Question: Physics Motion Lab Questions Given Information + Instructions : Please give detailed explanations as well as going through the simulations to examine the questions below


Physics Motion Lab Questions
Given Information + Instructions :
Please give detailed explanations as well as going through the simulations to examine the questions below
* Don't use previously written answers which also has distinctive questions

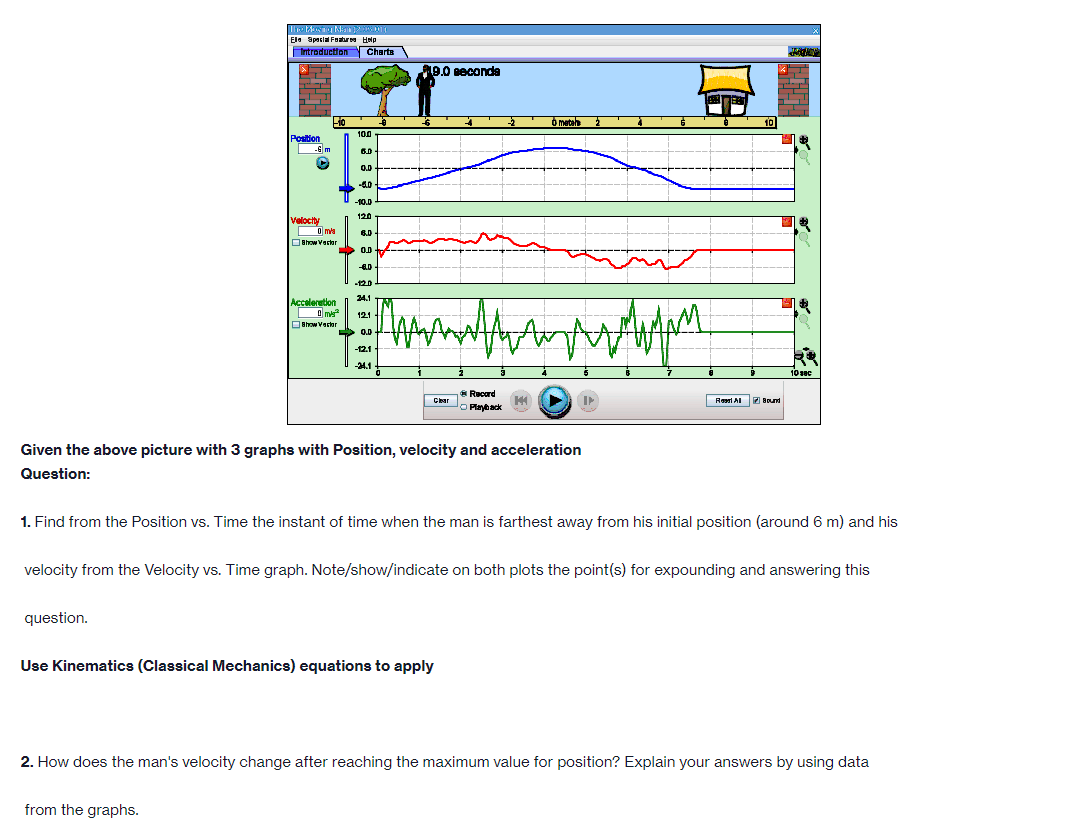

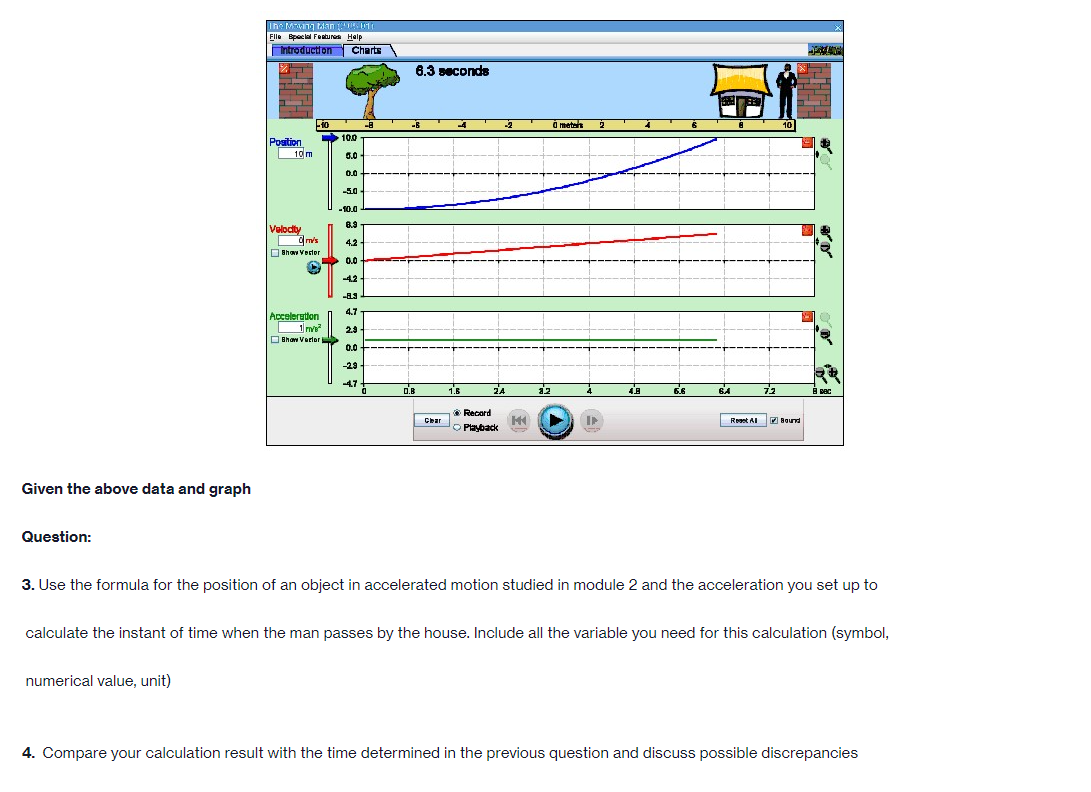

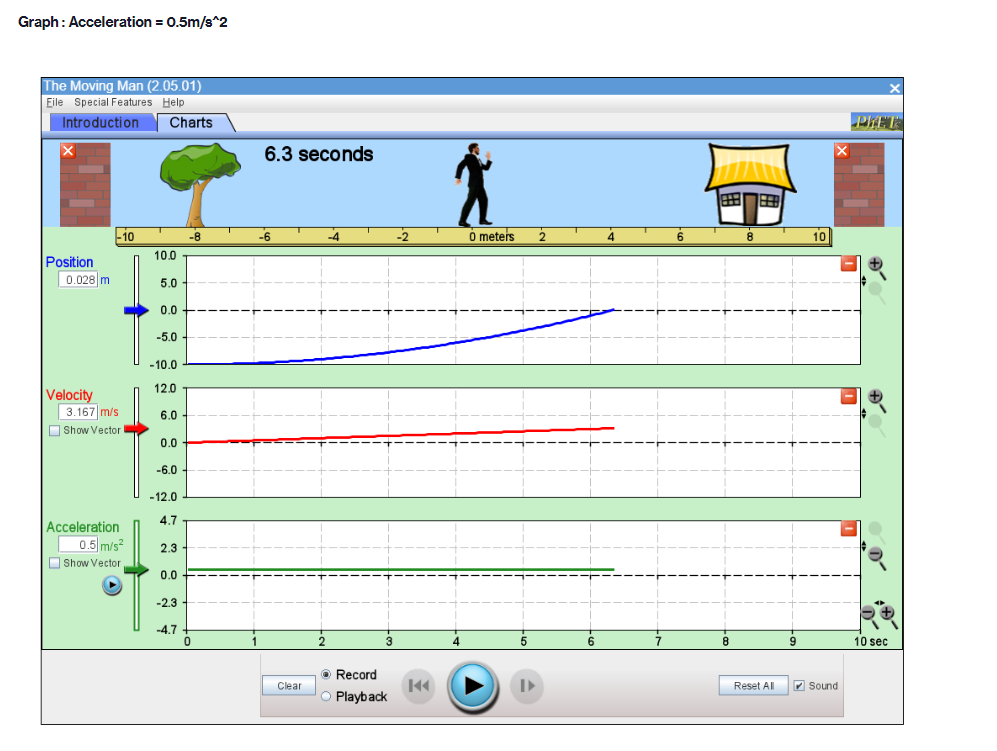
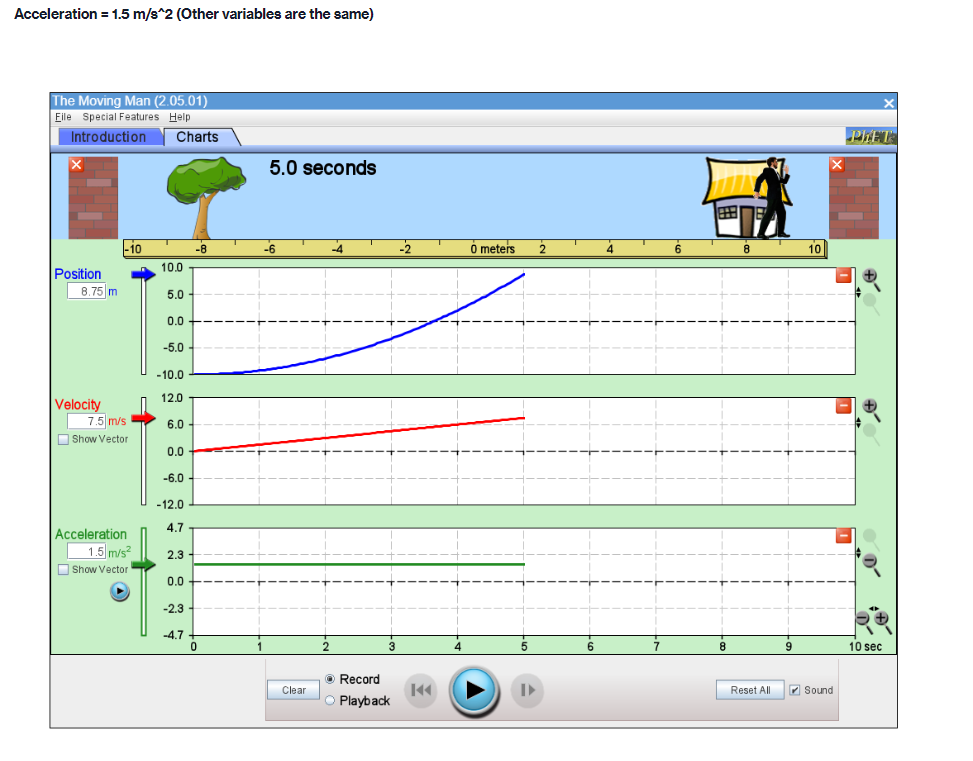
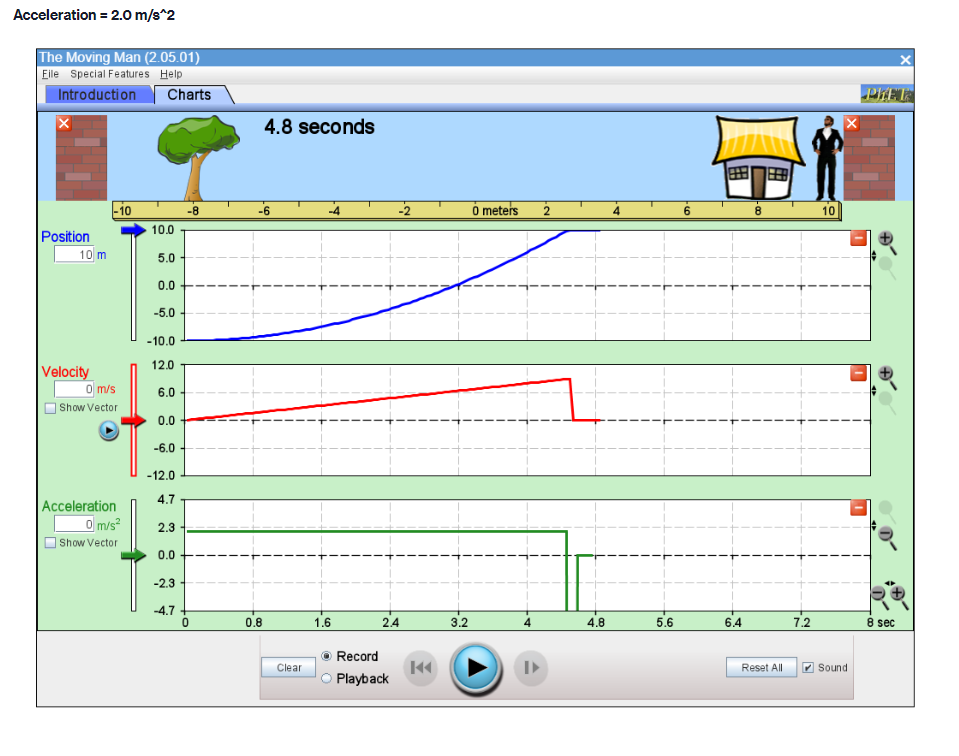
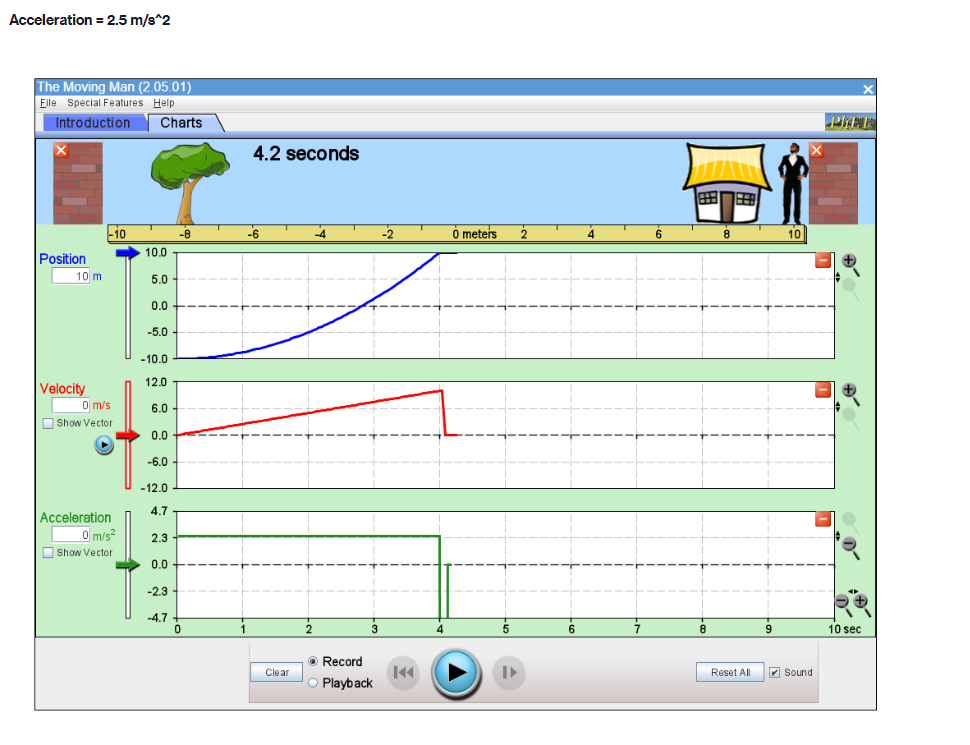
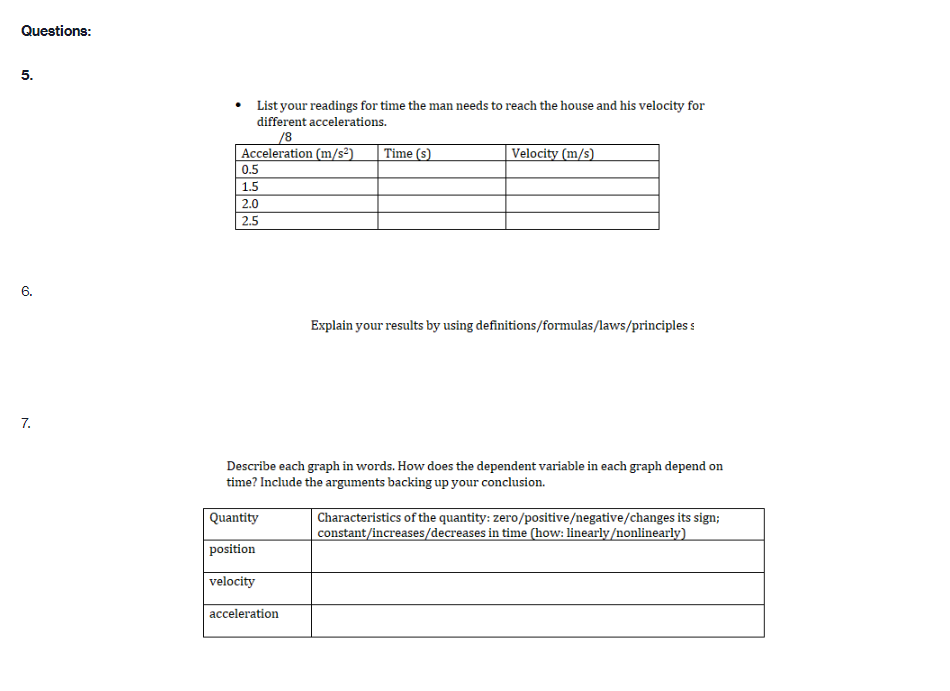
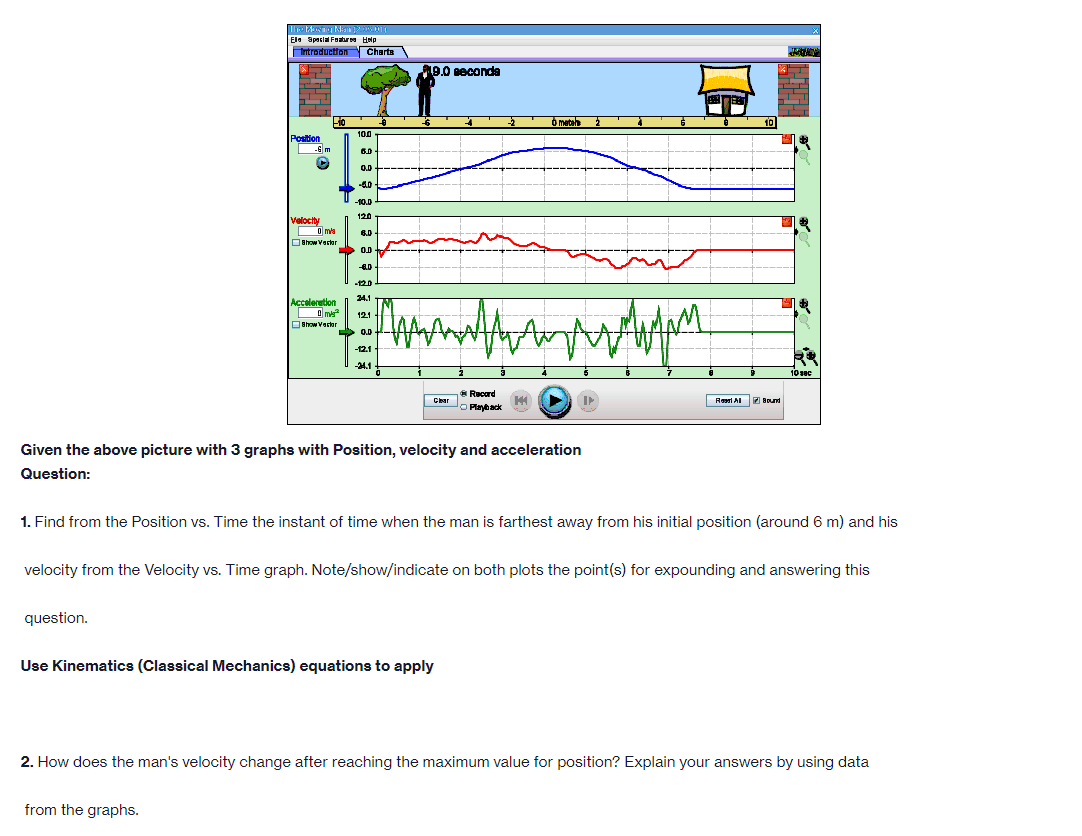
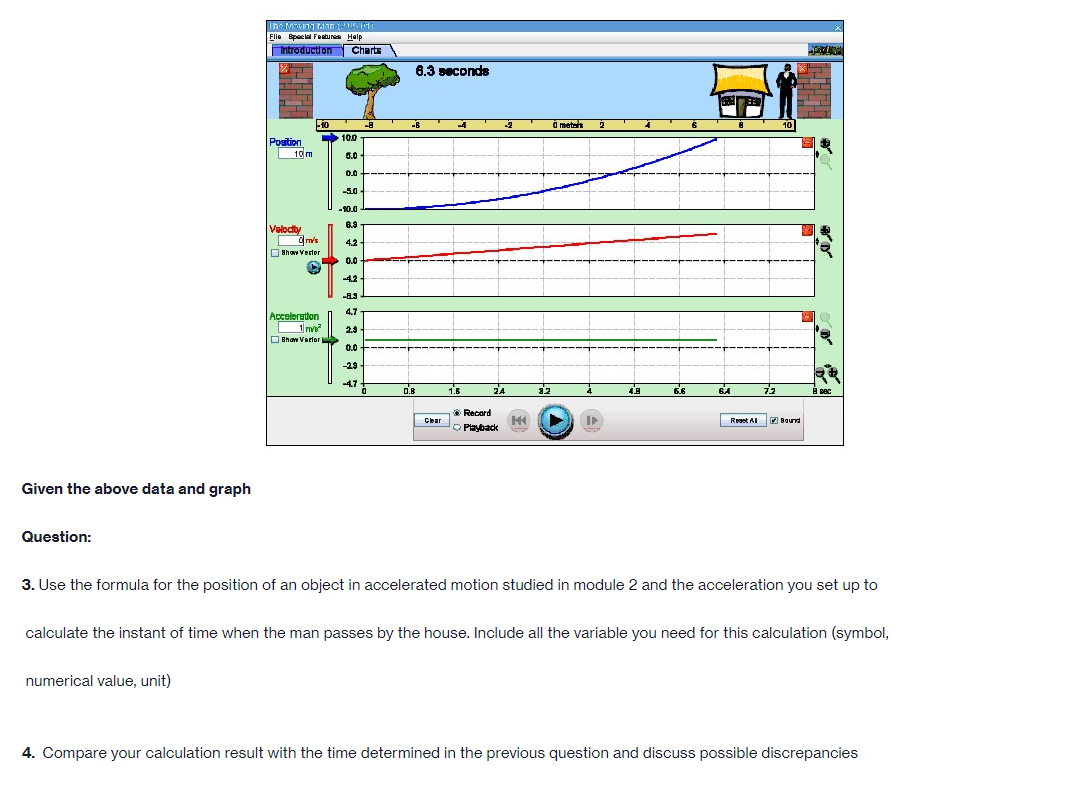
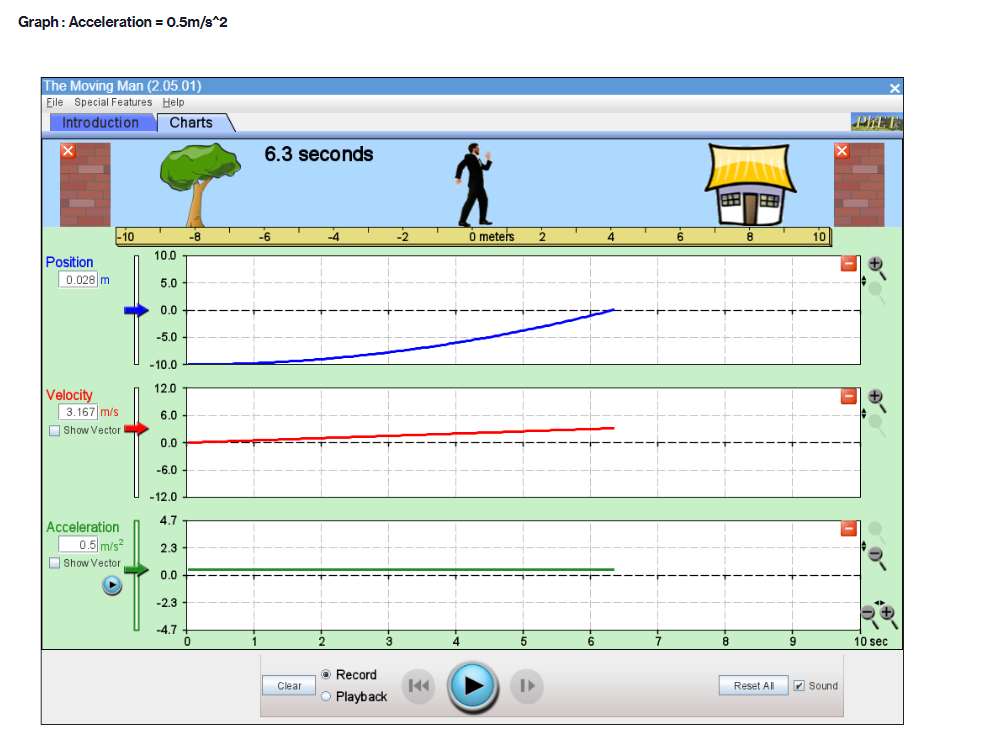
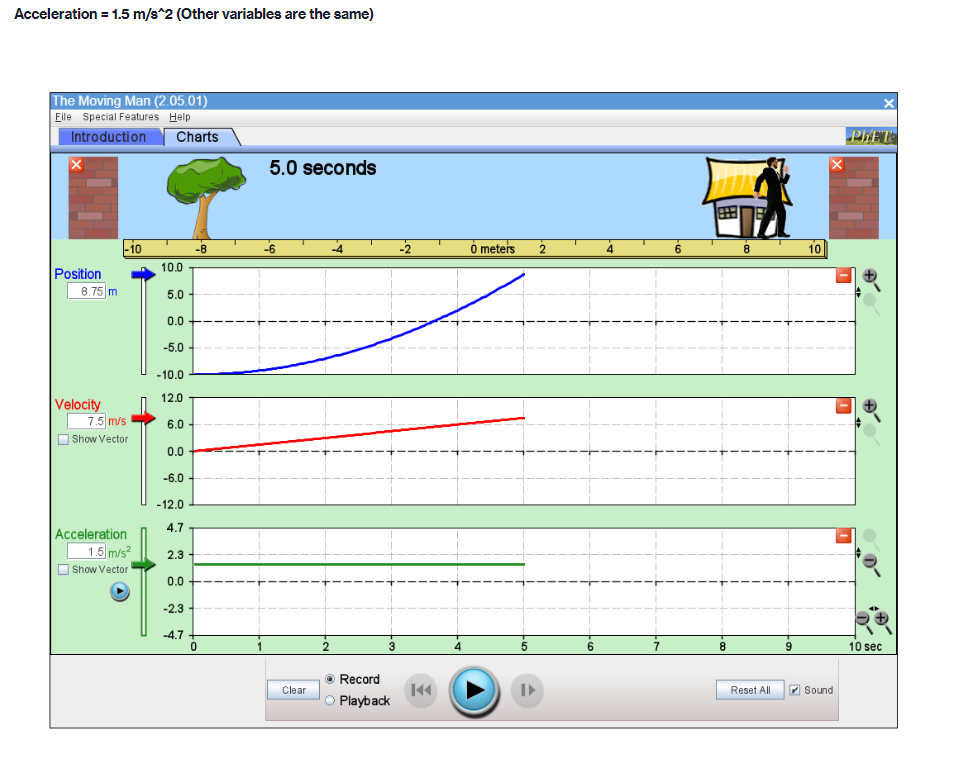
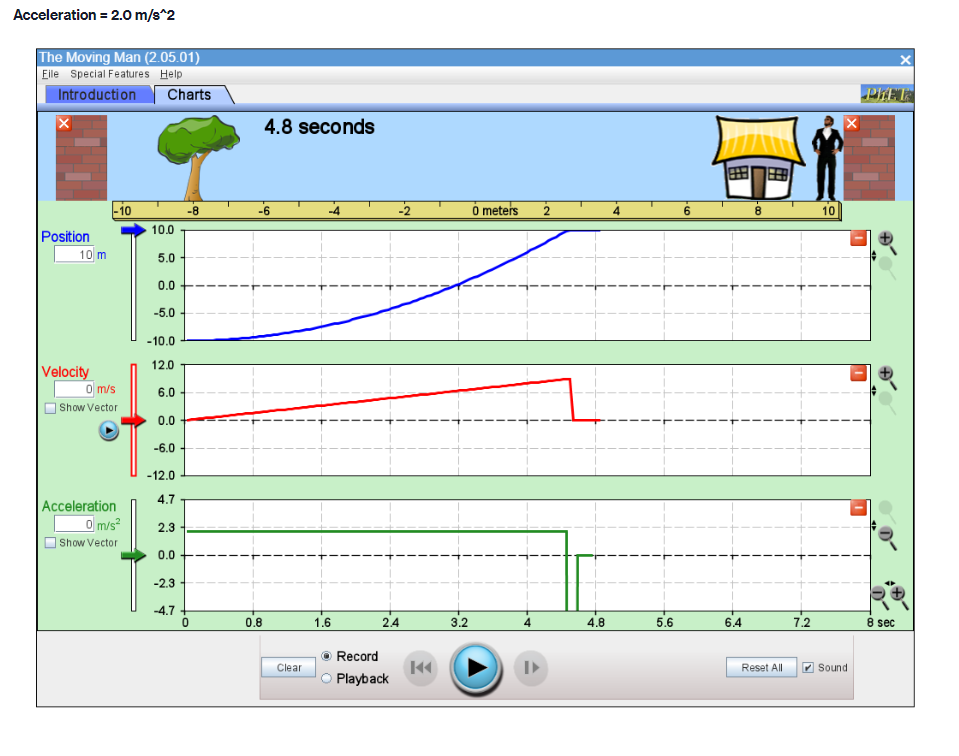
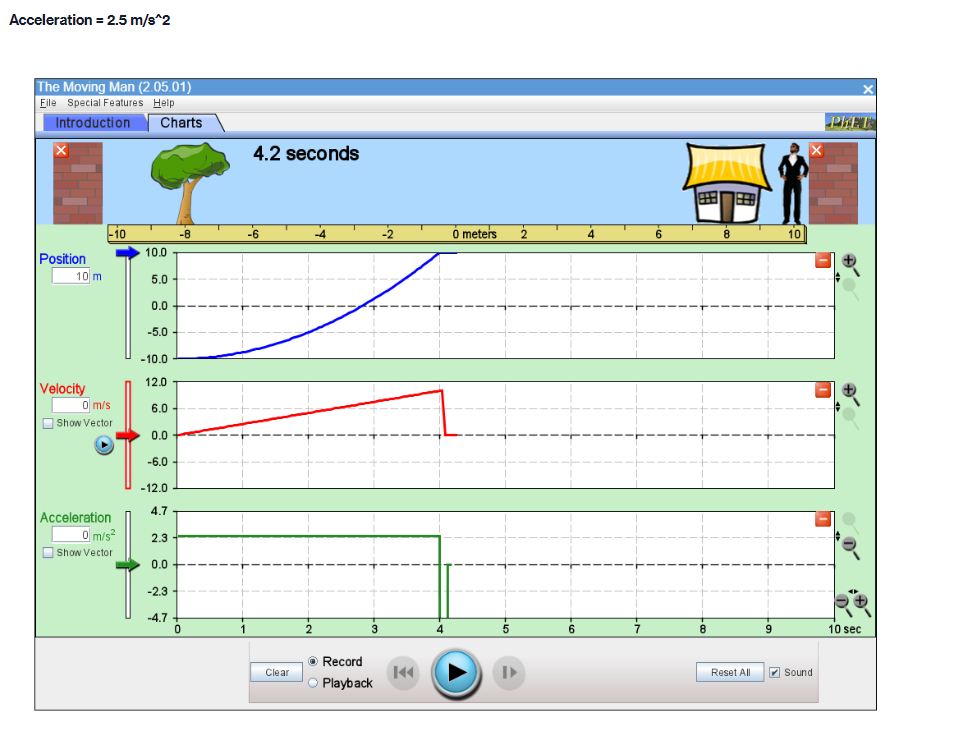
