Question: Objectives 1. Understand the design, implementation, usage and limitation of ADT based on fixed- sized arrays. 2. Gain experience implementing abstract data types using already

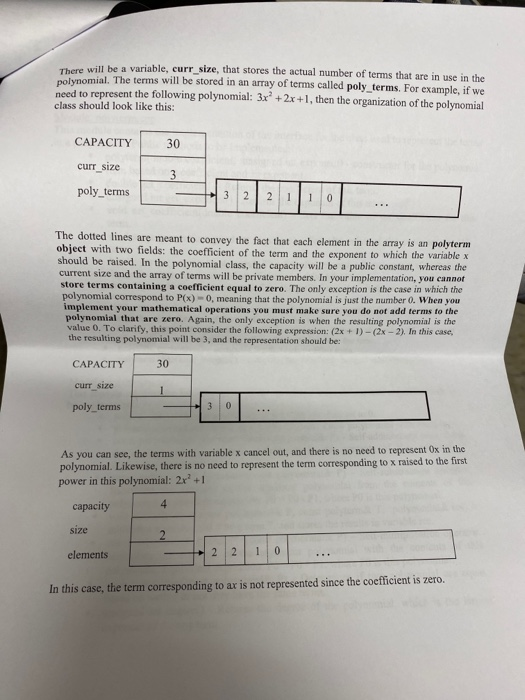



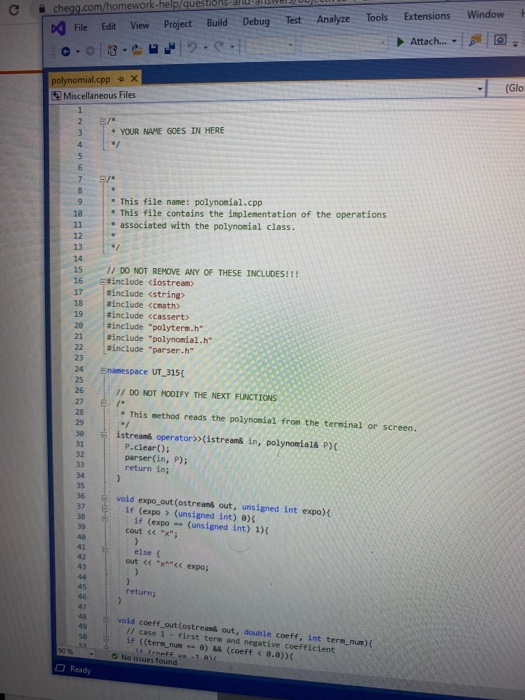
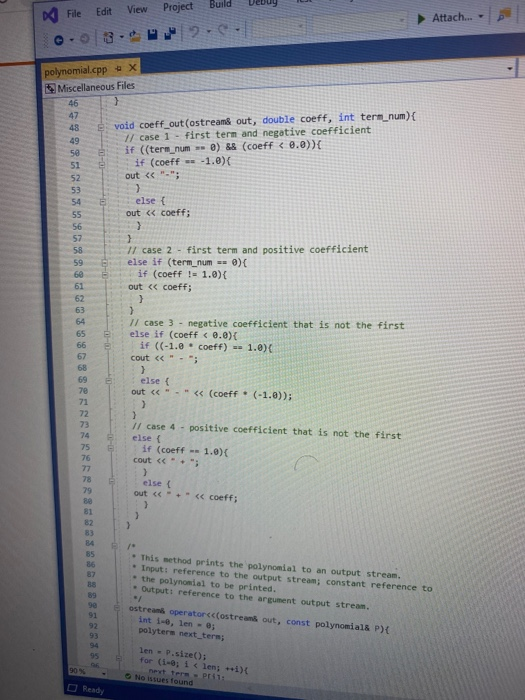
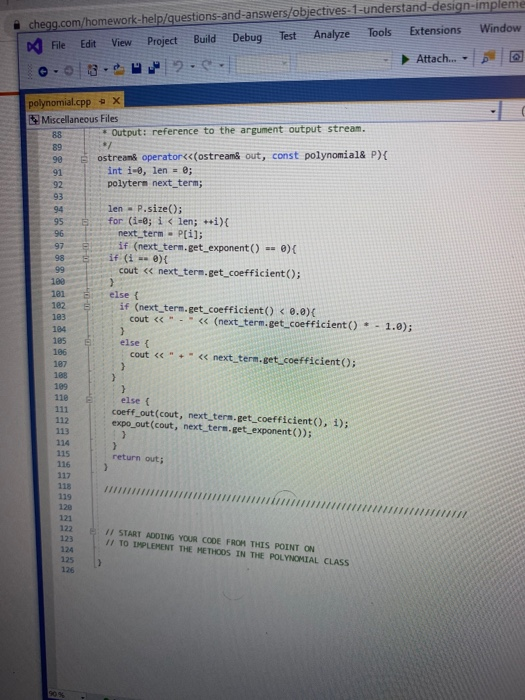
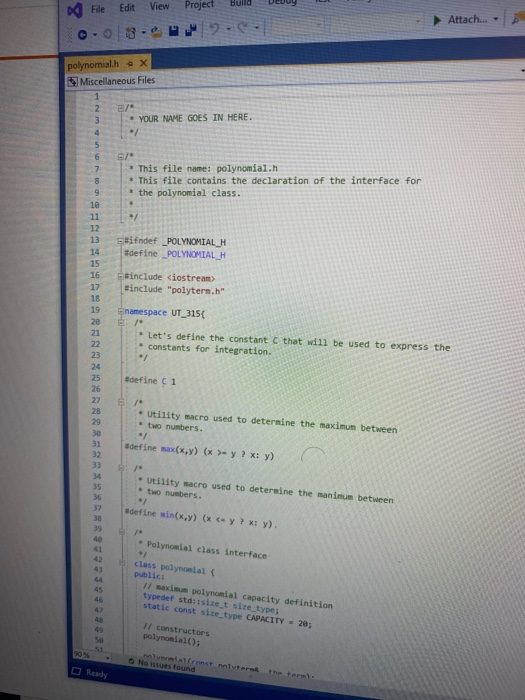
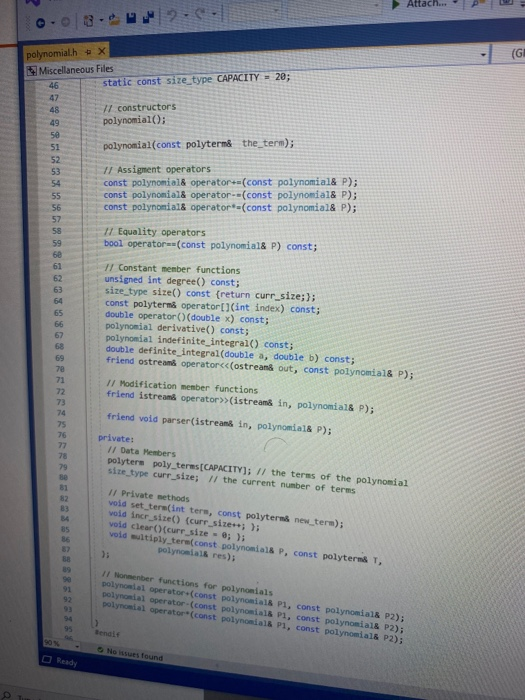
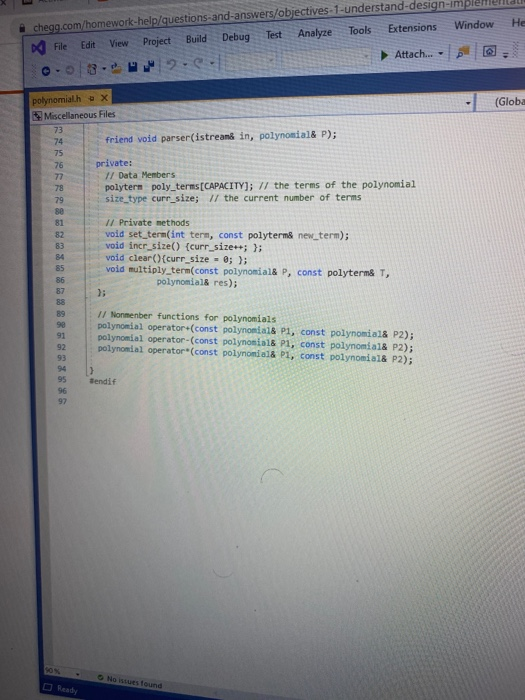
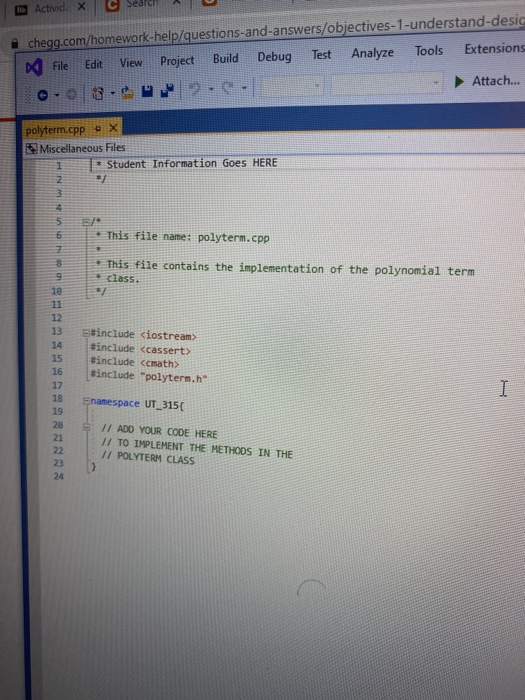
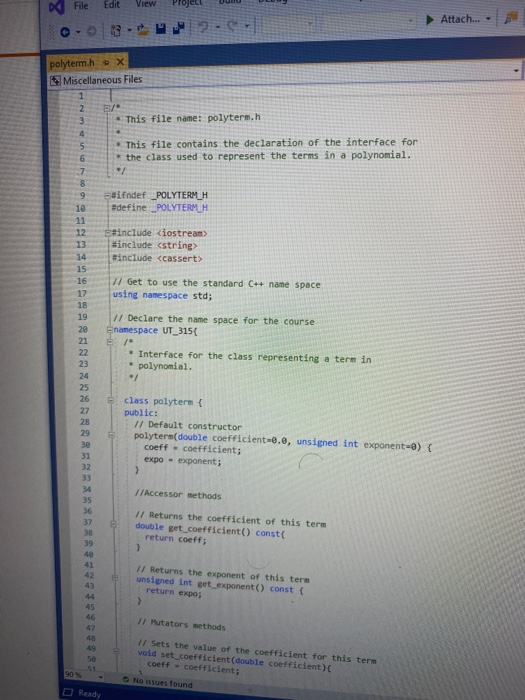
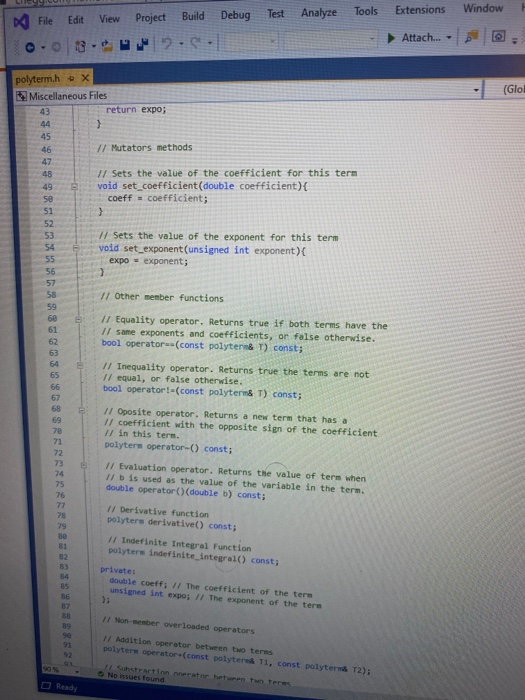
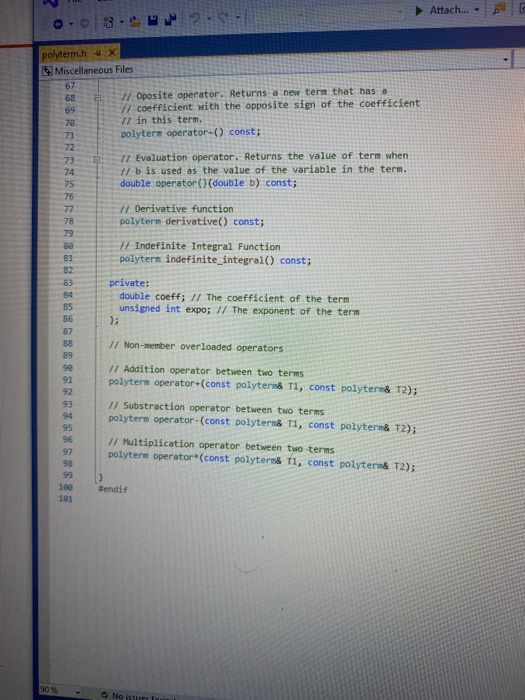
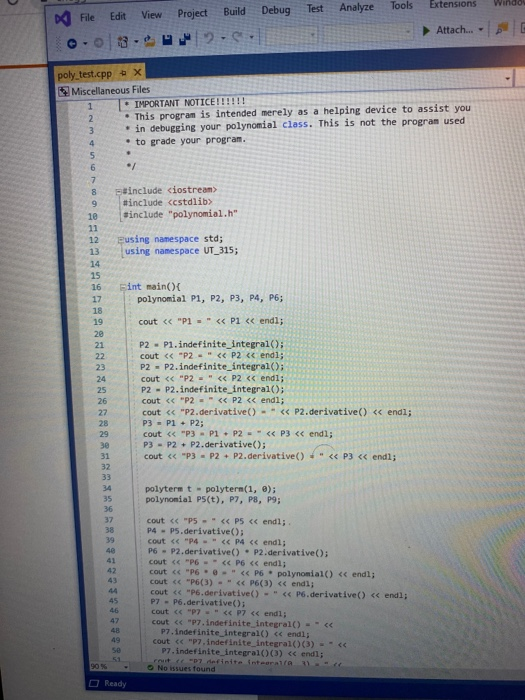
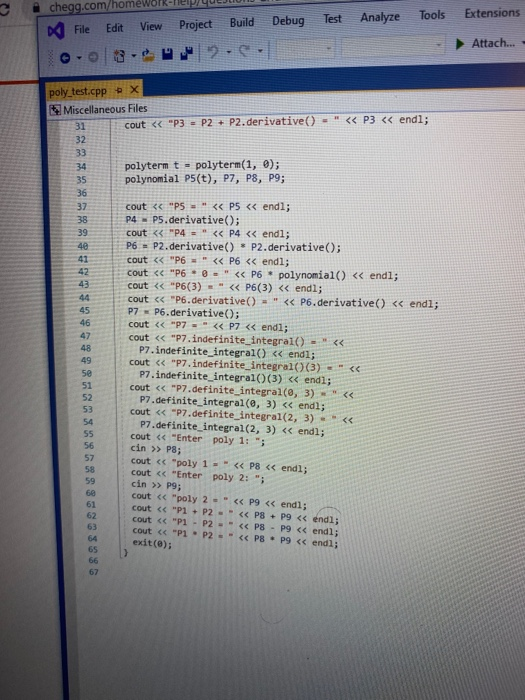
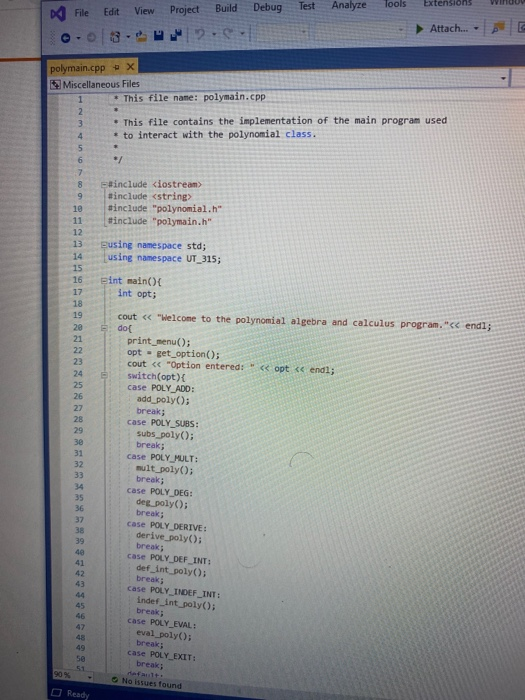
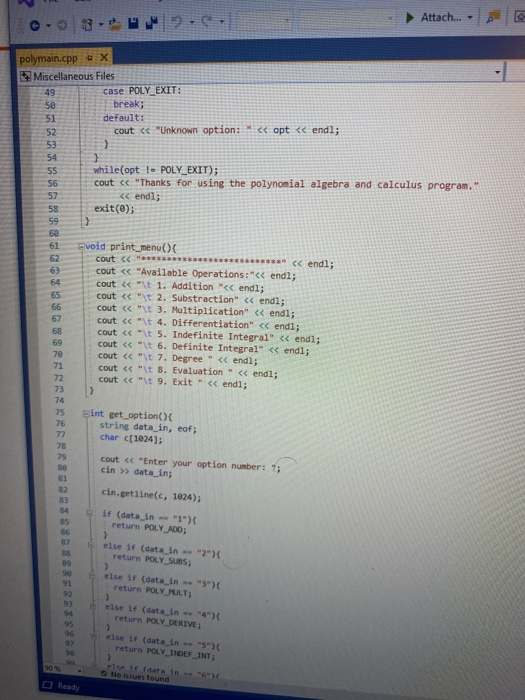
Objectives 1. Understand the design, implementation, usage and limitation of ADT based on fixed- sized arrays. 2. Gain experience implementing abstract data types using already developed data structures. 3. Gain experience with object-oriented programming abstractions, especially constructors and operator overloading Overview You will implement and test a polynomial class, using fixed-sized array as the data structure to store the terms in a polynomial. Each term in the polynomial is also a class that you will need to implement. Recall that the general form of a polynomial is as follows: P(x)=,x' +_-" +...+2x+a, Here, each term has a coefficient, denoted as a,, and a exponenti, which represent the power of the variable x. Your polynomial class must implement the following operations: 1. Addition - given two polynomials P and Ps, compute the polynomial P, = P + P, 2. Subtraction - given two polynomials P. and P, compute the polynomial P = P.