Question
PART ONE Greenscape Pty Ltd provides commercial landscaping services. Linda Drake, the firms owner, wants to develop cost estimates that she can use to prepare
PART ONE
Greenscape Pty Ltd provides commercial landscaping services. Linda Drake, the firms owner, wants to develop cost estimates that she can use to prepare bids on jobs. After analysing the firms costs, Drake has developed the following preliminary cost estimates for each 1 000 square metres of landscaping:

Drake is quite certain about the estimates for direct materials and direct labour, but she is not as comfortable with the overhead estimate. As indirect costs, overhead costs cannot be traced directly to landscaping. Instead, Drake has used a common method of estimating an overhead rate per direct labour hour. However, the estimate for overhead is based on the overhead costs that were incurred during the past 12 months, as presented in the following schedule. The estimate of $18 per direct labour hour was determined by dividing the total overhead costs for the 12-month period ($648 000) by the total direct labour hours (36 000).
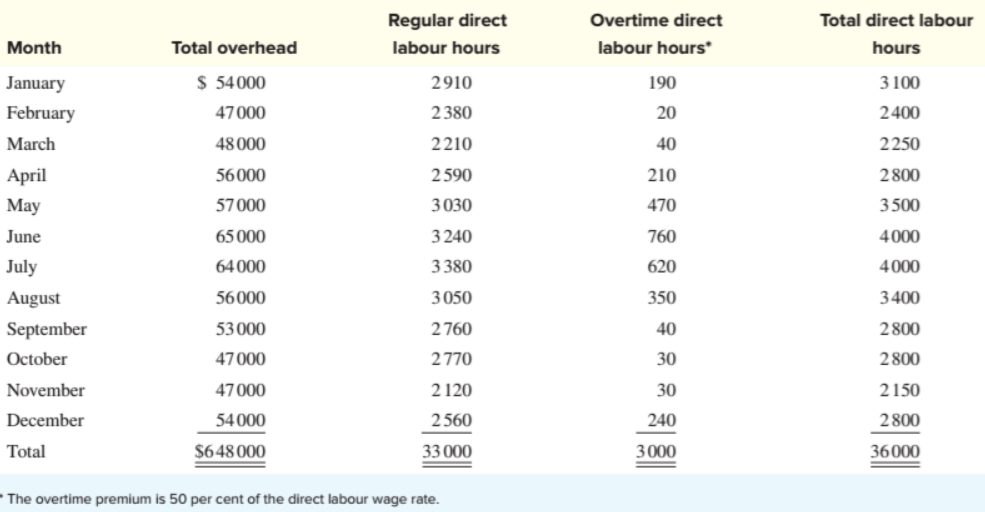
Drake believes that overhead is affected by total monthly direct labour hours. She decided to perform a regression analysis of overhead (OH) on total direct labour hours (DLH). The following regression formula was obtained:
OH = $26 201 + $9.27DLH
1. The overhead rate developed from the regression analysis is different from Linda Drakes preliminary estimate of $18 per direct labour hour. Explain the difference in the two overhead rates.
2. Using the overhead formula that was derived from the regression analysis, determine a total variable cost estimate for each 1 000 square metres of landscaping.
3. Linda Drake has been asked to submit a bid on a landscaping project for Melbourne City Council, consisting of 50 000 square metres. Drake estimates that 30 per cent of the direct labour hours required for the project will be on overtime. Calculate the variable costs per 1 000 metres of landscaping that should be included in any bid that Drake would submit on this project. Use the overhead formula derived from the regression analysis.
4. Should Greenscape rely on the overhead formula derived from the regression analysis as the basis for the variable overhead component of its cost estimate? Explain your answer.
5. After attending a seminar on activity-based costing, Drake decided on a further analysis of Greenscapes activities and costs. She discovered that a more accurate portrayal of the firms cost behaviour could be achieved by dividing overhead into three separate cost poolsadministration, seeding and individual plantingeach with its own cost driver. After discussions with some of the landscapers who work within the firm, Drake came to the conclusion that possible cost drivers for each of these cost pools were direct labour hours, the number of square metres of turf seeded, and the number of individual trees and shrubs planted, respectively. A separate regression equation was estimated for each overhead cost pool, with the following results:
Administration OH1 = $10 000 + $4.10DLH, where DLH denotes direct labour hours;
Seeding OH2 = $9 100 + $13.50STS, where STS denotes the number of square metres of turf seeded (in thousands);
Planting OH3 = $8 000 + $6.60TSP, where TSP denotes the number of individual plantings (such as trees and shrubs).
Assume that 5 direct labour hours are needed to landscape each 1 000 square metres, regardless of the specific planting material that is used.
(a) Suppose the landscaping project for the city will involve seeding all 50 000 square metres of turf and planting 70 trees and shrubs. Calculate the variable overhead cost that Drake should include in the bid.
(b) recalculate the variable overhead cost for the citys landscaping project, assuming that half of the 50 000 square metre landscaping area will be seeded and there will be 230 individual plantings.
(c) Explain why the costs differ in parts (a) and (b).
PART TWO
After a more sophisticated analysis of Greenscape's costs, Drake has access to the following additional data.
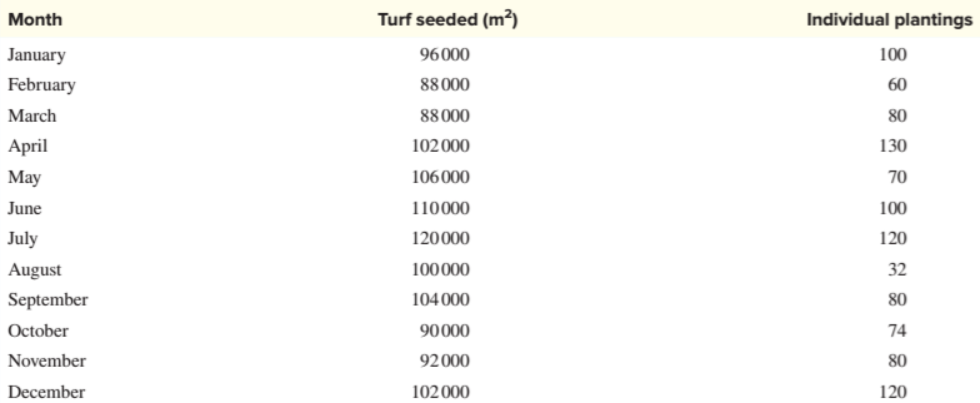
Refer to the data in part one, as well as the additional data above.
6. Use the data for the three cost drivers to formulate a single multiple regression equation to predict total overhead cost.
7. Does the new cost model (from requirement 1) provide a more accurate estimate of total overhead cost compared to the regression analysis Drake performed (which only included DLH)? Explain your answer.
Direct materials Direct labour (5 direct labour hours@$19 per hour) Overhead ( $18 per direct labour hour) Total cost per 1000 square metres $400 95 90 $585 Month January February March April May June Turf seeded (m) 96000 88000 88000 102000 06000 110000 20000 Individual plantings 100 60 80 130 70 100 120 32 80 74 80 120 August September October November December 04000 90000 92000 02000 Direct materials Direct labour (5 direct labour hours@$19 per hour) Overhead ( $18 per direct labour hour) Total cost per 1000 square metres $400 95 90 $585 Month January February March April May June Turf seeded (m) 96000 88000 88000 102000 06000 110000 20000 Individual plantings 100 60 80 130 70 100 120 32 80 74 80 120 August September October November December 04000 90000 92000 02000Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


