 please answer fully
please answer fully
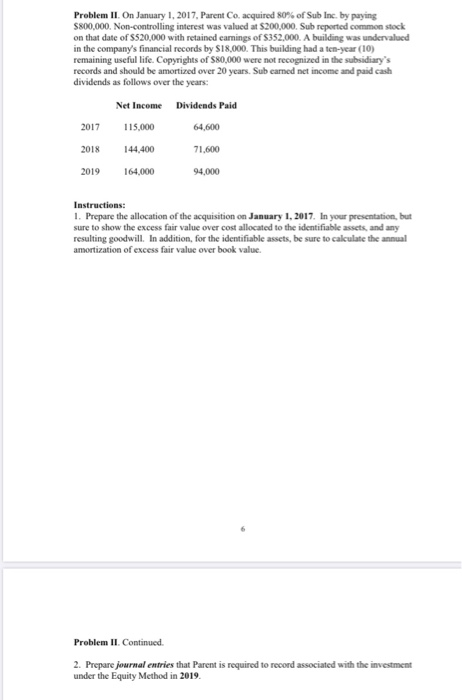
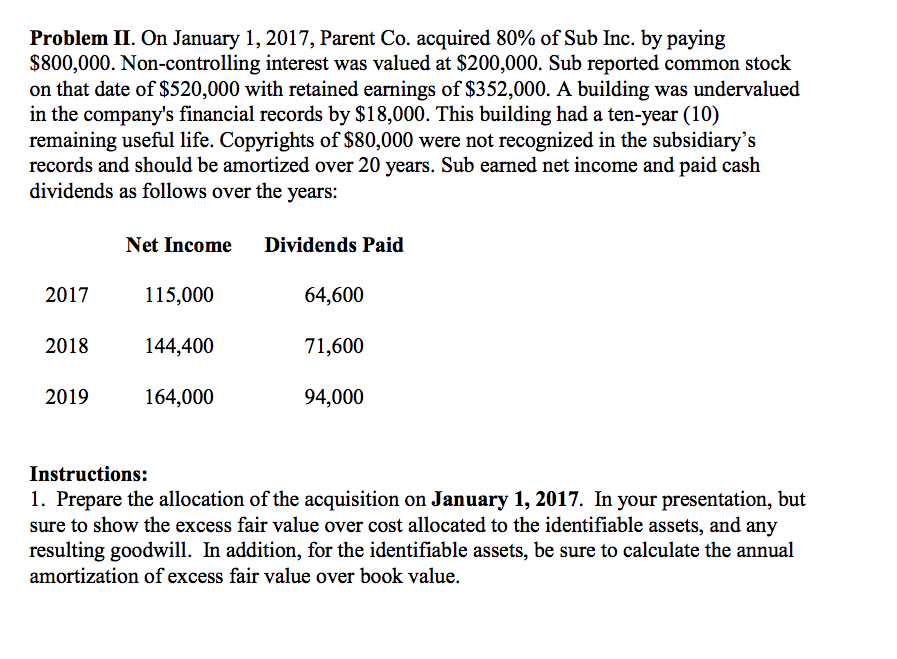
Problem I. (60 points). Paramount Corporation owns 100 percent of Sacker Company. Paramount acquired Sacker on January 1, 2016, where the fair value of the net assets and book value were the same. The resulting excess fair value was allocated to a trademark for $110,000 indefinite life), with the remainder allocated to a client list for $400,000 (20-year remaining life at acquisition date). No goodwill resulted from this acquisition. The following intra-entity transactions occurred in 2019: Paramount had sold inventory to Sacker in 2018 for $40,000. The inventory cost Paramount $30,000. At December 31, 2018, Sacker had sold approximately sixty (60) percent of the goods. The remaining inventory was sold to outside customers in 2019. Paramount sold inventory to Sacker in 2019 for $50,000. The inventory cost Paramount $40,000. At December 31, 2019, Sacker had sold approximately eighty (80) percent of the goods. The remaining inventory was sold to outside customers in 2020. On March 1, 2018, Paramount transferred Land to Sacker for $280,000; Paramount acquired the land in 2002 for $200,000. Sacker borrowed $280,000 from Paramount as a result of the transfer. On January 1, 2018, Paramount transferred equipment with a book value of $80,000 to Sacker for $120,000; the equipment has a remaining useful life of ten (10) years. Paramount acquired the equipment at $140,000. In addition to the intra-entity transactions above, during 2019, Sacker declared and paid a $12,000 dividend; the subsidiary also had net income of $130,000. At January 1, 2019, Sacker's equity consisted of common stock $180,000, additional paid-in capital, $20,000, and retained earnings, $140,000. Problem II. On January 1, 2017, Parent Co. acquired 80% of Sub Inc. by paying $800,000. Non-controlling interest was valued at $200,000. Sub reported common stock on that date of $520,000 with retained earnings of $352,000. A building was undervalued in the company's financial records by $18,000. This building had a ten-year (10) remaining useful life. Copyrights of $80,000 were not recognized in the subsidiary's records and should be amortized over 20 years. Sub earned net income and paid cash dividends as follows over the years: Net Income Dividends Paid 2017 115,000 64,600 2018 144,400 71,600 2019 164,000 94,000 Instructions: 1. Prepare the allocation of the acquisition on January 1, 2017. In your presentation, but sure to show the excess fair value over cost allocated to the identifiable assets, and any resulting goodwill. In addition, for the identifiable assets, be sure to calculate the annual amortization of excess fair value over book value. Problem I (60 points). Paramount Corporation owns 100 percent of Sacker Company. Paramount acquired Sacker on January 1, 2016, where the fair value of the net assets and book value were the same. The resulting excess fair value was allocated to a trademark for $110,000 (indefinite life), with the remainder allocated to a client list for $400,000 (20-year remaining life at acquisition date). No goodwill resulted from this acquisition. The following intra-entity transactions occurred in 2019: Paramount had sold inventory to Sacker in 2018 for $40,000. The inventory cost Paramount $30,000. At December 31, 2018, Sacker had sold approximately sixty (60) percent of the goods. The remaining inventory was sold to outside customers in 2019. Paramount sold inventory to Sacker in 2019 for $50,000. The inventory cost Paramount $40,000. At December 31, 2019, Sacker had sold approximately eighty (80) percent of