Question: Part III: Case Application and Written Answers (9 marks) (ILO's: A1, B1, C1, C2, D4) The following is an extract from a Home Insurance Policy.
Part III:
Case Application and Written Answers (9 marks) (ILO's: A1, B1, C1, C2, D4)
The following is an extract from a Home Insurance Policy.
We "the insurer" will provide cover for loss or damage to your "the insureds" home structure and content caused by fire or storms. But not loss or damage occurring whilst the home has been left unoccupied for over one year or losses resulting from war. We will also cover acts of violent theft or attempted violent theft but not loss or damage caused by your guests, residents or domestic helpers. The sum insured must at all times represent the full cost of replacing the property insured without deduction for wear and tear and depreciation. You and any other person to whom this insurance applies shall take all reasonable precautions to prevent accidents, loss or damage and shall maintain the home in good condition. You shall on the happening of any event likely to lead to a claim under this Policy notify us within 24 hours if any property is stolen or damaged. You must provide a police report or fire department report in the case of theft or fire.
Identify two perils covered in the policy (0.5 marks)
Identify two exclusions in the policy (0.5 marks)
Identify two conditions in the policy (0.5 marks)
Explain the principle of subrogation and provide an example of how it would be applied (1 mark)
Karim is a financial advisor for a large private equity firm. From his years of work, he accumulated some savings and wants to start his own business by building a hotel. He approached Ahli United Bank in order to secure a loan for his upcoming venture. With his equity and loan, he was able to purchase a land from Purple Bricks Realty and finance the construction of his project through signing an agreement with TKO Contractors to build the Hotel in Muharraq.
Determine the insurable interest in the project for the following parties; (1 mark)
Karim:
Ahli United Bank:
Purple Bricks Realty:
TKO Contractors:
After completing the project, and worried about potential losses, Karim wanted to acquire a property insurance coverage plan. While completing the application for the policy, Karim's insurance agent informed him that there are circumstances that will lead to the insurer denying payment of losses. Explain any three reasons that will render the contract void and the compensation denied to Karim if they occur. (1.5 marks)
Two years after the policy was issued an electrical fire destroyed five guest rooms. The fire damage amounted to a loss of $85,000. The agent had placed the insurance coverage with three property insurers. Insurer A provided $1,850,000 of coverage; insurer B covered $2,100,000 while insurer C had $1,050,000 of coverage. The policy contained a pro rata liability provision. How much will Karim collect from each insurer? (1 mark)
Reem owns a storage warehouse that is insured for $312,000 under a commercial property insurance policy. The policy contains an 80% coinsurance clause. The warehouse sustained a $42,000 loss due to a fire. The replacement cost of the warehouse at the time of loss was $400,000. How much will the insurer pay? (1 mark)
Ahmed had a medical health insurance policy with a $300 calendar year deductible and a 25% coinsurance clause. He needed medical treatment that cost $14,000. How much will he pay? (1 mark)
A $70,000 medical malpractice claim was covered under three liability insurance contracts. Policy A contained a $400,000 limit of liability, Policy B contained a $110,000 limit of liability while Policy C contained a $20,000 limit of liability. The contracts provided for contribution by equal shares. How much will the hospital collect from each insurer? (1 mark)
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Identify two perils covered in the policy
The two perils covered in the policy is:
i) loss or damage to the home structure caused by fire or storm.
ii) loss due to violent theft or sttempted violent theft.
Identify two exclusions in the policy.
The exclusion in the policy are:
i) it doesn't include when the damage occured when the house left unoccupied for a year or more.
ii) damage done due to guests , relatives and domestic helpers are not included.
Identify two conditions in the policy
The two conditions in the policy are:
i ) the insured must take all precautions to avoid loss and damages.
ii) The loss , damage or theft must be notified within 24 hrs to the insurer as cnditioned in the policy.
Explain the principle of subrogation and provide an example of how it would be applied
it is the right which are entitled to the insurance carriers to legally pursue a third party for any loss or damages caused to the insured. it is done to recover some or all part of the amount which is covered under the insurance for the loss and damages.
