Question: please answer all parts from a to h accurately and clearly. Your efforts will be highly appreciated. Thank you A Telescope is an optical instrument
 please answer all parts from a to h accurately and clearly. Your efforts will be highly appreciated. Thank you
please answer all parts from a to h accurately and clearly. Your efforts will be highly appreciated. Thank you
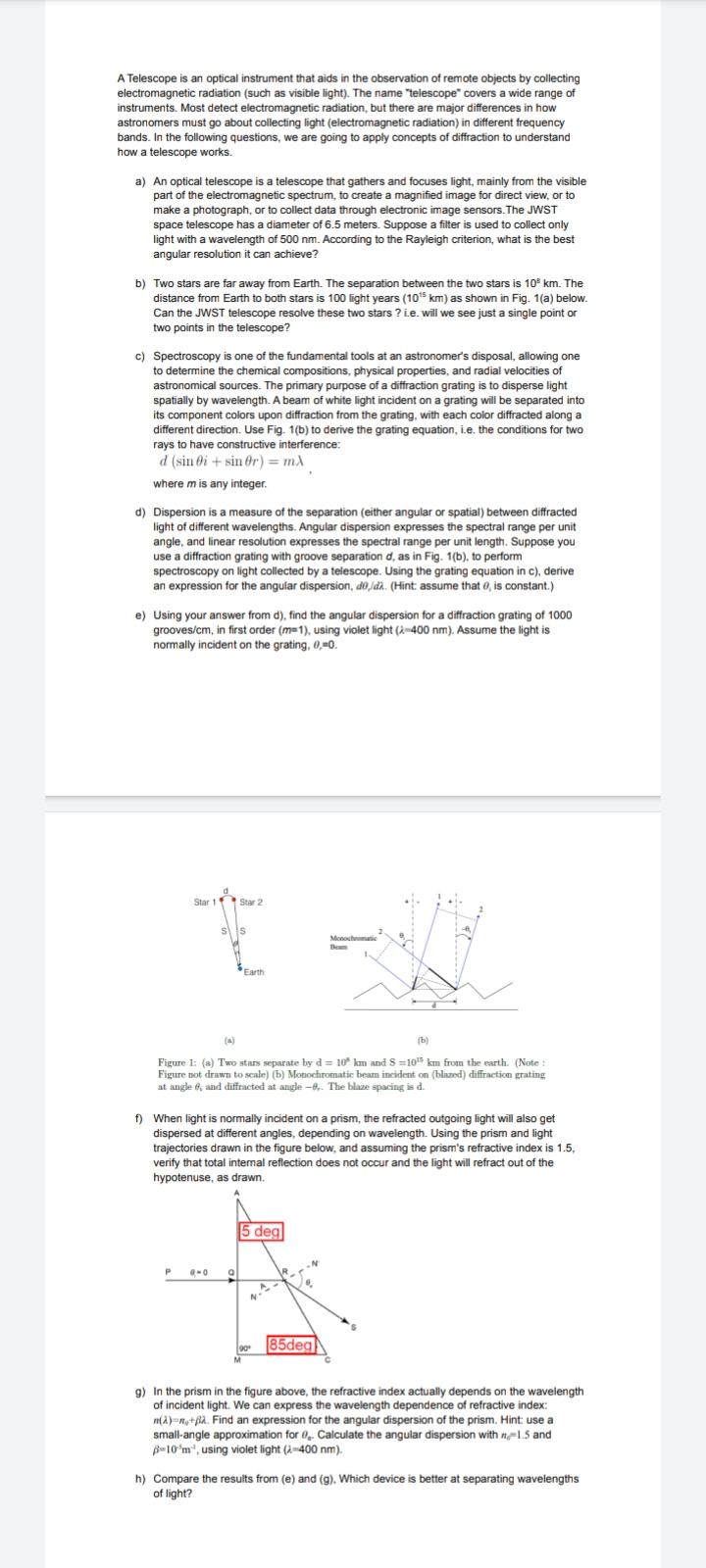
A Telescope is an optical instrument that aids in the observation of remote objects by collecting electromagnetic radiation (such as visible light). The name "telescope" covers a wide range of instruments. Most detect electromagnetic radiation, but there are major differences in how astronomers must go about collecting light (electromagnetic radiation) in different frequency bands. In the following questions, we are going to apply concepts of diffraction to understand how a telescope works. a) An optical telescope is a telescope that gathers and focuses light, mainly from the visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum, to create a magnified image for direct view, or to make a photograph, or to collect data through electronic image sensors. The JWST space telescope has a diameter of 6.5 meters. Suppose a filter is used to collect only light with a wavelength of 500nm. A. b) Two stars are far away from Earth. The separation between the two stars is 103km. The distance from Earth to both stars is 100 light years (1015km) as shown in Fig. 1( a ) below. two points in the telescope? c) Spectroscopy is one of the fundamental tools at an astronomer's disposal, allowing one to determine the chemical compositions, physical properties, and radial velocities of astronomical sources. The primary purpose of a diffraction grating is to disperse light spatially by wavelength. A beam of white light incident on a grating will be separated into its component colors upon diffraction from the grating, with each color diffracted along a different direction. Use Fig. 1(b) to derive the grating equation, i.e. the conditions for two rays to have constructive interference: d(sini+sinr)=m where m is any integer. d) Dispersion is a measure of the separation (either angular or spatial) between diffracted light of different wavelengths. Angular dispersion expresses the spectral range per unit angle, and linear resolution expresses the spectral range per unit length. Suppose you use a diffraction grating with groove separation d, as in Fig. 1(b), to perform spectroscopy on light collected by a telescope. Using the grating equation in c), derive an expression for the angular dispersion, d,/d. (Hint: assume that , is constant.) e) Using your answer from d), find the angular dispersion for a diffraction grating of 1000 grooves/cm, in first order (m=1), using violet light (=400nm). Assume the light is normally incident on the grating, ,=0. at angle t and diffracted at angle 1. The blaze spacing is d. f) When light is normally incident on a prism, the refracted outgoing light will also get trajectories drawn in the figure below, and assuming the prism's refractive index is 1.5, verify that total intemal reflection does not occur and the light will refract out of the hypotenuse, as drawn. g) In the prism in the figure above, the refractive index actually depends on the wavelength of incident light. We can express the wavelength dependence of refractive index: n()=n0+. Find an expression for the angular dispersion of the prism. Hint: use a small-angle approximation for