the goods. The remaining inventory was sold to outside customers in 2020. On March 1, 2018, Paramount transferred Land to Sacker for $280,000; Paramount acquired the land in 2002 for $200,000. Sacker borrowed $280,000 from Paramount as a result of the transfer. On January 1, 2018, Paramount transferred equipment with a book value of 80,000 to Sacker for $120,000; the equipment has a remaining useful life of ten (10) years. Paramount acquired the equipment at $140,000. In addition to the intra-entity transactions above, during 2019, Sacker declared and paid a $12,000 dividend; the subsidiary also had net income of $130,000. At January 1, 2019, Sacker's equity consisted of common stock $180,000, additional paid-in capital, $20,000, and retained earnings, $140,000. Problem II. On January 1, 2017, Parent Co. acquired 80% of Sub Inc. by paying $800,000. Non-controlling interest was valued at $200,000. Sub reported common stock on that date of $520,000 with retained earnings of S352.000. A building was undervalued in the company's financial records by S18,000. This building had a ten-year (10) remaining useful life. Copyrights of $80,000 were not recognized in the subsidiary's records and should be amortized over 20 years. Sub earned net income and paid cash dividends as follows over the years: Net Income Dividends Paid 2017 115,000 64,600 2018 144,400 71,600 2019 164,000 94,000 Instructions: 1. Prepare the allocation of the acquisition on January 1, 2017. In your presentation, but sure to show the excess fair value over cost allocated to the identifiable assets, and any resulting goodwill. In addition, for the identifiable assets, be sure to calculate the annual amortization of excess fair value over book value. Problem II. Continued. 2. Prepare journal entries that Parent is required to record associated with the investment under the Equity Method in 2019. Problem I. (60 points). Paramount Corporation owns 100 percent of Sacker Company. Paramount acquired Sacker on January 1, 2016, where the fair value of the net assets and book value were the same. The resulting excess fair value was allocated to a trademark for $110,000 indefinite life), with the remainder allocated to a client list for $400,000 (20-year remaining life at acquisition date). No goodwill resulted from this acquisition. The following intra-entity transactions occurred in 2019: Paramount had sold inventory to Sacker in 2018 for $40,000. The inventory cost Paramount $30,000. At December 31, 2018, Sacker had sold approximately sixty (60) percent of the goods. The remaining inventory was sold to outside customers in 2019. Paramount sold inventory to Sacker in 2019 for $50,000. The inventory cost Paramount $40,000. At December 31, 2019, Sacker had sold approximately eighty (80) percent of the goods. The remaining inventory was sold to outside customers in 2020. On March 1, 2018, Paramount transferred Land to Sacker for $280,000; Paramount acquired the land in 2002 for $200,000. Sacker borrowed $280,000 from Paramount as a result of the transfer. On January 1, 2018, Paramount transferred equipment with a book value of $80,000 to Sacker for $120,000; the equipment has a remaining useful life of ten (10) years. Paramount acquired the equipment at $140,000. In addition to the intra-entity transactions above, during 2019, Sacker declared and paid a $12,000 dividend; the subsidiary also had net income of $130,000. At January 1, 2019, Sacker's equity consisted of common stock $180,000, additional paid-in capital, $20,000, and retained earnings, $140,000. Problem II. On January 1, 2017, Parent Co. acquired 80% of Sub Inc. by paying $800,000. Non-controlling interest was