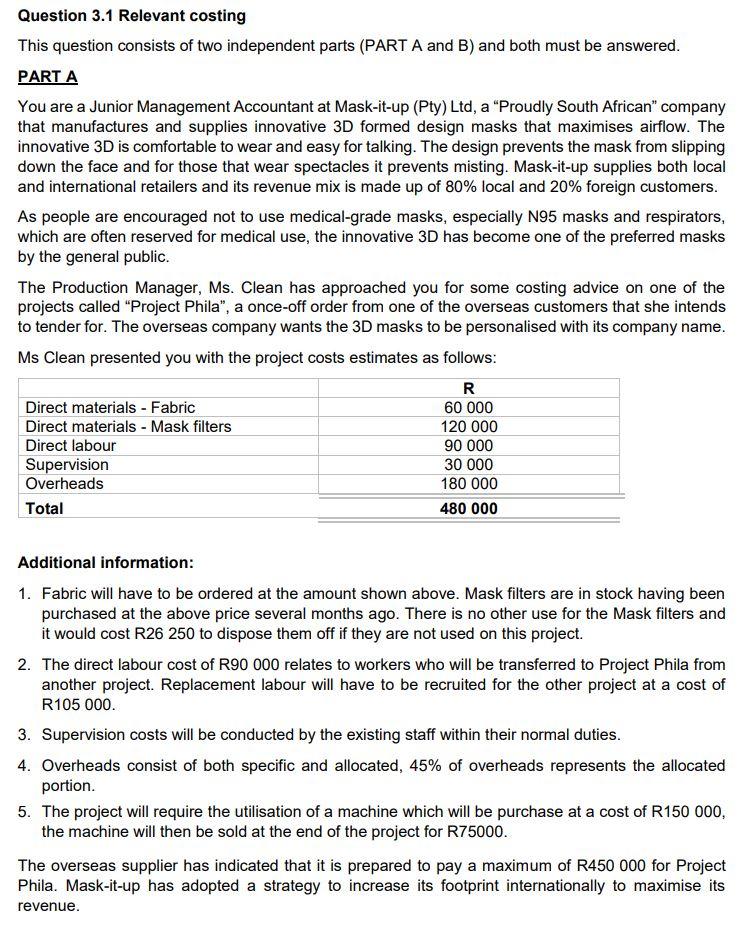
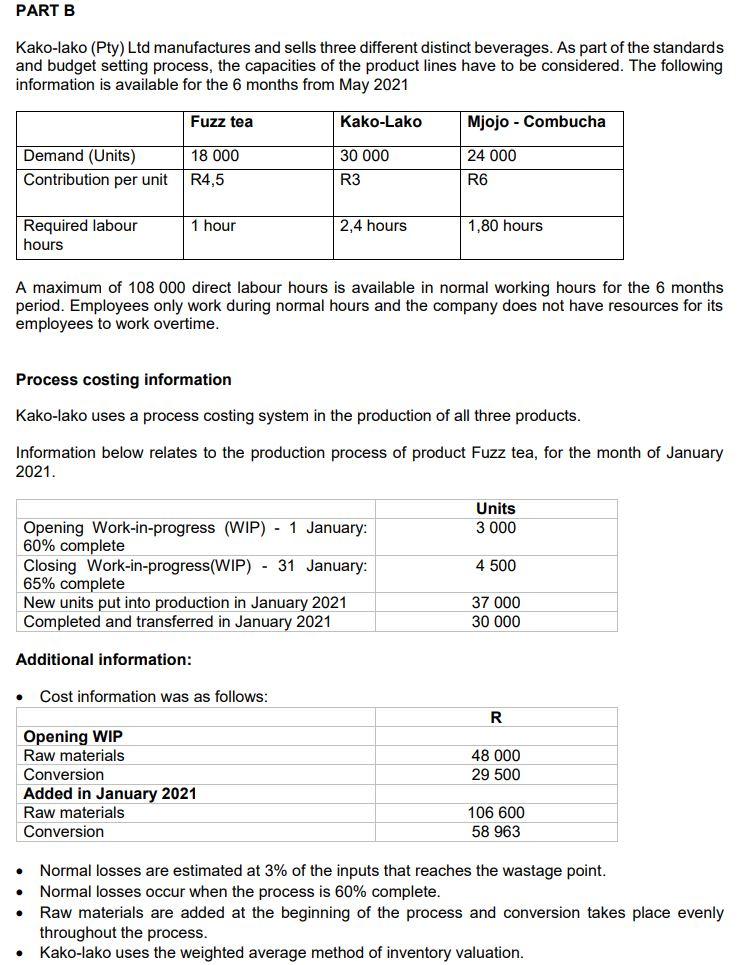
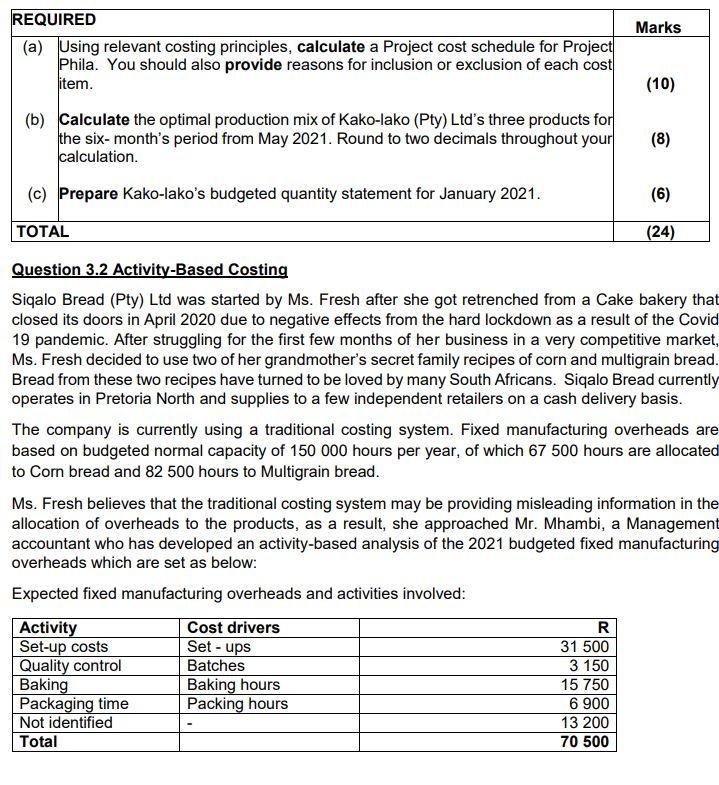
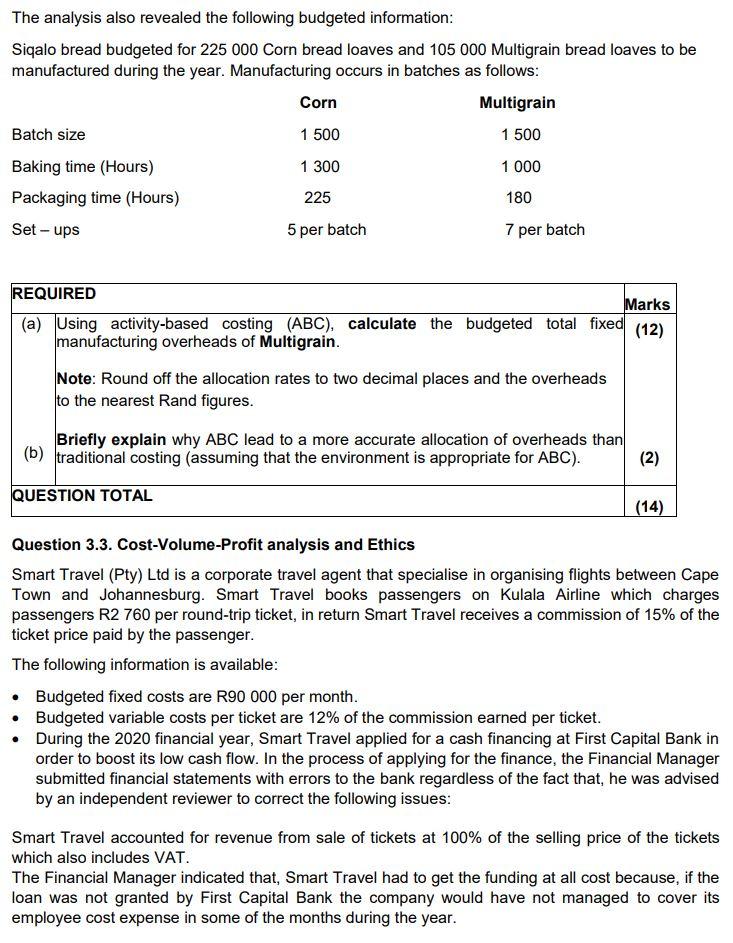
PART B Kako-lako (Pty) Ltd manufactures and sells three different distinct beverages. As part of the standards and budget setting process, the capacities of the product lines have to be considered. The following information is available for the 6 months from May 2021 Fuzz tea Kako-Lako Mjojo - Combucha 30 000 Demand (Units) Contribution per unit 18 000 R4,5 24 000 R6 R3 1 hour 2,4 hours 1,80 hours Required labour hours A maximum of 108 000 direct labour hours is available in normal working hours for the 6 months period. Employees only work during normal hours and the company does not have resources for its employees to work overtime. Process costing information Kako-lako uses a process costing system in the production of three products. Information below relates to the production process of product Fuzz tea, for the month of January 2021. Units 3 000 4 500 Opening Work-in-progress (WIP) - 1 January: 60% complete Closing Work-in-progress( WIP) - 31 January: 65% complete New units put into production in January 2021 Completed and transferred in January 2021 37 000 30 000 Additional information: . Cost information was as follows: R Opening WIP Raw materials Conversion Added in January 2021 Raw materials Conversion 48 000 29 500 106 600 58 963 . Normal losses are estimated at 3% of the inputs that reaches the wastage point. Normal losses occur when the process is 60% complete. Raw materials are added at the beginning of the process and conversion takes place evenly throughout the process. Kako-lako uses the weighted average method of inventory valuation. Marks REQUIRED (a) Using relevant costing principles, calculate a Project cost schedule for Project Phila. You should also provide reasons for inclusion or exclusion of each cost item. (10) (b) Calculate the optimal production mix of Kako-lako (Pty) Ltd's three products for the six-month's period from May 2021. Round to two decimals throughout your calculation. (8) (c) Prepare Kako-lako's budgeted quantity statement for January 2021. (6) TOTAL (24) Question 3.2 Activity-Based Costing Siqalo Bread (Pty) Ltd was started by Ms. Fresh after she got retrenched from a Cake bakery that closed its doors in April 2020 due to negative effects from the hard lockdown as a result of the Covid 19 pandemic. After struggling for the first few months of her business