranking with respect to Key Factor, it is not profitable to produce. Hence, the next best profitable product, i.e. Product A should be preferred. 2. Computation of Contribution per unit during Off-Season (Figures in ) 690 Product 290 (a) Selling Price per unit 149 (b) Variable costs per unit:Direct Material 130 Direct Labour 569 Variable Overhead - Production 430 130 Sub-Total Variable Cost (c) Contribution per unit (a - b) (d) Ranking based on Contribution per unit (e) Maximum Demand are available for analysis - Since Overall Total Possible production is only 215 units and there are specific Fixed Costs for B and C, the following options Item Contri- Option 1 Option 2 bution p.u. Units Contribution Units Contribution Product A 120 Nil Nil 100 12,000 Product B 125 115 314,375 115 14,375 Product C 135 * 16,335 121 100 12,100 Nil Total * 25,935 215 215 26,475 215 26,375 Less: Fixed Cost 324,780 Profit/ (Loss) *26,780 22,000 1,155 (305) 4,375 B 604 260 99 120 479 125 IT 115 units 120 100 units 135 units Option 3 Units Contribution 80 39,600 Nil Nil Nil Best option is to produce 100 units of Product A and 115 units of Product B during off-season. Maximum Profit = 4,375. N 07 Z Y 76.00 58.50 10.6 Key Factor - Optimur Product Mix Decision A Manufacturer produces 3 products whose cost data are as follows - Particulars Direct Materials / Unit) 32.00 Direct Labour Dept. Rate / hour (*) Hours 1 2.50 18 3.00 5 2.00 10 Variable Overheads () 8 ixed Overheads 4,00,000 per annum. Hou Hours 10 4 5 4.50 10 9.102 CVP Analysis and the budget was prepared a time when market was gish The Bulgte Ouantities & Selling Prices are Product Selling Price ) 135 140 200 Budgeted Quantity Units) 19.500 15.600 To the market improved and eve Satos Quantities could be increased by 20% for product X and 25% each tor pretoets and ante Sales Manager confirmed that the increased sales could be achieved at the prices originally budgeted. The production dager stated that the output could not be recreated beyond the budgeted level etue to the limitation of Direct Labpur Hillers in 1. Sequired: Z 200.00 58.50 Solution: Prepare a Statement of Budgeted Profitability Set Optimal Product Mix and calculate the Optimal Profit 1. Statement showing Budgeted Profitability Particulars 135.00 32.00 Y * 140.00 76.00 Fla) Selling Price per unit D) Direct Material Cost per unit (c) Direct Labour Cost per unit Department 1 Department II Department Sub-Total 18 x 2.50 = 45.00 5 X 3.00 - 15.00 10 x 2.00 = 20.00 80.00 78.00 120.00 15.00 19,500 units 2,92,500 10 x 2.50 = 25.00 4 x 3.00 - 12.00 5 x 2.00 = 10.00 7 47.00 4.50 127.50 * 12.50 15,600 units 1,95,000 20 x 2.50 = 50.00 7 x 3.00 - 21.00 20 x 2.00 = 40.00 111.00 2 10.50 180.00 3 20.00 15,600 units 33,12,000 (d) Variable OH e) Total Variable Cost per unit (b+c+d) Contribution per unit (a -e) 9) Quantity Sold (Original Budget) h) Total Contribution (f x g) 7,99,500 4,00,000 3,99,500 Gross Contribution from all products To Fixed OH 3) Budgeted Profit (h-i) Dept I II Total 2. Statement showing No. of Direct Labour hours used presently in hours) Y Z Total 19,500 x 18 = 3,51,000 hrs 15,600 x 10 = 1,56,000 hrs 15,600 x 20 = 3,12,000 hrs 8,19,000 19,500 x 5 = 97,500 hrs 15,600 x 4 = 62,400 hrs 15,600 x 7 = 1,09,200 hrs 2,69,100 19,500 x 10 = 1,95,000 hrs 15,600 x 5 = 78,000 hrs 15,600 x 20 = 3,12,000 hrs 5,85,000 6,43,500 hrs 2,96,400 hrs 7,33,200 