valued at $200,000. Sub reported common stock on that date of $520,000 with retained earnings of $352,000. A building was undervalued in the company's financial records by $18,000. This building had a ten-year (10) remaining useful life. Copyrights of $80,000 were not recognized in the subsidiary's records and should be amortized over 20 years. Sub earned net income and paid cash dividends as follows over the years: Net Income Dividends Paid 2017 115,000 64,600 2018 144,400 71,600 2019 164,000 94,000 Instructions: 1. Prepare the allocation of the acquisition on January 1, 2017. In your presentation, but sure to show the excess fair value over cost allocated to the identifiable assets, and any resulting goodwill. In addition, for the identifiable assets, be sure to calculate the annual amortization of excess fair value over book value. Problem I (60 points). Paramount Corporation owns 100 percent of Sacker Company. Paramount acquired Sacker on January 1, 2016, where the fair value of the net assets and book value were the same. The resulting excess fair value was allocated to a trademark for $110,000 (indefinite life), with the remainder allocated to a client list for $400,000 (20-year remaining life at acquisition date). No goodwill resulted from this acquisition. The following intra-entity transactions occurred in 2019: Paramount had sold inventory to Sacker in 2018 for $40,000. The inventory cost Paramount $30,000. At December 31, 2018, Sacker had sold approximately sixty (60) percent of the goods. The remaining inventory was sold to outside customers in 2019. Paramount sold inventory to Sacker in 2019 for $50,000. The inventory cost Paramount $40,000. At December 31, 2019, Sacker had sold approximately eighty (80) percent of the goods. The remaining inventory was sold to outside customers in 2020. On March 1, 2018, Paramount transferred Land to Sacker for $280,000; Paramount acquired the land in 2002 for $200,000. Sacker borrowed $280,000 from Paramount as a result of the transfer. On January 1, 2018, Paramount transferred equipment with a book value of 80,000 to Sacker for $120,000; the equipment has a remaining useful life of ten (10) years. Paramount acquired the equipment at $140,000. In addition to the intra-entity transactions above, during 2019, Sacker declared and paid a $12,000 dividend; the subsidiary also had net income of $130,000. At January 1, 2019, Sacker's equity consisted of common stock $180,000, additional paid-in capital, $20,000, and retained earnings, $140,000. Problem II. On January 1, 2017, Parent Co. acquired 80% of Sub Inc. by paying $800,000. Non-controlling interest was valued at $200,000. Sub reported common stock on that date of $520,000 with retained earnings of S352.000. A building was undervalued in the company's financial records by S18,000. This building had a ten-year (10) remaining useful life. Copyrights of $80,000 were not recognized in the subsidiary's records and should be amortized over 20 years. Sub earned net income and paid cash dividends as follows over the years: Net Income Dividends Paid 2017 115,000 64,600 2018 144,400 71,600 2019 164,000 94,000 Instructions: 1. Prepare the allocation of the acquisition on January 1, 2017. In your presentation, but sure to show the excess fair value over cost allocated to the identifiable assets, and any resulting goodwill. In addition, for the identifiable assets, be sure to calculate the annual amortization of excess fair value over book value. Problem II. Continued. 2. Prepare journal entries that Parent is required to record associated with the investment under the Equity Method in 2019

 please answer fully
please answer fully