Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
package jsjf; import jsjf.exceptions.*; import java.util.Arrays; * An array implementation of a stack in which the * bottom of the stack is fixed at
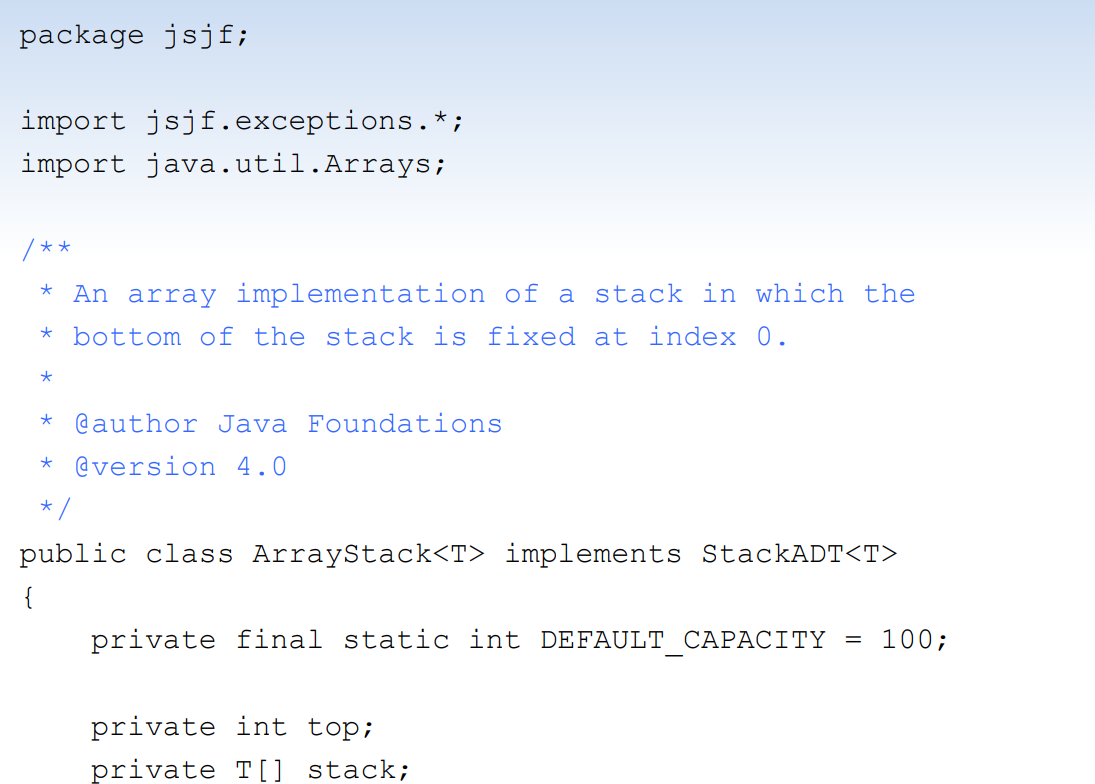
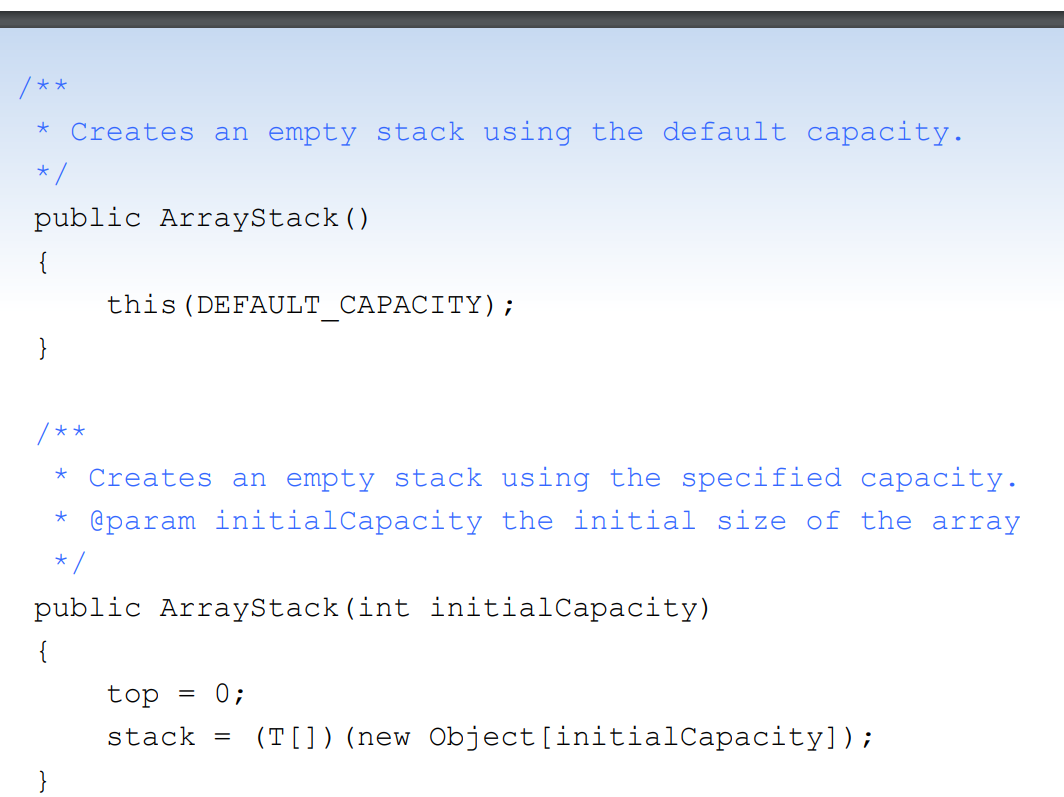
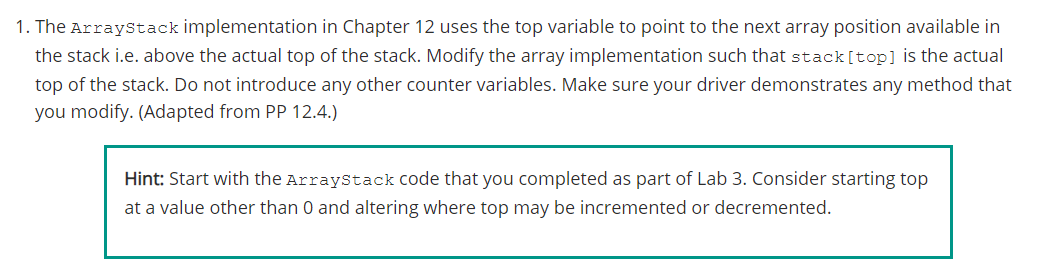
package jsjf; import jsjf.exceptions.*; import java.util.Arrays; * An array implementation of a stack in which the * bottom of the stack is fixed at index 0. * * @author Java Foundations * @version 4.0 */ public class ArrayStack implements StackADT { private final static int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 100; private int top; private T[] stack; /** * Creates an empty stack using the default capacity. */ public ArrayStack() { this (DEFAULT CAPACITY); } /** * Creates an empty stack using the specified capacity. * @param initialCapacity the initial size of the array * public ArrayStack (int initialCapacity) { top = 0; stack = (T[]) (new Object[initialCapacity]); 1. The ArrayStack implementation in Chapter 12 uses the top variable to point to the next array position available in the stack i.e. above the actual top of the stack. Modify the array implementation such that stack [top] is the actual top of the stack. Do not introduce any other counter variables. Make sure your driver demonstrates any method that you modify. (Adapted from PP 12.4.) Hint: Start with the ArrayStack code that you completed as part of Lab 3. Consider starting top at a value other than 0 and altering where top may be incremented or decremented.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


