Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
please answer all questions & explain were need be, carefully. a) Some application areas of AI among many others are: (i) Virtual Assistant or Chatbots



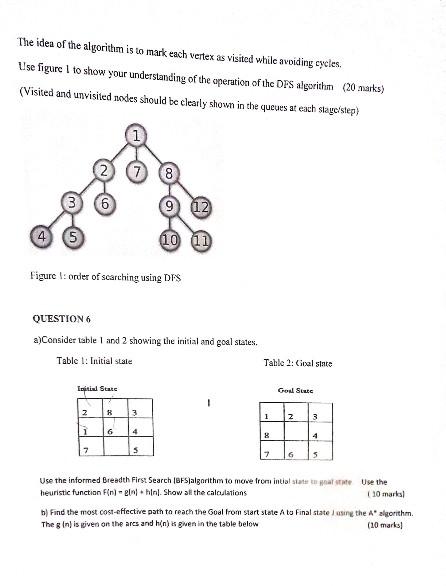
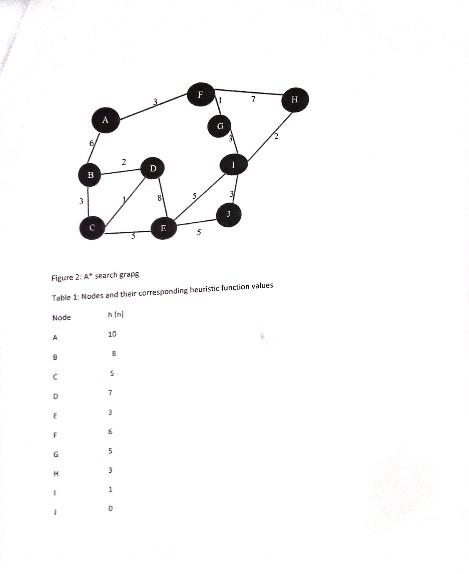

please answer all questions & explain were need be, carefully.
a) Some application areas of AI among many others are: (i) Virtual Assistant or Chatbots (ii) Autonomous Flying (iii)Security and Surveillance (iv) Autonomous cars Explain using real examples how AI is used in the above examples (8 marks) b) Early research in AI was done in game playing such as chess, checkers, draft, 8 and 15 square puzzles. Give and explain reasons for the choice of games? (Any 5 reasons) (5 marks) c) What is involved in intelligence? (Any 3) (3 marks) d) Name and explain any two types of knowledge (4 marks) QUESTION 2 a) What are the differences between a database and knowledge base in terms of? (i) What is stored (2 marks) (ii) Decision making (2 marks) b) What is the difference between Propositional calculus and Predicate calculus? ( 3 marks) c) Consider the Universal Quantifier (W) and the statements below: All people do not like paying pay as you earn (PAYE) tax. Assume you are to evaluate this statement, when will it be wrong and when will it be correct? VXD,P(X) (3 marks) d) Consider the following statements: "All human beings are mortal" "Samara is a human being" Does it follow that Samars is mortal? Show how you will prove that Samara is mortal using predicate logic ( 5 marks) e) What is the difference between propositional and predicate logic? Give examples ( 5 marks) a) Represent the English statements below into predicate calculus: (i)If wishes were horses beggars would ride (ii) Nobody likes taxes 1(f) lime (fx)xs) \{iiillf it doesn't rain on Monday. Tom will go to the mountains (iv) All basketball players are tall (v) Everybody loves him/her self b) Consider the statements: If it is raining. (P) I will need an Umbrella (C) It is raining (P) I will need an umbrella (Q) Represent the above statements in logic as inference rules b) If it is raining (P) I will need an Umbrella (Q) It is not raining. (P) 1 will not need an umbrella {Q} Represent the above statements in logic as inference rules (3 marks) c) Consider the statement below: Peter is an engineer by profession, and his age is 25 and is single, he lives in city London, and the country is England. He weighs 75kg.Produce an entity frame for Peter (5 marks) d) The A* algorithm is an improved Breadth First Search and is said to be complete and optimal, Explain what is: (i) Complete about it (2) marks) (ii) Optimal about it pobnombea+b a) Consider the 8 puzzle below: (i) Calculate the number of steps needed to move from the initial state to goul state (6 marks) (ii) What rules will you use to move from initial state to goal state (4 marks) (iii)Use the rules in (ii) to move to goal state. All the steps should be shown ( 6 marks) (iv)Is this search from initial state to goal state informed or uninformed explain your answcrs in each case. (4 marks) QUESTION 5 A standard DFS implementation puts each vertex of the graph into one of two categoriesiqueues: - Visited - Not Visited Visited Stack The idea of the algoritkm is to mark each vertex as visited while avoiding cycles. Use figure 1 to show your understanding of the operation of the DFS algorithin (20 asarks) (Visited and unvisited nodes should be clearly shown in the quewes at each stageistep) Figure I: order of searching using DFS QUESTION 6 a)Consider table 1 and 2 showing the initial and goal states. Table I: Initial stsie Table 1: Cival stare Gon State Use the informed Breadth Firs: Search Ibrs]algarithm to move from intial simut un nat unne Use the heuristic functian F(n)=gn+hn. Show sil the calautations ( 10 maria) b) Find the most cost-effective path ta reach the Goal lrom saart state A ta Final state l asine the A* algorithen. The g(n) is given on the ares and hin) is ghen in the table below (10 mark) Figure 2: A search graps Table 1: Nodes and the ir correspanding heuristic lunction values a) Consider the instance of the travelling salesman's problem figure 3 . Figure 3: The travelling salesman's problem A,B,C,D,E are towns. The travelling salesman's home town is A,BC=50 (i) Use the nearest neighbor heuristic to find the shortest distance from home town A and back visiting each town once (5 marks) (ii) Use thick directed lines to show the path followed by the travelling salesman (2 marks) (iii) Show that this is not really the shortest path (5 marks) (iv) What defeats the nearest neighbor heuristic in this case? (2) marks) b) A number of factors can complicate the process of knowledge acquisition from human experts Name and explain problems associated with acquiring from experts (6 marks)Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