Example: Insured person's car got damages because ofthe fault of a third party, The insurer would pay for the loss and damages done, and pursue a legal action against the third party to recover for the loss.
ii.
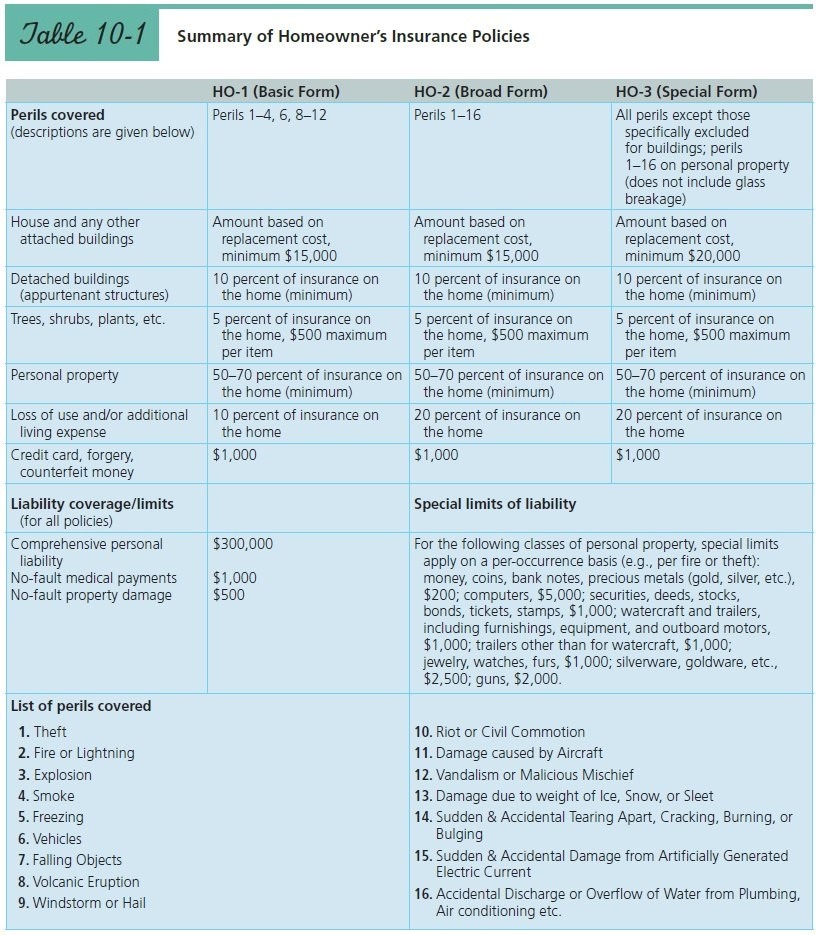
How Much of Fire Loss Will Be Covered? Toula and Ian Miller of Gainesville, Florida, recently suffered a fire at their home. The fire, which began in a crawl space at the back of the house, caused $51,000 of damage to the dwelling itself. Their garage, valued at $22,000, was totally destroyed but did not contain a car at the time of the fire. Replacement of the Millers' personal property damaged in the home and garage amounted to $25,000. In addition, $350 in cash and a stamp collection valued at $3,235 were destroyed. While the damage was being repaired, the Millers stayed in a motel for one week and spent $1,310 on food and lodging. The house had a value of $196,000 and was insured for $151,000 under an HO-3 policy with a $250 deductible. Use Table 10-1 to answer the following questions. (Hint: You must first determine whether the Millers have adequate dwelling replacement coverage and, if not, what percentage of the necessary 80 percent coverage they do have. The resulting answer will determine the percentage of the loss to the dwelling covered, and consequently the amount to be reimbursed by the insurance company.) Assuming that the deductible was applied to the damage to the dwelling, calculate the amount covered by insurance and the amount that the Millers must pay for each loss listed: the dwelling, the garage, the cash and stamp collection, and the extra living expenses.
Enter all amounts as positive numbers. Leave no cells blank. Enter "0" wherever required. Round your answers to the nearest dollar
amount covered by insurance amount millers must pay
the dwelling $ $
the garage $ $
the cash $ $
stamp collection $ $
the extra living expenses $ $
b. How much of the amount of the personal property loss would be covered by the insurance policy? Assume that the Miller's policy includes contents replacement-cost protection. Enter all amounts as positive numbers. Leave no cells blank. Enter "0" wherever required. Round your answers to the nearest dollar.