-P. 3. Multiplication - given two polynomials P, and P, compute the polynomial P, =P* P, 4. Derivative - given a polynomial P, finds its derivative. 5. Indefinite integral - given a polynomial P, finds its indefinite integral (anti-derivative). 6. Definite integral - given a polynomial P, evaluate its definite integral over an interval [a,b] 7. Degree - given a polynomial P, find its degree (the largest exponent in any term). 8. Evaluate - given a polynomial P, evaluate it at value x, to compute y = P(x). You must first implement the polyterm class, which implements a term in a polynomial. You will use a fixed-size array to store the terms in the polynomial, in decreasing order of exponent. Thus, each element in the array represents a term in the polynomial. The array will have a maximum size CAPACITY that limits the number of terms that can be added to the polynomial. are will be a variable, curr_size, that stores the actual number of terms that are in use in the olynomial. The terms will be stored in an array of terms called poly terms. For example, if we need to represent the following polynomial: 3x + 2x +1, then the organization of the polynomial class should look like this: CAPACITY 30 curr_size poly_terms LG 4322 ... The dotted lines are meant to convey the fact that each element in the array is an polyferm object with two fields: the coefficient of the term and the exponent to which the variable x should be raised. In the polynomial class, the capacity will be a public constant, whereas the current size and the array of terms will be private members. In your implementation, you cannot store terms containing a coefficient equal to zero. The only exception is the case in which the polynomial correspond to P(x)-0, meaning that the polynomial is just the number 0. When you implement your mathematical operations you must