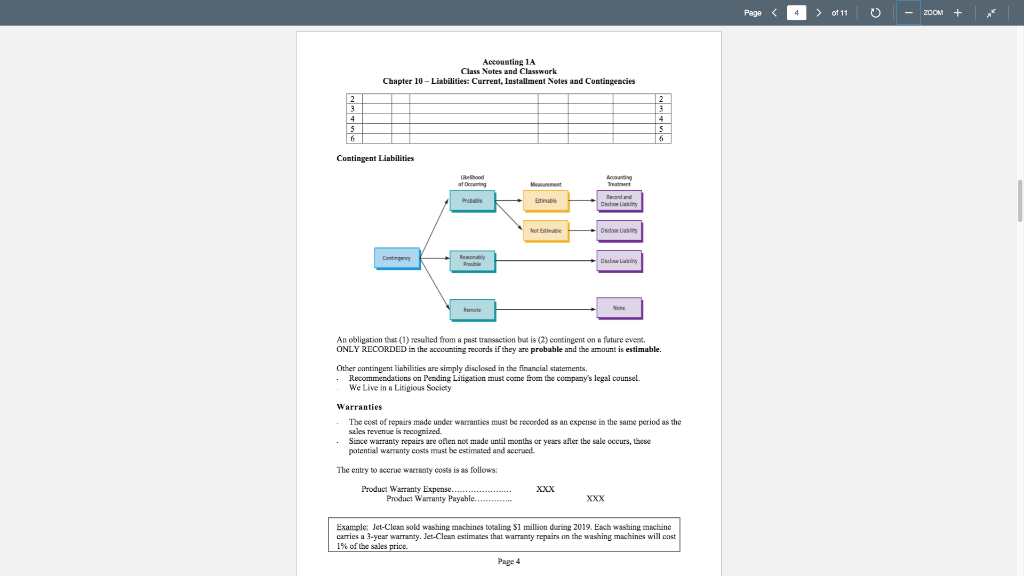
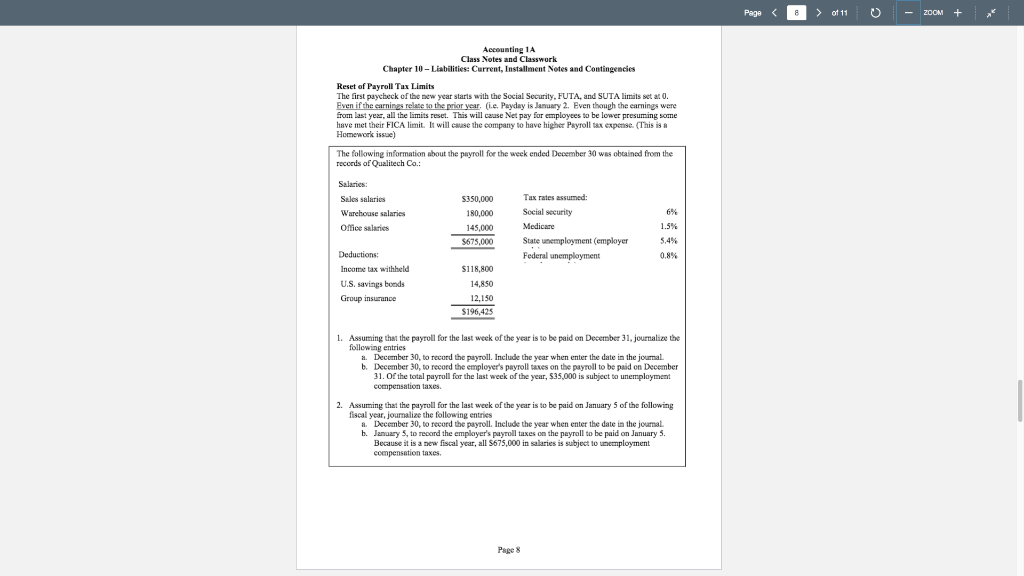
Page > of 11 - ZOOM + Class Notes and Classwork Chapter 10 - Liabilities: Current, Installment Notes and Contingencies Current Liabilities Current Liabilities = Obligations that will be paid or discharged within 12 months. Examples include: Accounts Payable, Notes Payable, Taxes Payable, Rent Payable, Interest Payable, Wages Payable, and Uncarned Rent Short Term Notes Payable Very much like Notes Receivable but from the view of the borrower. Book these from the perspective of the buyer and the seller: Apr 19 Spoke Co. sold $80,000 in Merchandise to Bryden Co. on account, 1/30 (Cost of Goods Sold was $50,000) May 19 Bryden signed an $80,000 90-day, 10% note as an extension of the A/R Aug 17 Hryden paid Spoke Co the maturity value Spoke Co. Date Description Debit Post ref Credit 1 2. 3 4 S 6 7 A 9 10 11 12 Bryden 1 2 3 4 S 6 7 & 9 10 11 12 Date Description Debit Credit Post ref 1 2 3 4 S 6 7 8 9 10 11 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 1,56 Page > of 11 - ZOOM + Accountine LA Class Notes and Classwork Chapter 10 - Liabilities: Current, Installment Notes and Contingencies Griffin Enterprises issues a $660,000, 45-day, 4% note to Romo Industries for merchandise inventory Required: A. Journalize Griffin Enterprises' entries to record (refer to the company's Chart of Accounts for exact wording of account titles): 1. the issuance of the note on January 1. 2. the payment of the note at maturity. Assume a 360-day year. B. Journalize Romu Industries' entries to record (refer to the company's Chart of Accounts for exact wording of account titles 1. the receipt of the note on January 1. 2. the receipt of the payment of the note at maturity. Assume a 360-day year. Griffin Enterprises. Date Description Dehit Post ref Credit 1 12 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Romo Industries Date 4 IS 16 7 Description Debit l'ost ref Credit 1 2 9 4 S 6 7 1 2 3 4 15 16 3 7 Non-Interest-Bearing Notes Payable-Discounted Note Terms Discount Discount Rate Proceeds Common when money is burrowed from the bank to have a non-interest-bearing note The interest is deducted from the cash proceeds received on the note At maturity, only the face value of the note is paid. Example: Borrowed $7,500 by signing 90 day non interest-bearing note discounted at 12%. Page 2 Page > of 11 - ZOOM + Accounting 1A Class Notes and Classwork Chapter 10 - Liabilities: Current, Installment Notes and Contingencies Step 1: Calculate the Discount on the Note Discount=Face x Discount Rate x Time Period (Discount Rate the interest the bank is charging on the note) (57,500 x 12% x 90/360 - $225) Step 2: Calculate the Cash Proceeds Received on the Note Proceeds - Face - Discount Example ($7,500 - 225 - $7275) . Debit Credit Step 3: Record the linbility resulting from the note and the cash received Date Description Post rer 1 2 3 1 2 3 Step 4: Record Payment when the note matures 4 Date Description Post rel Debit Credit 1 1 2 Question: Would you rather borrow S10,000 by issuing a 90 day 15% note