$____
paid for by the Millers? $_______
C. Assuming that they have contents replacement-cost protection on the personal property, what amount and percentage of the total loss must be paid by the Millers? Enter the values as positive numbers. Round your answer for amount to the nearest dollar and answer for percentage to two decimal places.
amount: $______
percentage: ______%
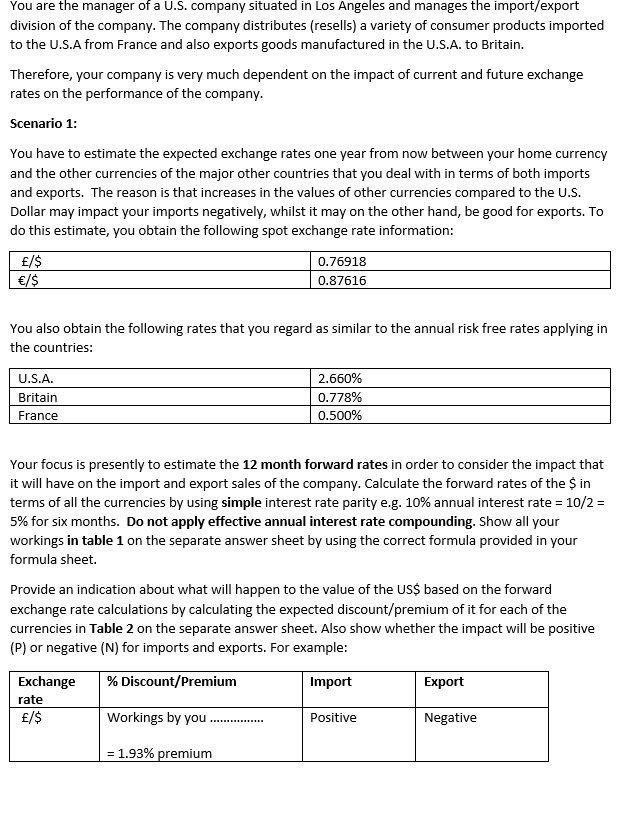
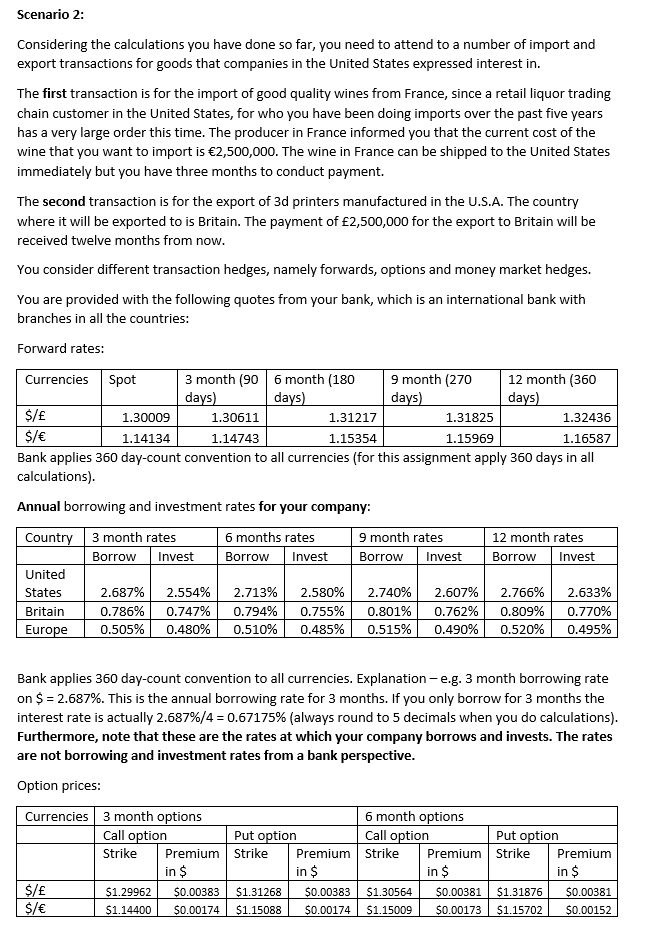
You are the manager of a U.S. company situated in Los Angeles and manages the import/export division of the company. The company distributes (resells) a variety of consumer products imported to the U.S.A from France and also exports goods manufactured in the U.S.A. to Britain. Therefore, your company is very much dependent on the impact of current and future exchange rates on the performance of the company. Scenario 1: You have to estimate the expected exchange rates one year from now between your home currency and the other currencies of the major other countries that you deal with in terms of both imports and exports. The reason is that increases in the values of other currencies compared to the U.S. Dollar may impact your imports negatively, whilst it may on the other hand, be good for exports. To do this estimate, you obtain the following spot exchange rate information: E/$ 0.76918 E/$ 0.87616 You also obtain the following rates that you regard as similar to the annual risk free rates applying in the countries: U.S.A. 2.660% Britain 0.778% France 0.500% Your focus is presently to estimate the 12 month forward rates in order to consider the impact that it will have on the import and export sales of the company. Calculate the forward rates of the $ in terms of all the currencies by using simple interest rate parity e.g. 10% annual interest rate = 10/2 = 5% for six months. Do not apply effective annual interest rate compounding. Show all your workings in table 1 on the separate answer sheet by using the correct formula provided in your formula sheet. Provide an indication about what will happen to the value of the US$ based on the forward exchange rate calculations by calculating the expected discount/premium of it for each of the currencies in Table 2 on the separate answer sheet. Also show whether the impact will be positive (P) or negative (N) for imports and exports. For example: Exchange % Discount/Premium Import Export rate E/$ Workings by you ...... Positive Negative = 1.93% premiumScenario 2: Considering the calculations you have done so far, you need to attend to a number of import and export transactions for goods that companies in the United States expressed interest in. The first transaction is for the import of good quality wines from France, since a retail liquor trading chain customer in the United States, for who you have been doing imports over the past five years has a very large order this time. The producer in France informed you that the current cost of the wine that you want to import is $2,500,000. The wine in France can be shipped to the United States immediately but you have three months to conduct payment. The second transaction is for the export of 