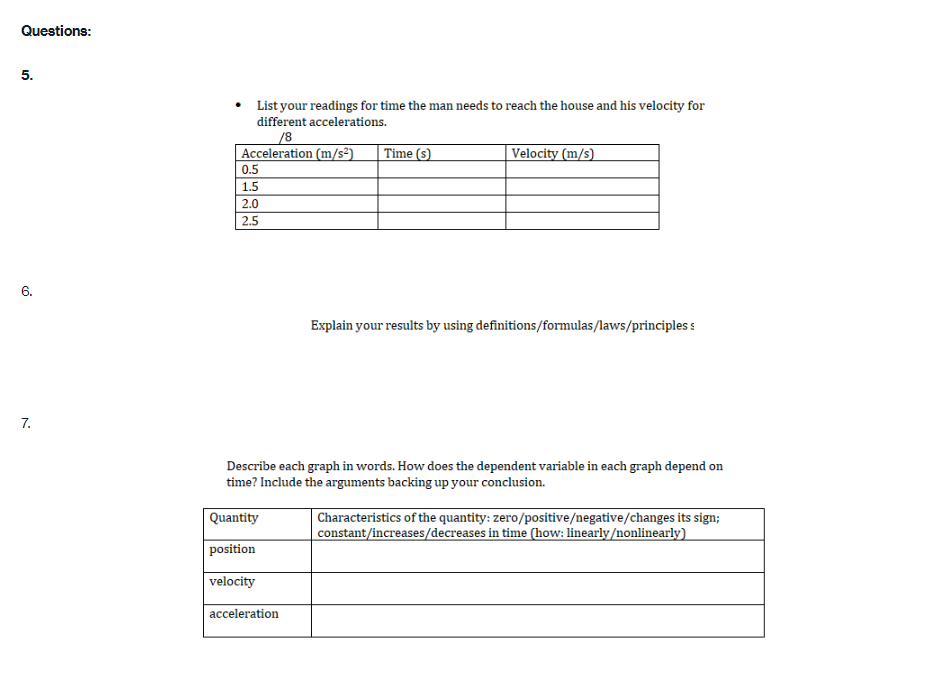
Part A PROCEDURE Go to blips:.-".-"_nhet.coloradoxdufe n.-"5in1Lilutions-"mov'ingmun then click on the arrow to open the Web-compatible simulation The Moving Man. This simulation allows you to drag a person badt and forth and look at the resulting position, velocity, and acceleration. You can also enter initial values for position. velocity and acceleration. F- First, focus on the relationship between velocity and position. Recall that velocity is the rate of change of position so the velocity is equal to the slope of the Position vs. Time graph. Vi NE-\" "f "i run at if ii . Move the person to the position x =6.0 m or enter 6.0 in the position box. If you dragged the person to position, click the Pause button and then the Clear button. Next, drag the person to the right to roughly x =6.0 m and reverse his direction, returning him to the original position, at x =6.0 m. . Move the person relatively quickly. about a