Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Over the past ten years, RAAT s capital - budgeting approach evolved into a somewhat elaborate procedure in which new proposals are categorized into profit,
Over the past ten years, RAATs capitalbudgeting approach evolved into a somewhat elaborate procedure in which new proposals are categorized into profit, research and development, and safety. Over the past several months, CBC has met monthly to consider the changes the Biden administration had proposed for the auto industry and how the company could utilize the government funding. On January the finance committee of Ross Austin Auto met to consider the changes proposed by the Energy Department and how they would affect the companys eight capitalbudgeting projects. Present at the meeting were Ross Austin, president and founder, his brother Robert Diamond, comptroller, and Chris Walken, head of research and development, who made a final judgment on all proposed capital outlays for review. projects falling into the profit or research and development areas are evaluated using present value techniques, using a percent cost of capital; those falling into the safety classification are evaluated in a more subjective framework. Although research and development projects must receive favorable results from the present value criteria, a total dollar limit is also assigned to projects of this category, typically running about $ million. This limitation was imposed by RAAT primarily because of the limited availability of quality researchers in the auto industry. RAAT felt that if more funds than that were allocated, we simply couldnt find the manpower to administer them properly. On the other hand, the benefits derived from safety projects are not in terms of cash flows; hence, present value methods are not used at all in their evaluation. The subjective approach used to evaluate safety projects results from the pragmatically difficult task of quantifying the benefits of these projects in dollar terms. Thus, these projects are subjectively evaluated by a managementworker committee with a limited budget. The committee agreed that all eight projects would be evaluated as research and development projects.Project Description and Financial Information
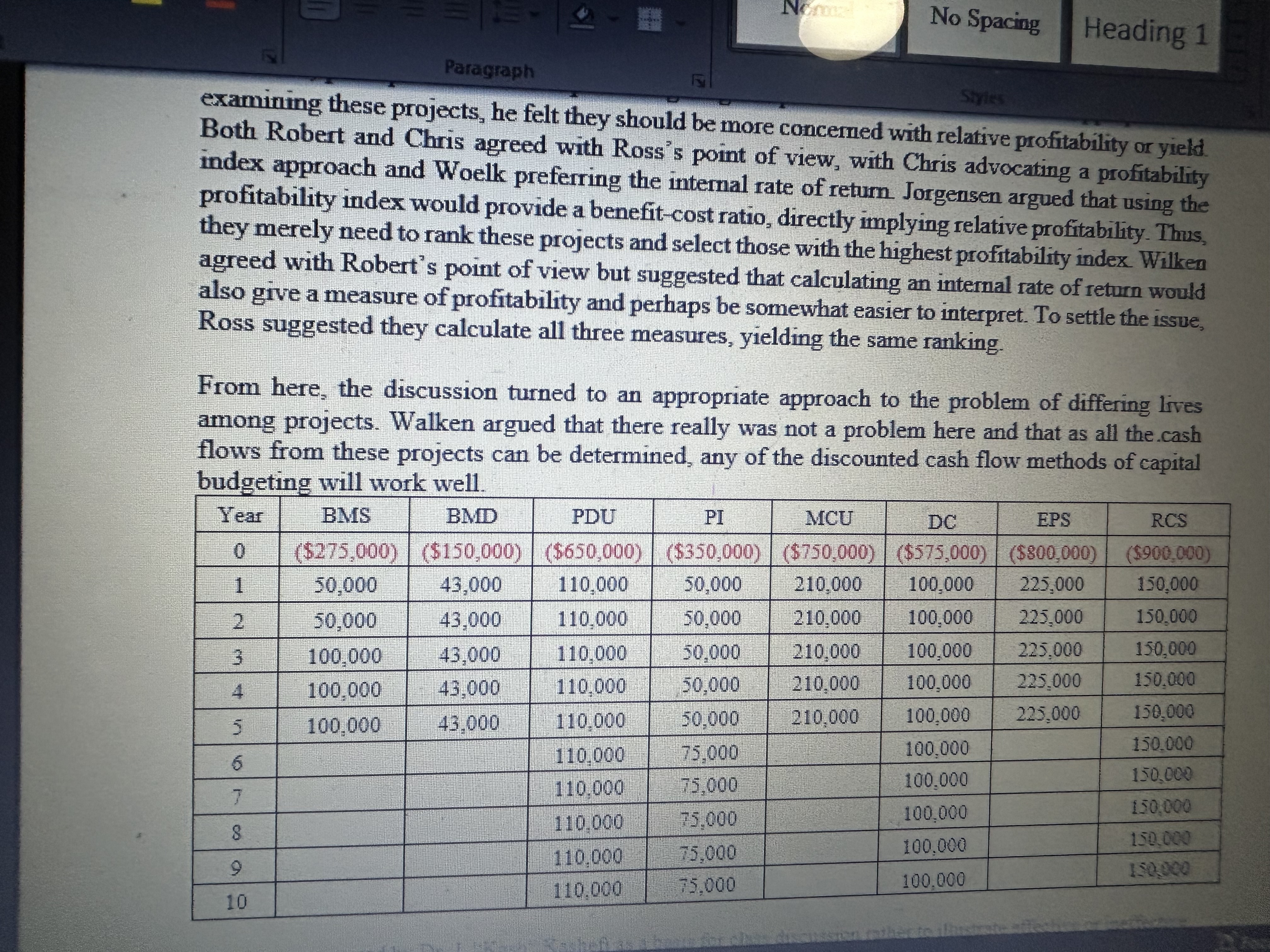
The first set of projects listed on the meetings agenda for examination involves the utilization of RAATs Senser equipment. The new suite of sensor equipment provides highaccuracy readings with lowtemperature drift in several electric vehicle applications, including Battery Management Systems BMS Power Distribution Systems PDUs and Battery Disconnect Units BDUs The second project involves manufacturing Power Inverters PI DCDC Converters, Battery & related parts, and Motor Control Units MCU some of the other essential parts that RAAT will manufacture over time to stay relevant in the market.The third project is lithium batteries that are built for use as house batteries in RVs Campers, Van builds, or any vehicle where you are camping or working off the grid in comfort, Aftermarket Auto Market
TRAAT has decided to enter the aftermarket parts to produce remote car starters RCS and electronic power steering EPS As the meeting opened, the debate immediately centered on the most appropriate method for evaluating all the projects. Ross suggested that, as the projects to be considered were mutually exclusive, perhaps their usual capitalbudgeting net present value criteria were inappropriate. In examining these projects, he felt they should be more concerned with relative profitability or yield. Both Robert and Chris agreed with Rosss point of view, with Chris advocating a profitability index approach and Woelk preferring the internal rate of return. Jorgensen argued that using the profitability index would provide a benefitcost ratio, directly implying relative profitability. Thus, they merely need to rank these projects and select those with the highest profitability index. Wilken agreed with Roberts point of view but suggested that calculating an internal rate of return would also give a measure of profitability and perhaps be somewhat easier to interpret. To settle the issue, Ross suggested they calculate all three measures, yielding the same ranking. From here, the discussion turned to an appropriate approach to the problem of differing lives among projects. Walken argued that there really was not a problem here and that as all the cash flows from these projects can be determined, any of the discounted cash flow methods of capital budgeting will work well. What are the NPV PI and IRR for projects? Are there any conflicts among the three methods? Was Ross correct in stating that the NPV PI and IRR necessarily will yield the same ranking order?? Under what situations might the NPV PI and IRR methods provide different rankings? Are these projects comparable even though they have unequal lives? Why? Which project should be chosen?
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


