Question
Part 2. Conducting a Chi-Square Test (15 points) 1. In the RCT by Knight et al, 70 patients were randomized to a Mediterranean diet and
Part 2. Conducting a Chi-Square Test (15 points)
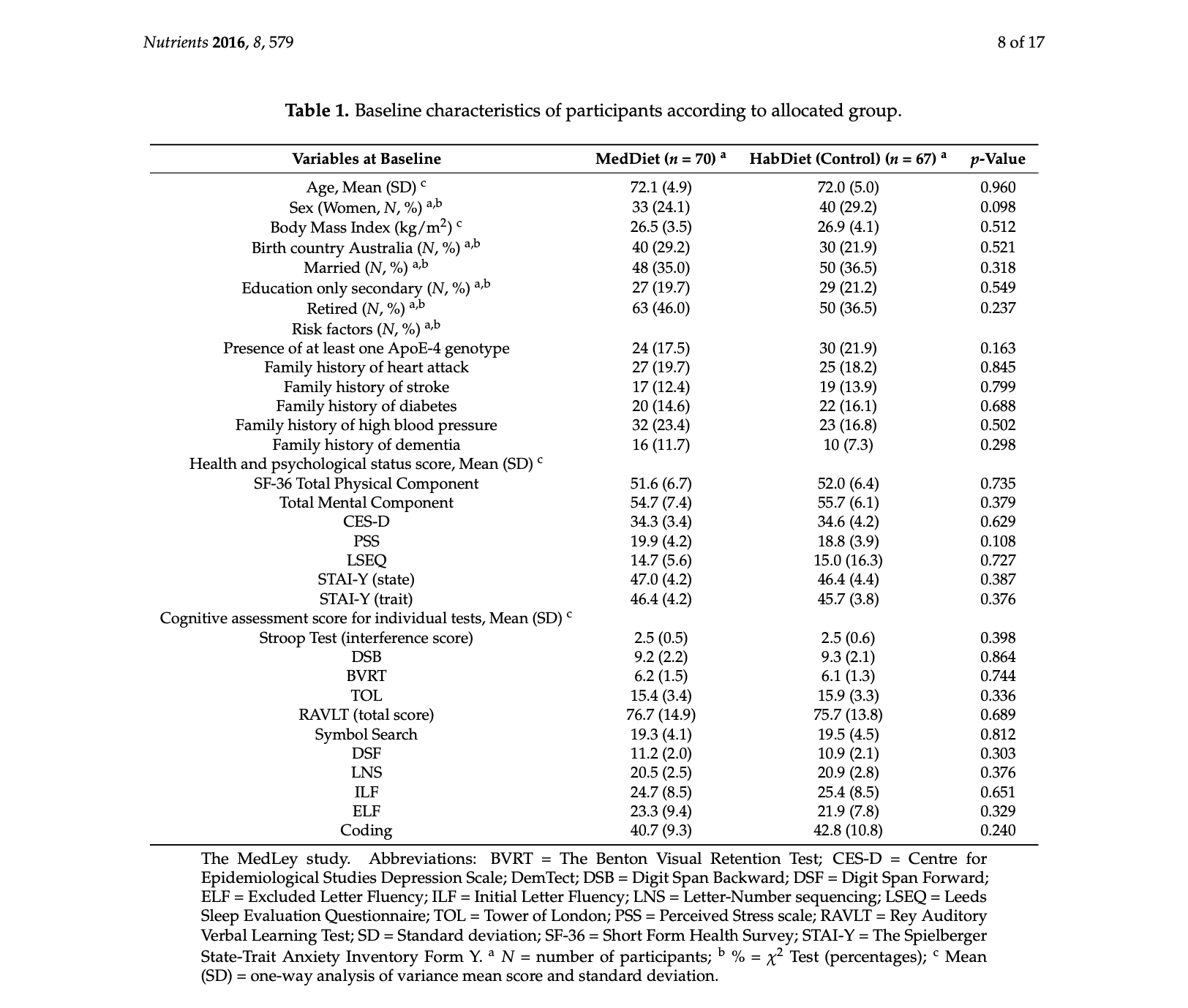
1.In the RCT by Knight et al, 70 patients were randomized to a Mediterranean diet and 67 were randomized to the control diet. Table 1 shows that 33 of the patients randomized to the Mediterranean diet were women compared to 40 randomized to the control diet. Construct a 2x2 table of the observed counts of gender by diet. Include row and column totals. (6 points: 2 pts for correctly labeling columns/rows, 2 pts for marginal/totals, 0.5 pt per observed count)
2.Construct a 2x2 table of the expected counts of gender by diet. Briefly compare the expected frequencies to the observed frequencies and summarize your results. (3 points: 0.5 pt per cell, 1 pt interpretation)
3.Calculate the chi-square statistic and conduct a chi-square test to determine if there is a significant relationship between gender and diet. State the null and alternative hypotheses, whether the conditions of the chi-square test are met, and your p-value. What do you conclude? (6 points: 2 pts hypotheses, 1 pt assumptions/conditions, 1 pt chi-square statistic, 1 pt p-value, 1 pt interpretation)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