few seconds for the round trip Your plots should look something like those shown below. Take a screenshot of your graphs and copy it in your report. Determine from the Position vs. Time graph the instant of time when the man is farthest away from his initial position (around 6 m). Determine from the Velocity vs. Time plot the velocity the man has when he reached the maximum distance from his initial position. Analyze how his velocity changes afterwards. Explain your answers by using denitions {formulas awslprinciples studied in module 2. Click Reset Ail. The Moving Man Is Spacial Futurea Help Introduction Charts 19.0 seconda 6 metsh 2 10 Qubon 0.D -10.0 Velocity 120 Show Yarlar -120 Acceleration 24.1 121 Show Yarkar -12.1 -24.1 10 38C Record Clear Playback IF Given the above picture with 3 graphs with Position, velocity and acceleration Question: 1. Find from the Position vs. Time the instant of time when the man is farthest away from his initial position (around 6 m) and his velocity from the Velocity vs. Time graph. Note/show/indicate on both plots the point(s) for expounding and answering this question. Use Kinematics (Classical Mechanics) equations to apply 2. How does the man's velocity change after reaching the maximum value for position? Explain your answers by using data from the graphs.Part B Instructions: Acceleration is the rate of change of the velocity, so it is the slope of the Velocity vs. Time graph. V 1 - Vi ax = ti - to 9. Because it is difficult to drag the person in a consistent and reproducible way, set up the initial values for position, velocity and acceleration as follows: x =-10.0 m. v = 0.0 m/s a = 1.0 m/s2 10. Click the Play button and let the simulation run roughly 6.3 simulation seconds before pressing the Pause button. Use the zoom buttons to adjust the graphs so they fit in the screen. 