Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Path Delay is a measure of the time it takes for a packet to traverse a route. - = Path delay sum of all
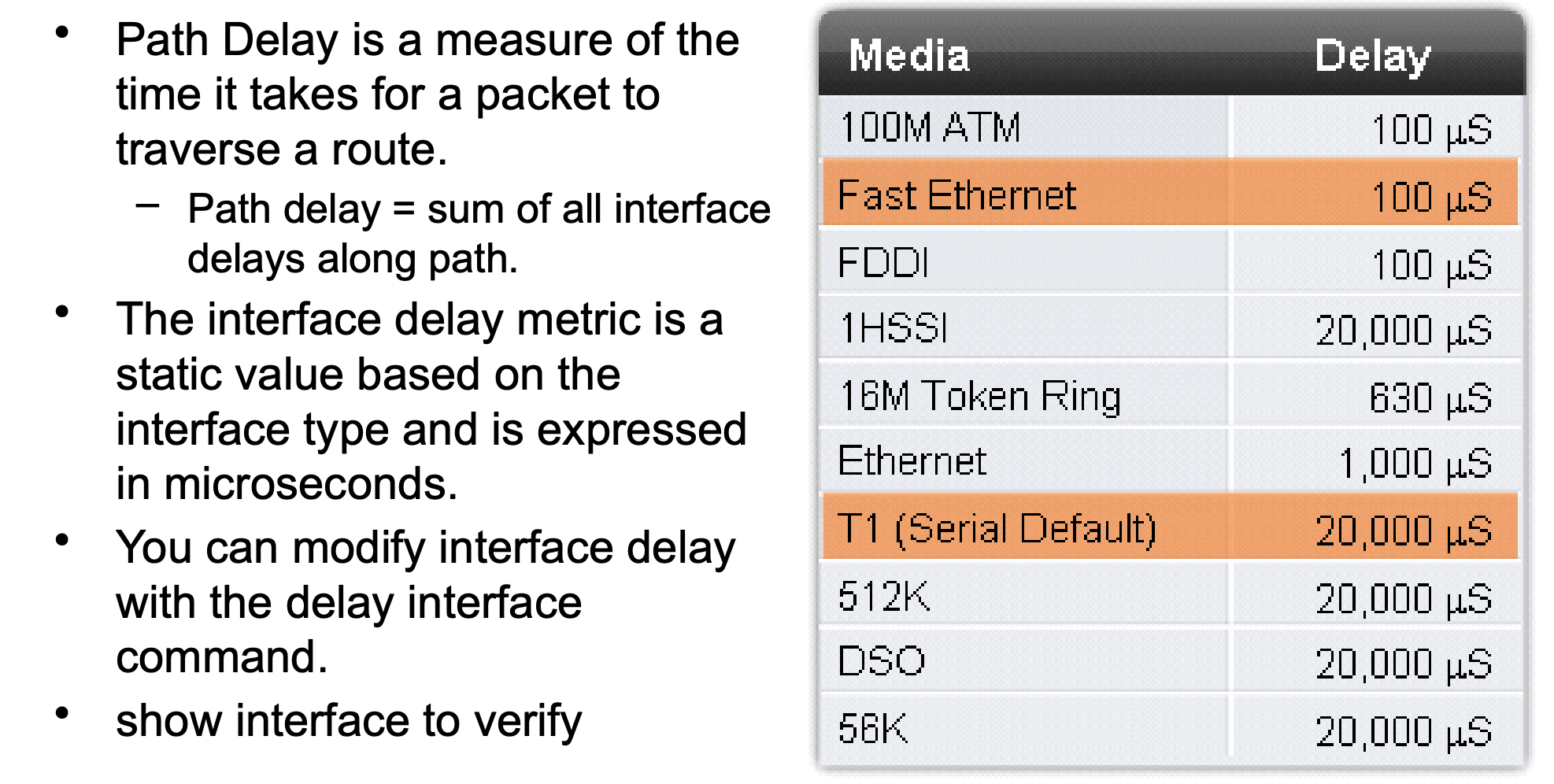
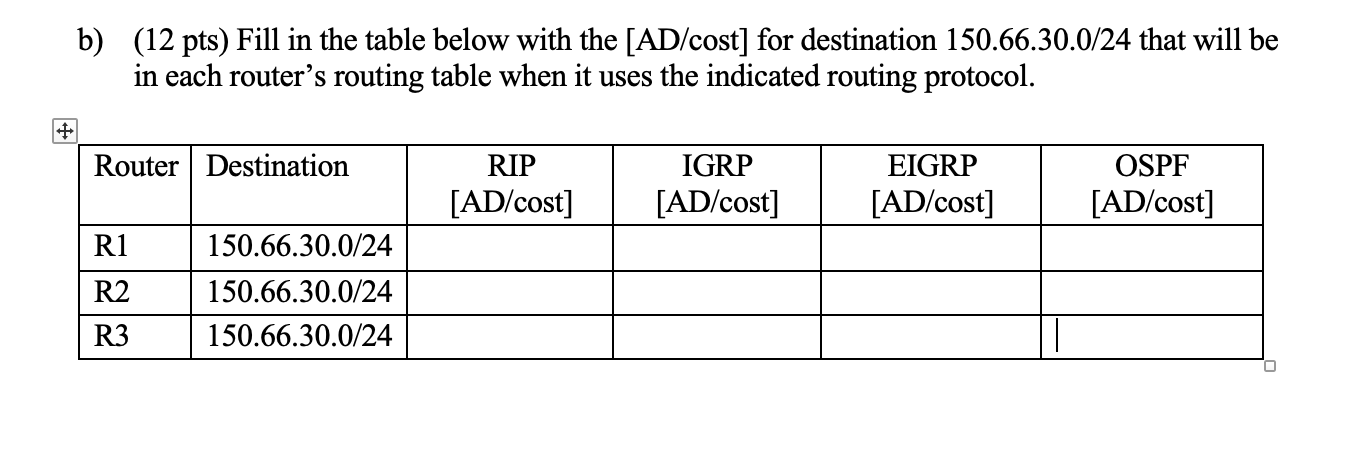
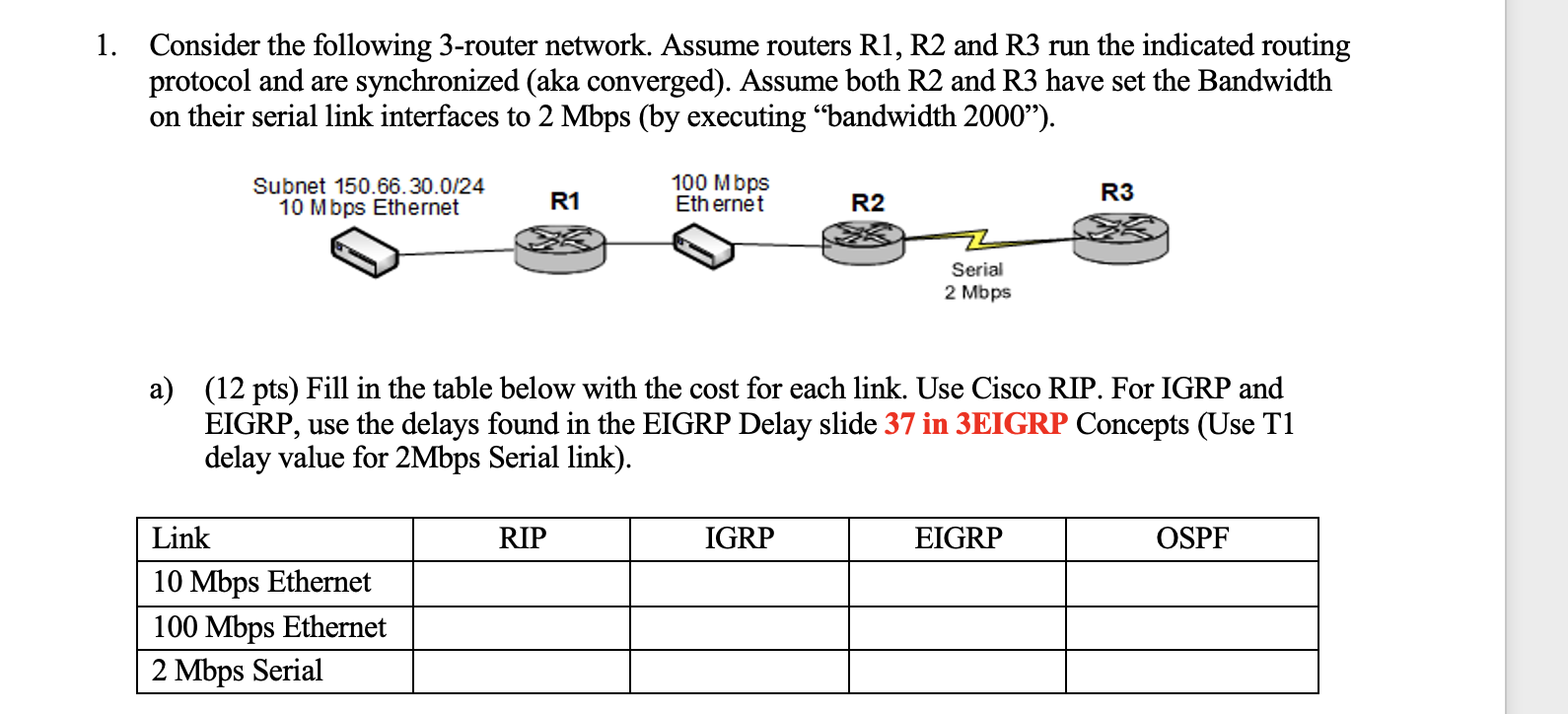
Path Delay is a measure of the time it takes for a packet to traverse a route. - = Path delay sum of all interface delays along path. The interface delay metric is a static value based on the interface type and is expressed in microseconds. You can modify interface delay with the delay interface command. show interface to verify Media Delay 100M ATM 100 S Fast Ethernet 100 S FDDI 100 S 1HSSI 20,000 S 16M Token Ring 630 S Ethernet 1,000 S T1 (Serial Default) 20,000 S 512K 20,000 S DSO 20,000 S 56K 20,000 S b) (12 pts) Fill in the table below with the [AD/cost] for destination 150.66.30.0/24 that will be in each router's routing table when it uses the indicated routing protocol. Router Destination RIP [AD/cost] IGRP [AD/cost] EIGRP [AD/cost] OSPF [AD/cost] R1 150.66.30.0/24 R2 150.66.30.0/24 R3 150.66.30.0/24 1. Consider the following 3-router network. Assume routers R1, R2 and R3 run the indicated routing protocol and are synchronized (aka converged). Assume both R2 and R3 have set the Bandwidth on their serial link interfaces to 2 Mbps (by executing bandwidth 2000"). Subnet 150.66.30.0/24 10 Mbps Ethernet R1 100 Mbps Ethernet R2 Serial 2 Mbps R3 a) (12 pts) Fill in the table below with the cost for each link. Use Cisco RIP. For IGRP and EIGRP, use the delays found in the EIGRP Delay slide 37 in 3EIGRP Concepts (Use T1 delay value for 2Mbps Serial link). Link 10 Mbps Ethernet RIP IGRP EIGRP OSPF 100 Mbps Ethernet 2 Mbps Serial
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