e. Calculate the angular dispersion with n=1.5 and =105m4, using violet light (=400nm). h) Compare the results from (e) and (g). Which device is better at separating wavelengths of light? A Telescope is an optical instrument that aids in the observation of remote objects by collecting electromagnetic radiation (such as visible light). The name "telescope" covers a wide range of instruments. Most detect electromagnetic radiation, but there are major differences in how astronomers must go about collecting light (electromagnetic radiation) in different frequency bands. In the following questions, we are going to apply concepts of diffraction to understand how a telescope works. a) An optical telescope is a telescope that gathers and focuses light, mainly from the visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum, to create a magnified image for direct view, or to make a photograph, or to collect data through electronic image sensors. The JWST space telescope has a diameter of 6.5 meters. Suppose a filter is used to collect only light with a wavelength of 500nm. A. b) Two stars are far away from Earth. The separation between the two stars is 103km. The distance from Earth to both stars is 100 light years (1015km) as shown in Fig. 1( a ) below. two points in the telescope? c) Spectroscopy is one of the fundamental tools at an astronomer's disposal, allowing one to determine the chemical compositions, physical properties, and radial velocities of astronomical sources. The primary purpose of a diffraction grating is to disperse light spatially by wavelength. A beam of white light incident on a grating will be separated into its component colors upon diffraction from the grating, with each color diffracted along a different direction. Use Fig. 1(b) to derive the grating equation, i.e. the conditions for two rays to have constructive interference: d(sini+sinr)=m where m is any integer. d) Dispersion is a measure of the separation (either angular or spatial) between diffracted light of different wavelengths. Angular dispersion expresses the spectral range per unit angle, and linear resolution expresses the spectral range per unit length. Suppose you use a diffraction grating with groove separation d, as in Fig. 1(b), to perform spectroscopy on light collected by a telescope. Using the grating equation in c), derive an expression for the angular dispersion, d,/d. (Hint: assume that , is constant.) e) Using your answer from d), find the angular dispersion for a diffraction grating of 1000 grooves/cm, in first order (m=1), using violet light (=400nm). Assume the light is normally incident on the grating, ,=0. at angle t and diffracted at angle 1. The blaze spacing is d. f) When light is normally incident on a prism, the refracted outgoing light will also get trajectories drawn in the figure below, and assuming the prism's refractive index is 1.5, verify that total intemal reflection does not occur and the light will refract out of the hypotenuse, as drawn. g) In the prism in the figure above, the refractive index actually depends on the wavelength of incident light. We can express the wavelength dependence of refractive index: n()=n0+. Find an expression for the angular dispersion of the prism. Hint: use a small-angle approximation for e. Calculate the angular dispersion with n=1.5 and =105m4, using violet light (=400nm). h) Compare the results from (e) and (g). Which device is better at separating wavelengths of light
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