in a very competitive market, Ms. Fresh decided to use two of her grandmother's secret family recipes of corn and multigrain bread. Bread from these two recipes have turned to be loved by many South Africans. Siqalo Bread currently operates in Pretoria North and supplies to a few independent retailers on a cash delivery basis. The company is currently using a traditional costing system. Fixed manufacturing overheads are based on budgeted normal capacity of 150 000 hours per year, of which 67 500 hours are allocated to Corn bread and 82 500 hours to Multigrain bread. Ms. Fresh believes that the traditional costing system may be providing misleading information in the allocation of overheads to the products, as a result, she approached Mr. Mhambi, a Management accountant who has developed an activity-based analysis of the 2021 budgeted fixed manufacturing overheads which are set as below: Expected fixed manufacturing overheads and activities involved: Activity Cost drivers R Set-up costs Set-ups 31 500 Quality control Batches 3 150 Baking Baking hours 15 750 Packaging time Packing hours 6 900 Not identified 13 200 Total 70 500 The analysis also revealed the following budgeted information: Siqalo bread budgeted for 225 000 Corn bread loaves and 105 000 Multigrain bread loaves to be manufactured during the year. Manufacturing occurs in batches as follows: Corn Multigrain Batch size 1 500 1 500 Baking time (Hours) 1 300 1 000 Packaging time (Hours) 225 180 Set-ups 5 per batch 7 per batch REQUIRED Marks (a) Using activity-based costing (ABC), calculate the budgeted total fixed (12) manufacturing overheads of Multigrain. Note: Round off the allocation rates to two decimal places and the overheads to the nearest Rand figures. Briefly explain why ABC lead to a more accurate allocation of overheads than (b) traditional costing (assuming that the environment is appropriate for ABC). (2) QUESTION TOTAL (14) Question 3.3. Cost-Volume-Profit analysis and Ethics Smart Travel (Pty) Ltd is a corporate travel agent that specialise in organising flights between Cape Town and Johannesburg. Smart Travel books passengers on Kulala Airline which charges passengers R2 760 per round-trip ticket, in return Smart Travel receives a commission of 15% of the ticket price paid by the passenger. The following information is available: Budgeted fixed costs are R90 000 per month. Budgeted variable costs per ticket are 12% of the commission earned per ticket. During the 2020 financial