hrs 16,73,100 Total 3. Statement showing ranking of products - based on Department II Labour hours Note: It is given that Department II Labour Hours are limited, so it constitutes the Key Factor. Particulars X Y Z La) Contribution per unit (WN 1) 15.00 12.50 20.00 (b) Hours required pu in Department II 5 hrs 4 hrs 7 hrs [(c) Contrib. per Labour Hr in Dept. II (a+b) 3.00 * 3.125 2.857 d) Rank (based on c above) II I UI (e) Revised Output required 19,500 + 20% 15,600 + 25% 15,600 + 25% = 23,400 units = 19,500 units = 19,500 units 3) Total hours required in Dept. II for the above 1,17,000 hrs 78,000 hrs 1,36,500 hrs revised output (bxe) 19) Hrs allocated (Total Hrs as per WN 2) 1,17,000 hrs 78,000 hrs (b/f)74,100 (h) Possible Prodn as per hrs allocated (g:b) 23,400 units 19,500 units 10,585 units 3,31,500 2,69,10 9.103 z Total 8,06,450 1,00,000 4,06,450 12.11,700 2,13,730 RTP, N 09 Book A2 200 40 250 81 300 45 300 Student Handbook on Strategic cost Management Performance Evaluation CA Final x Particulars (0) Total Contribution (1) 3,51,000 Fred OH Optimum Profit 107 Key Factor - Optimum Product Mix Decision with Minimum Quantity Condition B2 250 An agro-products Producer Company is planning its production for next year. The following information is relating to the current year- 60 A1 Products/Crops Area occupied (acres) 250 270 Yield per acre (ton) 50 Selling Price per ton ( ) 200 400 Variable Cost per acre) 250 Seeds 300 125 Pesticides 150 125 Fertilizers 125 5,700 Cultivations 125 Direct Wages 4,000 Fixed Overhead per annum) 53,76,000. being used for A1 and A2 can be used for either crop, but not for B1 and B2. In order to provide adequate market service, the The land that is being used for the products of B1 and B2 can be used for either crop, but not for A1 and A2. The land that is You are required to 1. Prepare a Statement of the profit for the current year. 2. Profit for the production mix by fulfilling market commitment. 3. Assuming that the land could be cultivated to produce any of the four products and there was no market commitment, value. calculate profit amount of most profitable crop and break-even point of most profitable crop in terms of acres and sales 250 200 75 75 4,500 450 300 100 100 5,000 B2 200 Solution: 1. Computation of Present Profits A1 A2 Particulars (a) Area presently occupied (acres) 250 40 (b) Yield per acre (tons) 50 (c) Total Yield (a x b) 12,500 8,000 (d) Sale Price per ton (given) 200 * 250 (e) Sale Price (of yield) per acreb xd) 10,000 * 10,000 ( Variable Cost per acre: Seeds 300 250 200 150 Pesticides 125 75 Fertilizers 75 Cultivations 125 Wages 4,000 4,500 Sub-Total Variable Cost per acre 4,700 5,100 (g) Contribution per acre (e-f) 5,300 34,900 (h) Total Contribution (a x g) 13,25,000 9,80,000 B1 300 45 13,500 * 300 13,500 450 300 100 100 5,000 5,950 7,550 *22,65,000 250 60 15,000 *270 * 16,200 400 250 125 125 5,70 36,60 9,60 24,00,0 (1) Fixed Costs (given) (1) Profit as at present 69,70,000 353,76,000 15,94,000 9.104 2,000 2,000 CVP Analysen 2. Computation of Profits with Land Usage Restriction and Market Commitment A2 AI B1 82 Particulars 1.800 1,800 1.80045 -40 2,000 10-50 1,800 6030 2,000 + 50 - 10 4,900 7,550 29.500 1 11 1 SO 40 550 - 10 - 510 450 for AI 8 A2 450 - 50 - 100 (balance) 550 for B1 & 2 (minimum) (minimum) (balance) 21,20,000Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