3d printers manufactured in the U.S.A. The country where it will be exported to is Britain. The payment of f2,500,000 for the export to Britain will be received twelve months from now. You consider different transaction hedges, namely forwards, options and money market hedges. You are provided with the following quotes from your bank, which is an international bank with branches in all the countries: Forward rates: Currencies Spot 3 month (90 6 month (180 9 month (270 12 month (360 days) days) days days $/E 1.30009 1.30611 1.31217 1.31825 1.32436 $/E 1.14134 1.14743 1.15354 1.15969 1.16587 Bank applies 360 day-count convention to all currencies (for this assignment apply 360 days in all calculations). Annual borrowing and investment rates for your company: Country 3 month rates 6 months rates 9 month rates 12 month rates Borrow Invest Borrow Invest Borrow Invest Borrow Invest United States 2.687% 2.554% 2.713% 2.580% 2.740% 2.607% 2.766% 2.633% Britain 0.786% 0.747% 0.794% 0.755% 0.801% 0.762% 0.809% 0.770% Europe 0.505% 0.480% 0.510% 0.485% 0.515% 0.490% 0.520% 0.495% Bank applies 360 day-count convention to all currencies. Explanation - e.g. 3 month borrowing rate on $ = 2.687%. This is the annual borrowing rate for 3 months. If you only borrow for 3 months the interest rate is actually 2.687%/4 = 0.67175% (always round to 5 decimals when you do calculations). Furthermore, note that these are the rates at which your company borrows and invests. The rates are not borrowing and investment rates from a bank perspective. Option prices: Currencies 3 month options 6 month options Call option Put option Call option Put option Strike Premium Strike Premium Strike Premium Strike Premium in $ n $ n $ in $ $/f 51.29962 50.00383 $1.31268 50.00383 51.30564 $0.00381 $1.31876 50.00381 $/E 51.14400 50.00174 $1.15088 50.00174 $1.15009 50.00173 $1.15702 50.00152Bank applies 35E} daycount convention to all currencies. [Students also have to apply BED days in all calculations]. CIption premium calculations should include time value calculations based on US 5 annual borrowing interest rates for applicable time periods e.g. 3 month 5 option premium is subject to 2.5ElTE-6f4 interest rate.} a. Calculate the cost of money market hedges for the imports from Franoe [Complete Table 3 on the separate answer sheet} b. Determine the option typa that you will consider based on the exchange rate quota provided by your bank. Remember we will long or short the base currencies [in this case study the currencies that are not 5} and the PU of premium cost is based on the borrowing cost of 5 for the time period of the option. For example if it is a 3 month option, then the interest rate that should be applied is United States 3 month borrowing rate of EEBTW-tl = .5?1?5%}. Calculate the total cost of using options as hedging instrument for the imports from France {Complete Table 4 on the separate answer sheet}. c. Compare the forwal'd quotes, money market hedges and options with each other to determine the best exchange rate hedges for France {Coitqllete Table 5 on the separate answer sheet}. d. Calculate the exchange rates that will apply if the money market