year, Smart Travel applied for a cash financing at First Capital Bank in order to boost its low cash flow. In the process of applying for the finance, the Financial Manager submitted financial statements with errors to the bank regardless of the fact that, he was advised by an independent reviewer to correct the following issues: Smart Travel accounted for revenue from sale of tickets at 100% of the selling price of the tickets which also includes VAT. The Financial Manager indicated that, Smart Travel had to get the funding at all cost because, if the loan was not granted by First Capital Bank the company would have not managed to cover its employee cost expense in some of the months during the year. Marks (3) REQUIRED (a) Calculate the following: (1) Number of tickets that Smart Travel must sell per month to break-even. (ii) The number of tickets that Smart Travel must sell to make a profit of R45000 per month (iii) The margin of safety ratio if Smart Travel sells 300 tickets per month (3) (3) Note: Round off figures to two decimal places. (b)(0) (3) Identify and discuss two ethical concerns and/or other qualitative factors that may have an adverse effect on the business and/or reputation of Smart Travel. Note: For this part of the required, assume that Smart Travel is a registered VAT vendor. Total (12) PART B Kako-lako (Pty) Ltd manufactures and sells three different distinct beverages. As part of the standards and budget setting process, the capacities of the product lines have to be considered. The following information is available for the 6 months from May 2021 Fuzz tea Kako-Lako Mjojo - Combucha 30 000 Demand (Units) Contribution per unit 18 000 R4,5 24 000 R6 R3 1 hour 2,4 hours 1,80 hours Required labour hours A maximum of 108 000 direct labour hours is available in normal working hours for the 6 months period. Employees only work during normal hours and the company does not have resources for its employees to work overtime. Process costing information Kako-lako uses a process costing system in the production of three products. Information below relates to the production process of product Fuzz tea, for the month of January 2021. Units 3 000 4 500 Opening Work-in-progress (WIP) - 1 January: 60% complete Closing Work-in-progress( WIP) - 31 January: 65% complete New units put into production in January 2021 Completed and transferred in January 2021 37 000 30 000 Additional information: . Cost information was as follows: R Opening WIP Raw materials