11. Use the Playback and Slow buttons to find from the Position vs. Time graph the instant of time when the man is passing by the house (approximately 8 m to the right of the origin). 12. Find from the Velocity vs. Time graph the velocity and acceleration when the man is passing by the house. 13. Click Reset All.Elle Special Factureon Halp Introduction | Charts 6.3 seconds --T -10 10 Poation 100 10 m 5.0 0.0 -50 -10.0 Velocity 8.9 Show Verior 0.0 42 Acceleration 4.7 2.9 Bhow Vacior 0.0 47- O.B 1 .6 24 2.2 6.6 6.A 72 Record char playback Given the above data and graph Question: 3. Use the formula for the position of an object in accelerated motion studied in module 2 and the acceleration you set up to calculate the instant of time when the man passes by the house. Include all the variable you need for this calculation (symbol, numerical value, unit) 4. Compare your calculation result with the time determined in the previous question and discuss possible discrepanciesPart C Data: Investigate how the time the man needs to reach the house depends on his acceleration when he starts from rest. 14. Set up new initial values for position, velocity and acceleration as follows: x =-10.0 m. v = 0.0 m/s a = 0.5 m/s 15. Click the Play button and let the simulation run until the man passes by the house, then press the Pause button. 16. Use the Playback and Slow buttons to find from the graphs the instant of time when the man is passing by the house (approximate 8 m to the right of the origin) and his velocity. 17. Repeat points 14, 15 and 16 for the same initial position and velocity but with three different accelerations: 1.5 m/s', 2.0 m/s' and 2.5 m/s?. Summarize your data in Table 1. 18. Explain your results by using definitions/formulas/laws/principles studied in module 2. Graph : Acceleration = 0.5m/s^2Graph : Acceleration = 0.5m/s*2 The Moving Man (2.05.01) File Special Features Help Introduction Charts X 6.3 seconds X -10 -8 - 6 -4 -2 0 meters 2 T 4 6 8 10 Position 10.0 0.028 m 5.0 0.0 - -5.0 -10.0 Velocity 12.0 3.167 m/s 6.0 Show Vector 0.0 -6.0 -12.0 Acceleration 4.7 - 0.5 m/s2 2.3 Show Vector 0.0 .2.3 47 7 10 sec Record Clear Reset All Sound O PlaybackAcceleration = 1.5 m/s*2 (Other variables are the same) The Moving Man (2.05.01) File Special Features Help Introduction Charts PHET X 5.0 seconds X - 10 -8 -6 -4 -2 0 meters 2 4 6 8 10 Position 10.0 8.75 m 5.0 0.0 -5.0 -10.0 Velocity 12.0 7.5 m/'s 6.0 Show Vector 0.0 6.0 -12.0 Acceleration 4.7 - 1.5 m/s 2.3 Show Vector 0.0 -2.3 -4.7 N- 4 on - 6 7 8 9 10 sec Record Clear 141 O Playback Reset All SoundAcceleration = 2.0 m/s*2 The Moving Man (2.05.01) X File Special Features Help Introduction Charts PIET X 4.8 seconds X 1-10 -6 -4 -2 0 meters 2 4 6 10 Position 10.0 10 m 5.0 - 0.0- -5.0 -10.0 Velocity 12.0 0 m/s 6.0 Show Vector 0.0 -6.0 -12.0 4.7 Acceleration - 0 m/s? 2.3 Show Vector 0.0 -2.3 -4.7 0 0.8 1.6 2.4 3.2 4 4.8 5.6 6.4 7.2 8 sec Record Clear Reset All Sound O PlaybackAcceleration = 2.5 m/s*2 The Moving Man (2.05.01) File Special Features Help Introduction Charts PLET X 4.2 seconds X -10 -8 -6 -4 -2 0 meters 2 4 6 8 10 Position 10.0 10 m 5.0 0.0 -5.0 -10.0 Velocity 12.0 + 0 m/s 6.0 Show Vector 0.0 -6.0 -12.0 Acceleration 4.7 0 m/s2 2.3 Show Vector 0.0 - 2.3 -4.7 3 5 B 10 sec Record Clear Reset All Sound O PlaybackQuestions: 5. List your readings for time the man needs to reach the house and his velocity for different accelerations. /8 Acceleration (m/s?) Time (S) Velocity (m/s) 0.5 1.5 2.0 2.5 6. Explain your results by using definitions/formulas/laws/principles s 7. Describe each graph in words. How does the dependent variable in each graph depend on time? Include the arguments backing up your conclusion. Quantity Characteristics of the quantity: zero/positiveegative/changes its sign; constant/increases/decreases in time (how: linearly onlinearly) position velocity acceleration
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