or a 90 day non-interest bearing note discounted at 15%? Interest cost either way is $375 BUT with a non-interest bearing note you only receive S9,625 at the a beginning 5375 / 510,000 360/90 - 15 5375 / 59.625 160/90 - 15.6% Juno issued a 120 day note for $120,000 to Thor for merchandise inventory. The note is discounted 10% Journalize the transaction for both Juno and Thor Juno Date Description Post Debit Credit 1 2 3 4 5 S 6 THOR 1 2 3 4 5 6 Date Description l'ost Debit Credit 1 1 Page 3 Page 4 > of 11 o - ZOOM + Accountine 1A Class Notes and Classwork Chapter 10 - Liabilities: Current, Installment Notes and Contingencies 2 3 4 5 6 2 3 4 5 6 Contingent Liabilities at ring Probable Accounting Treatment facand und Delone Estimable Met Estimable Desde Contingen Pouble Dado None An obligation that (1) resulted from a pest transaction but is (2) contingent on a future event. ONLY RECORDED in the accounting records if they are probable and the amount is estimable. . Other contingent liabilities are simply disclosed in the financial statements. Recommendations on Peading Litigation must come from the company's legal counsel We Live in a Litigious Society Warranties The cost of repairs made under warranties must be recorded as an expense in the same period as the sales revenue is recognized Since warranty repairs are often not made until months or years after the sale occurs, these potential warranty costs must be estimated and accrued. The entry to accrue wroty costs is as follows: XXX Product Warranty Expense Product Warranty Payable........... XXX Example: Jet-Clean sold washing machines totaling $1 million during 2019. Each washing machine carries a 3-year warranty. Jet-Clean estimates that warranty repairs on the washing machines will cost 1% of the sales price. Page 4 Page 5 > of 11 - ZOOM + Accounting 1 Class Notes and Classwork Chapter 10 - Liabilities: Current, Installment Notes and Contingencies Credit 1. Record the entry to accrue Je-Clear's warranty costs at the end of 2019. Date Description Post Debit ref 1 2 3 1 2. 3 2. During the first quarter of 2020, Jet-Clean paid $750 for washing machine repairs under warranty Date Description Post Debit Credit rel 1 1 2 2 3 3 Payroll Liabilities Payroll is often the largest expense for most service businesses Payroll Department is often segregated from the rest of Accounting. Requires controls and honesty Terminology Gross Pay-the expense of the employer Net Pay Regular Pay Overtime Pay Exempt employees are exempt from the Fair Labors Standards Act requiring that employees be paid 1 1/2 times the regular wage rate for all hours worked in excess of 40 hours per week. . (aka Salaried employees) Non-exempt employees (a.k.a. hourly employees) receive an overtime differential. FICA Tax FICA - Federal Insurance Contributions Act. Social Security and Medicare. Tax rates are set by Congress, and they may change The textbook uses a social security rate of 6% on all earnings (Wrong. Social Security is 6.2% of the first $132.900 (in 2019) of earnings.) Medicare rate of 1.5% on all earnings. (Wrong Medicare