make sure you do not add terms to the polynomial that are zero. Again, the only exception is when the resulting polynomial is the value 0. To clarify, this point consider the following expression: (2x + 1)-(2x - 2). In this case, the resulting polynomial will be 3, and the representation should be: CAPACITY 30 curr size poly_terms As you can see, the terms with variable x cancel out, and there is no need to represent Ox in the polynomial. Likewise, there is no need to represent the term corresponding to X raised to the first power in this polynomial: 2r? + 1 capacity size 2 elements .22 10 In this case, the term corresponding to ar is not represented since the coefficient is zero. Implementation Your implementation will consist of adding CH code to implement two modules: polyterm.cpp and polynomial.cpp. Module: polyterm.cpp This module contains the implementation of the interface for the class used to represent the terms in a polynomial. Public methods to be implemented: . polyterm(double coefficient, unsigned int exponent) - constructor for the polynomial term based on a coefficient and an exponent. double get_coefficient) - Returns the coefficient of this term. unsigned int get_exponent() - Returns the exponent of this term void set_coefficient(double coefficient) - Sets the value of the coefficient for this term. void set_exponent(unsigned int exponent) - Sets the value of the exponent for this term. bool operator (const polyterm& T) - Equality operator. Returns true if both terms have the same exponents and coefficients, or false otherwise. bool operator! (const polyterm& T) - Inequality operator. Returns true if the terms are not equal, or false otherwise. - polyterm operator). Oposite operator. Returns a new term that has a coefficient with the opposite sign of the coefficient