Question
Pasteurization in the food industry is one of the most applied heating processes to render pathogenic microorganisms harmless (Figure 2). It is often used in
Pasteurization in the food industry is one of the most applied heating processes to render pathogenic microorganisms harmless (Figure 2). It is often used in the production of milk, ice cream juices and beer. With the specified time/temperature treatment, it ensures minimum deterioration in the nutritional and organoleptic properties of the product, while inactivating harmful microorganisms. The pasteurization process includes 4 main stages; 1. Preheat 2. Final heating to pasteurization temperature using hot water 3. Holding at this temperature for a period of time to achieve the desired microbial effect 4. Re-cooling the product using cooling water The following conditions are necessary for the microbiologically safe and efficient operation of the pasteurization unit. 1. Correct selection of pasteurization conditions 2. Prevention of product contamination in the pasteurization unit. 3. The holding tube is clean, the heat exchanger is not corroded, and there is no change in the raw material. The main units in the pasteurization system are: Heat exchanger, holding tube, flow reversing system and process control. - The main task of the heat exchanger in the pasteurization process is to heat or cool the product to the desired temperature. The most commonly used types are plate and tube heat exchangers. - The task of the flow control system is to ensure that the flow rate of the current entering the pasteurizer is constant. - The pipeline (holding tube) used for holding at the pasteurization temperature ensures that the product can be subjected to the desired heating process for sufficient time. This period is very short. - Flow reversing system is used when the product leaving the holding unit does not reach the pasteurization temperature. Pneumatic valves are exemplary devices for flow reversing devices. These valves are placed at the end of the holding tube. - The main function of process controllers is to control critical temperatures. In case of product leaving the holding unit at low temperatures, it activates the flow diverter valve and ensures that the liquid goes back to the balancing tank. - Milk taken from the balance (balancing) tank by pump enters the regeneration section of the plate heat exchanger. Here, pre-pasteurized milk coming from the holding pipe is preheated to approximately 58C. - Then the milk goes to the heating section, where it is heated with hot water to the predetermined pasteurization temperature. - The milk coming out of the heating section is sent to the holding pipe, where it is kept at the pasteurization temperature for the desired time. - There is a diverter valve at the end of the holding pipe. If the milk has not reached the required temperature when it leaves the heating section, this is determined by the thermocouple in the system and the flow reversing valve automatically changes the flow path, allowing the milk to return to the balancing tank. Response speed, accuracy and precision of the temperature measuring element are crucial to achieving the desired temperature profile. - Milk kept at the desired time (15-40 seconds) and at the desired pasteurization temperature (71-74 oC) in the holding section of the pasteurizer is returned to the regeneration section. - Pasteurized milk cooled to a certain temperature in the regeneration sections passes to the cooler section, where it is cooled with ice water and leaves the system at 5C.
Answer the following questions in the light of the information given above. a) The basic adjustable variables in the pasteurization unit are ___________________________________ , __________________________________ , _______________________________. The controlled variable is ___________________________ and the load variables are __________________________ , ___________________________. b) Add the necessary temperature control cycle to the figure so that the milk can reach the constant pasteurization temperature (74 oC) after the heater. (With this match, the water entering the water heater and the water leaving the water heater are evaluated together in the controller.) c) Add a device to the figure that will control the required flow rate so that the desired time (40 seconds) remains in the holding tube. d) Add a control loop to the figure that allows the milk that has not reached the pasteurization temperature to go to the balancing tank with the help of the flow reversing valve. e) Add a system that will prevent overflow in the balancing tank to the figure.
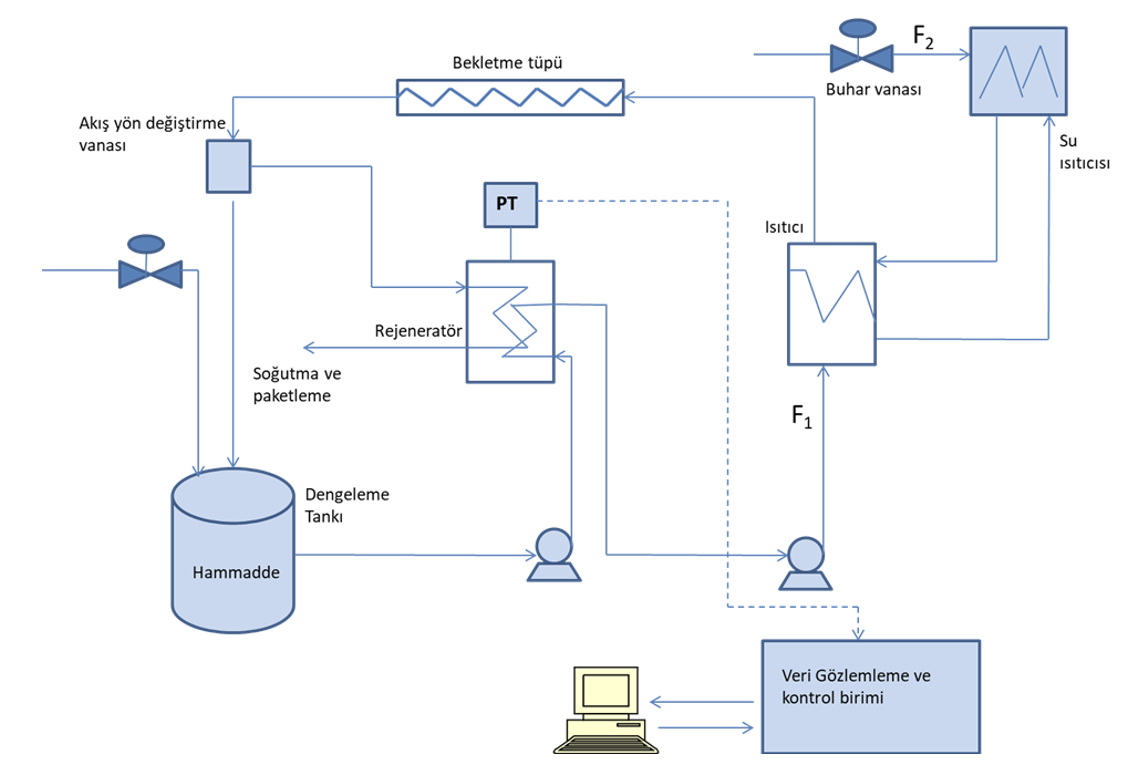
Figure 2. High temperature short time (HTST) Pasteurization Process
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