is 1.45%). Federal Income Tax The amount withheld for federal income tax depends on your tax filing status (married, single, etc.) and the number of withholding allowances claimed (one for yourself, one for a spouse, and one for cach dependent). W-4 form. The IRS publishes withholding tables An employee earns $32 per hour and 1.5 times that rate for all hours in excess of 40 hours per week. Assume that the employee worked 55 hours during the week. Assume further that the social security tax rate was 6.0% the Medicare tax rate was 1.5%, and federal income tax to be withheld was $398 Pages Page 6 > of 11 - ZOOM + Accounting 1A Class Notes and Classwork Chapter 10 - Liabilities: Current, Installment Notes and Contingencies a. Determine the gross pay for the week b. Determine the net pay for the week K. Mello Company has three employees consultant, a computer programmer, and an administrator, The following payroll information is available for each employee: Consultant Computer Programmer Administrator Regular earnings rute $5,000 per week $50 per hour S60 per hour Overtime earnings rate Not applicable 2 times hourly rate 1.5 times hourly rate Federal income tax withheld $1,150 $428 $572 For hourly employees, overtime is paid for hours worked in excess of 40 hours per week. For the current pay period, the computer programmer worked 48 hours and the administrator worked 51 hours. Assume that the social security tax rate was 6.0%, and the Medicare tax rate was 1.5% Determine the gross pay and the net pay for each of the three employees for the current pay period. Journalize on the following page Date Description Post Debit Credit 1 1 2 3 1 1 2 3 4 S 5 6 IS 6 Page 6 Page 8 > of 11 - ZOOM + Accounting 14 Class Notes and Classwork Chapter 10 - Liabilities: Current, Installment Notes and Contingencies Reset of Payroll Tax Limits The first paycheck of the new year starts with the Social Security, FUTA, and SUTA limits set at 0. Even if the earnings relate to the prior year, i.e. Payday is January 2. Even though the earnings were from last year, all the limits reset. This will cause Net pay for employees to be lower presuming some have met their FICA limit. It will cause the company to have higher Payroll tax expense. (This is a Homework issue) The following information about the payroll for the week ended December 30 was obtained from the records of Qualitech Co.: Salaries: Sales salaries Warehouse salaries Office salaries $350,000 180,000 145,000 69% Tax rates assumed: Social security Medicare State unemployment employer Federal unemployment 5675.000 1.5% 5.4% 0.8% Deductions: Income tax withheld U.S. savings bonds Group insurance S118,800 14,850 12,150 $196,425 1. Assuming that the payroll for the last week of the year is to be paid on December 31, journalize the following entries a. December 30, to record the payroll. Include the year when enter the date in the journal. b. December 30, to record the employer's payroll taxes on the payroll to be paid on December 31. Of the total payroll for the last week of the year, $35,000 is subject to unemployment compensation taxes. 