Conversion Added in January 2021 Raw materials Conversion 48 000 29 500 106 600 58 963 . Normal losses are estimated at 3% of the inputs that reaches the wastage point. Normal losses occur when the process is 60% complete. Raw materials are added at the beginning of the process and conversion takes place evenly throughout the process. Kako-lako uses the weighted average method of inventory valuation. Marks REQUIRED (a) Using relevant costing principles, calculate a Project cost schedule for Project Phila. You should also provide reasons for inclusion or exclusion of each cost item. (10) (b) Calculate the optimal production mix of Kako-lako (Pty) Ltd's three products for the six-month's period from May 2021. Round to two decimals throughout your calculation. (8) (c) Prepare Kako-lako's budgeted quantity statement for January 2021. (6) TOTAL (24) Question 3.2 Activity-Based Costing Siqalo Bread (Pty) Ltd was started by Ms. Fresh after she got retrenched from a Cake bakery that closed its doors in April 2020 due to negative effects from the hard lockdown as a result of the Covid 19 pandemic. After struggling for the first few months of her business in a very competitive market, Ms. Fresh decided to use two of her grandmother's secret family recipes of corn and multigrain bread. Bread from these two recipes have turned to be loved by many South Africans. Siqalo Bread currently operates in Pretoria North and supplies to a few independent retailers on a cash delivery basis. The company is currently using a traditional costing system. Fixed manufacturing overheads are based on budgeted normal capacity of 150 000 hours per year, of which 67 500 hours are allocated to Corn bread and 82 500 hours to Multigrain bread. Ms. Fresh believes that the traditional costing system may be providing misleading information in the allocation of overheads to the products, as a result, she approached Mr. Mhambi, a Management accountant who has developed an activity-based analysis of the 2021 budgeted fixed manufacturing overheads which are set as below: Expected fixed manufacturing overheads and activities involved: Activity Cost drivers R Set-up costs Set-ups 31 500 Quality control Batches 3 150 Baking Baking hours 15 750 Packaging time Packing hours 6 900 Not identified 13 200 Total 70 500 The analysis also revealed the following budgeted information: Siqalo bread budgeted for 225 000 Corn bread loaves and 105 000 Multigrain bread loaves to be manufactured during the year. Manufacturing