Please fill in the table below with the information given
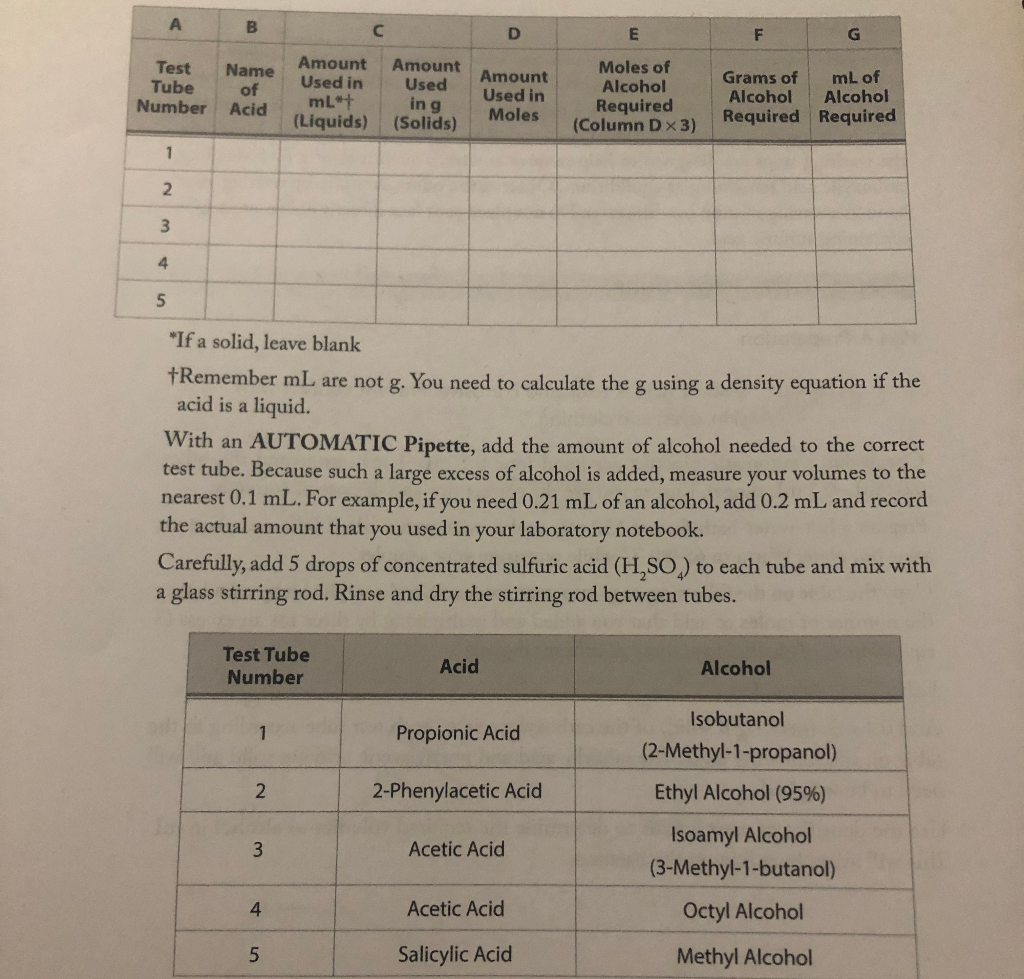


"If a solid, leave blank Remember mL are not g. You need to calculate the g using a density equation if the acid is a liquid. With an AUTOMATIC Pipette, add the amount of alcohol needed to the correct test tube. Because such a large excess of alcohol is added, measure your volumes to the nearest 0.1mL. For example, if you need 0.21mL of an alcohol, add 0.2mL and record the actual amount that you used in your laboratory notebook. Carefully, add 5 drops of concentrated sulfuric acid (H2SO4) to each tube and mix with a glass stirring rod. Rinse and dry the stirring rod between tubes. Check out 2 automatic pipettes per hood (one 0.1mL1mL range and the other 0.02mL0.2mL range). Ensure you use the correct tips and dispose of correctly. Prepare a hot-water bath from a 150mL beaker with water ( half full) and place on your hot plate. Warm to 6580C while preparing your samples. Copy the table on the following page into your notebook, and complete it by calculating the number of moles of acid that you added and multiplying by three for an excess ( 3 equivalents) of alcohol (use three significant digits). Label 5 test tubes, 15. Add 0.1mL (or 0.1g if solid) of the carboxylic acid to each test tube according to the table on the following page. The salicylic acid and phenylacetic acid are solid and will need to be weighed. Use the densities of your liquids to determine the required volumes of alcohol in mL. Add 2mL water and 1mLt-butyl methyl ether ( t-BME) to each test tube. Mix the solution by bubbling the air gently from a pipette placed in the solution. Continue mixing until all solids dissolve. Two layers should form; the top layer is an ether solution containing the ester. Using a clean pipette, remove the water layer (lower) and place in a small beaker for disposal. Add 1mL5% aqueous sodium bicarbonate dropwise using a Pasteur pipette. If foaming occurs, slow the addition process to a controllable rate. After addition of the base is complete, mix by gently bubbling air from a Pasteur pipette. Remove the lower aqueous layer and place in the beaker for disposal. Add a small spatula of drying agent (Na2SO4) to the remaining ester layer and allow the test tube to sit undisturbed for 5min. It is now safe to "smell" the odor of your esters by gently wafting the vapor toward your nose or by placing a few drops of the ether solution of the ester onto a watch glass and allow the ether to evaporate. Do not put your nose directly over the test tubes to smell