2. Assuming that the payroll for the last week of the year is to be paid on January 5 of the following fiscal year, journalize the following entries a December 30, to record the payroll. Include the year when enter the date in the journal b. January 5, to record the employer's payroll taxes on the payroll to be paid on January 5. Because it is a new fiscal year, all 5675,000 in salaries is subject to unemployment compensation taxes Page 8 Page > of 11 - ZOOM + Accounting 1A Class Notes and Classwork Chapter 10 - Liabilities: Current, Installment Notes and Contingencies Description Post Debit Credit Date 1 2 3 4 S 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 13 16 12 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 - 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 1 2 3 14 15 6 17 18 19 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 20 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 Page 9 Page 10 > of 11 - ZOOM + Accounting 1A Class Notes and Classwork Chapter 10 - Liabilities: Current, Installment Notes and Contingencies The following items were selected from among the transactions completed by Aston Martin Inc. Apr 15 Borrowed S225,000 from Audi Company, issuing a 30-day, 6% note for that amount. May 1 Purchased equipment by issuing a $320,000, 180-day note to Spyder Manufacturing Co., which discounted the note at the rate of 6% 15 Paid Audi Company the interest due on the note of April 15 und renewed the loan by issuing a new 60-day, 8% note for $225,000. (Record both the debit and credit to the notes payable account) Jul 14 Paid Audi Company the amount due on the note of May 15. Aug 16 Purchased merchandise on account from Exige Co., 590,000, terms, 1/30 Sep 15 Issued a 45-day, 6% note for $90,000 to Exige Co., on account. Oct 28 Paid Spyder Manufacturing Co the amount due on the note of May 1. 30 Paid Exige Co. the amount owed on the note of September 15. Nov 16 Purchased store equipment from Gallardo Co. for $450,000, paying $50,000 and issuing a series of twenty 9% notes for $20,000 each, coming due at 45-day intervals. Dec. 16 Paid the amount due Gallardo Co. on the first note in the series issued on Nov. 16. 28 Settled a personal injury lawsuit with a customer for S87,500, to be paid in January Aston Martin Inc. accrued the loss in a litigation claims payable account. 1. Journalize the transactions 2. Journalize the adjusting entry for each of the following accrued expenses at the end of the current year A. Product warranty cost, S26,800 B. Interest on the 19 remaining notes owed to Gallardo Co. Assume a 360-day year. GENERAL JOURNAL Page Date Post Debit Credit ref 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 5 IS 6 5 7 7 17 7 8 8 9 9 10 10 11 12 12 13 13 Page 10 Description 1 Page 11 of 11 - ZOOM + Accounting 1A Class Notes and Classwork Chapter 10 - Liabilities: Current, Installment Notes and Contingencies 141 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 Account Classification Account Name Type type Normal Balance ormal Balance Financial Statement Page 11
