in this term. - double operator (double b) - Evaluation operator. Returns the value of the term when the value b is used as the value of the variable x in the term. - polyterm derivative() - computes the derivative of this term. polyterm indefinite integral - computes the indefinite integral (anti-derivative). Module: polynomial.cpp This module contains the implementation of the interface for the polynomial class. Methods to be implemented: - polynomial - Creates a new polynomial with one term set to 0. polynomial(const polyterm& new term) - Creates a new polynomial with one term. const polynomial& operator+(const polynomial& P) - Self-addition operator. Adds the contents of the argument polynomial to the contents of this polynomial. Equivalent expression: PO - PO + Pl; const polynomial& operator-(const polynomial& P) - Self-substraction operator. Substracts the contents of the argument polynomial from the contents of this polynomial. Equivalent expression: PO - PO - P1, where PO is this polynomial. void multiply_term(const polynomial& P, const polyterm& T polynomial& res) - multiplies a polynomial P by a term T, and stores the results in variable res. const polynomial& operator (const polynomial& P) - Self-multiplication operator Multiplies the contents of the argument polynomial with the contents of this polynomial. Equivalent expression: PO = PO P1, where PO is this polynomial. bool operator=(const polynomial& P) - Determines if two polynomial are equal, based on wether or not they have the same terms. unsigned int degree() - Returns the degree of the polynomial, which is the largest exponent of the any term. const polyterm& operator[(int index) - This operator allows access to a term in the polynomial, whose position is given by the argument index. This method must assert