occurs in batches as follows: Corn Multigrain Batch size 1 500 1 500 Baking time (Hours) 1 300 1 000 Packaging time (Hours) 225 180 Set-ups 5 per batch 7 per batch REQUIRED Marks (a) Using activity-based costing (ABC), calculate the budgeted total fixed (12) manufacturing overheads of Multigrain. Note: Round off the allocation rates to two decimal places and the overheads to the nearest Rand figures. Briefly explain why ABC lead to a more accurate allocation of overheads than (b) traditional costing (assuming that the environment is appropriate for ABC). (2) QUESTION TOTAL (14) Question 3.3. Cost-Volume-Profit analysis and Ethics Smart Travel (Pty) Ltd is a corporate travel agent that specialise in organising flights between Cape Town and Johannesburg. Smart Travel books passengers on Kulala Airline which charges passengers R2 760 per round-trip ticket, in return Smart Travel receives a commission of 15% of the ticket price paid by the passenger. The following information is available: Budgeted fixed costs are R90 000 per month. Budgeted variable costs per ticket are 12% of the commission earned per ticket. During the 2020 financial year, Smart Travel applied for a cash financing at First Capital Bank in order to boost its low cash flow. In the process of applying for the finance, the Financial Manager submitted financial statements with errors to the bank regardless of the fact that, he was advised by an independent reviewer to correct the following issues: Smart Travel accounted for revenue from sale of tickets at 100% of the selling price of the tickets which also includes VAT. The Financial Manager indicated that, Smart Travel had to get the funding at all cost because, if the loan was not granted by First Capital Bank the company would have not managed to cover its employee cost expense in some of the months during the year. Marks (3) REQUIRED (a) Calculate the following: (1) Number of tickets that Smart Travel must sell per month to break-even. (ii) The number of tickets that Smart Travel must sell to make a profit of R45000 per month (iii) The margin of safety ratio if Smart Travel sells 300 tickets per month (3) (3) Note: Round off figures to two decimal places. (b)(0) (3) Identify and discuss two ethical concerns and/or other qualitative factors that may have an adverse effect on the business and/or reputation of Smart Travel. Note: For this part of the required, assume that Smart Travel is a registered VAT vendor. Total (12)