hedges are used for the exports to Britain {Complete Table ti on the separate answer sheet} e. Compare the forward quotes and money market hedges with each other to determine the best exchange rate hedges for Britain {Complete Table I" on the separate answer sheet]. f. Assume you entered into the forward hedge for the import from France. Two months have passed since you entered into the hedge. Interest rates are the same as before. The spot exchange rate of the HE is now 1.14320. Calculate the value of your forward position. Please use a 360 daycount convention, since the bank also used a 350 day-count convention with the forward quotes provided to you. Also remember for interest rates use risk free rates provided under soenario 1. Show your calculation in table 3 on the separate arster sheet. END 01: QUEEI'IDHS Perils covered Perils 1 {descriptions are given below] House and any other attached buildings Detached buildings {appurtenant structures] Trees, shrubs, plants, etc. Personal property Loss of use andfor additional living expense Amount based on replacement cost, minimum $15,000 10 percent of insurance on the home {minimum} 5 percent of insurance on the home, $500 maximum per item 50?0 percent of insurance on the home {minimu mi 10 percent of insurance on the home Summary of Homeowner's Insurance Policies Amount based on replacement cost, minimum $15,000 10 percent of insurance on the home {minimum} 5 percent of insurance on the borne, $500 maximum per item -:r .-- -m All perils except th ose specically excluded for buildings; perils l1E on personal property {does not include glass breakage} Amount based on replacement cost, minimum $20,000 10 percent of insurance on the home {minimum} 5 percentot insurance on the home, $500 maximum per item 50?0 percent of insurance on 50?0 percent of insurance on the home {minimum} 20 percent of insurance on the home the home {minimum} 20 percent of insurance on the home Credit card, forgew. $1,000 $1,000 $1,000 counterfeit money Liability coveragel'limits Special limits of liability {for all policies] Comprehensive personal liability lilo-fault medical payments lilo-fault property damage List of perils covered 1. Theft 2. Fire or Lightning 3. Explosion all. Smoke 5. Freezing 5. Vehicles 3'. Falling Objects 8. Volcanic Eruption 9. Windstorm or Hail For the following classes of personal property, sperial limits apply on a peroccurrence basis [e.g., per fire or theft]: money, coins, bank notes, precious metals {gold, silver, etc], $200; computers, $5,000; securities, deeds, stocks, bonds, tickets, stamps, $1,000; watercraft and trailers, including furnishings, equipment, and outboard motors, $1,000; trailers other than for watercraft, $1,000; jeiyelry, watches, furs, $1,000; silverware, goldware, etc, $2,500; guns, $2,000. 10. Riot or Chill Commotion 11. Damage caused by Aircraft 12. Vandalism or Malicious Mischief 13. Damage due to weight of ice, Snow, or Sleet 14. Sudden ll: Accidental Tearing Apart, Cracking, Burning, or Bulging 15. Sudden it: Accidental Damage from Artificially Generated Electric Current iii. Accidental Discharge or Overflow of Water from Plumbing, Air conditioning etc