whether or not the index is within the bound of the array of terms in the polynomial. double operator(double x) - Evaluates the value of a polynomial, given the value of the variable x. This method evaluates the expression y - Pa), where a is some constant number. polynomial derivative(). This method computes and returns the derivative of a polynomial. You must ensure that the method returns 0 if the polynomial is merely a term with a constant value (e.g. P(x)=2). polynomial indefinite_integral - This method computes the indefinite integral of this polynomial. The method uses the convention that the constant C, used in the expression F(x) + C, will be set to 1. double definite integral(double a, double b) - This method computes the definite integral of this polynomial, on the interval (a,b). polynomial operator+(const polynomial& Pl, const polynomial& P2) - This method adds two polynomials Pl and P2, and returns the result. Equivalent expression: P3 = PIP2 polynomial operator-(const polynomial& P1,const polynomial& P2) - This method substracts two polynomials Pl and P2, and returns the result. Equivalent expression: P3-P1-P2 polynomial operator(const polynomial& PI, const polynomial& P2) - This method multiplies two polynomials Pl and P2, and returns the result. Equivalent expression: P3-P-P2 All operations must ensure that there is enough room to add terms into the resulting polynomials. If not, an assertion should be thrown. You will receive all the .h files necessary for this project. In addition, you will be provided with a main program that uses the polynomial class, and interacts with the user to ask his/her input on the operations and polynomials to be evaluated. Finally, you will be given a Makefile with all the commands needed to compile your project. In summary, your program will consist of the following files: 1. polyterm.h - interface for the polyterm class. 2. polyterm.cpp - implementation of the polyterm class. YOU MUST IMPLEMENT THE METHODS THAT APPEAR IN THIS FILE. 3. polynomial.h - interface for the polynomial class. 4. polynomial.cpp - implementation of the polynomial class. YOU MUST IMPLEMENT THE METHODS THAT APPEAR IN THIS FILE. 5. poly test.cpp - test program for the polynomial class. 6. polymain.cpp-menu-driven main program that interacts with user to perform operations on polynomials. 7. Makefile - the makefile with the commands to compile and submit this project. 8. testl.in - test input file number one. NOTE: YOUR PROGRAM MUST PASS THESE TESTS TO BE CONSIDERED A RUNNING PROGRAM 9. testl.out-expected output from file test1.in 10. test2.in - test input file number two. 11. test2.out - expected output from file test2.out. 12. test3.in - test input file number three. 13. test3.out - expected output from file test3.out. PROJECT DUE DATE: Wednesday, March 4, 2020 Tools Window chego.com/homework-help/questions and answISUULLIVE! File Edit View Project Build Debug Test Analyze 0.08. 2- Extensions Attach.. Help . a (Global Sco parser.cpp - X Miscellaneous Files 1 / *This file name: parser.cc *This file contains the implementation of the parser method which is used to parse the input terms of the polynomial. #include "parser.h" 10 11 Enamespace UT_315 11 Quick and Dirty polynomial parser void parse_error(string err) { cerr Illegal input string: while((str_pos Illegal input string: " + string(str_but); 1/ clear the x if (str_buf[str pos] != '') parse_error(err); else { // clear the x str pos++; Il check if we have a non- value if (str_buf[str_pos) - result - (unsigned int) 1; 87 else 1 clear the + I read the exponent while((str pos 1.0 : -1.0; 13 131 1/ first skip white spaces while((strpos = str_len) { err = "get_term() -> Illegal input string: ".string(str_buf); parse_error(err); 136 139 14 11 first read the coefficient coeff - get_coeff(str_buf, str_pos, str_len); Il correct sign factor coeff factors 142 11 now get the exponent if (str pos astr_len) expo - get expo(str buf, strpos, str len); 146 148 149 else expo = 0; No insues found 90% - O Ready Type here to search (Global Sco parser.cpp = X Miscellaneous Files 142 coeff = factor; 143 1/ now get the exponent 145 if (str_pos #include #include "polynomial.h" Eusing namespace std; using namespace UT_315; 16 Fint main(){ polynomial P1, P2, P3, P4, P6; 18 cout > P8; cout > P9; cout #include #include "polynomial.h" #include "polymain.h" Busing namespace std; using namespace UT_315; XXXWWWXXNXXNNNXB e int main int opt; cout > data_in; cin.getline(s, 1924); if (date_in -- "1) return POLY ADO; 88 else if (date_in - return POLY_SUBS; "2") else if (data in return POLY_JULT; "3") else if (data in = 4) return POLY_DERIVE; else if (data in . g.) return POLY_INDEF_INT; 905 - D Ready No istues found x Activid. x C Search X C includ x c This Is Need auto) chegg.com/homework-help/questions-and-answers/objectives-1-understand-design-implementation-u. A File Edit View Project Build Debug Test Analyze Tools Extensions Window Help 0.08. 2- Attach... . . (Global Scop polymain.cpp + X Miscellaneous Files 112 cout > P1; cout > P2; cout > P1; cout > P2; cout > P1 cout > P2; cout > P: cout > P; 161 cout > P; cout > a; cout > b; cout > P; cout > P; cout > a; cout > P; cout > a; cout > P; cout include #include





![an interval [a,b] 7. Degree - given a polynomial P, find its](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/answers/2024/09/66df114b8f906_98666df114ad7cc6.jpg)