Question: PLEASE HELP!!!!!!!! Lab Result 1: OH benzyl alcohol . In this experiment, the pH of benzyl alcohol is set to neutral, e.g., if a solution
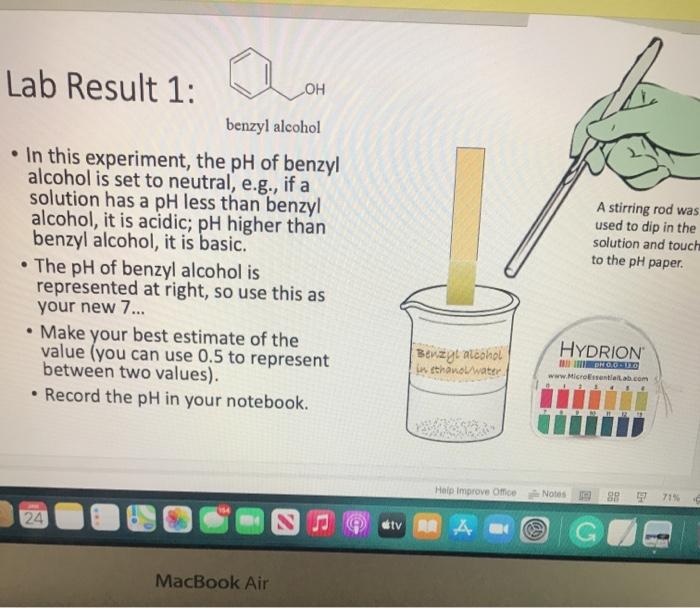
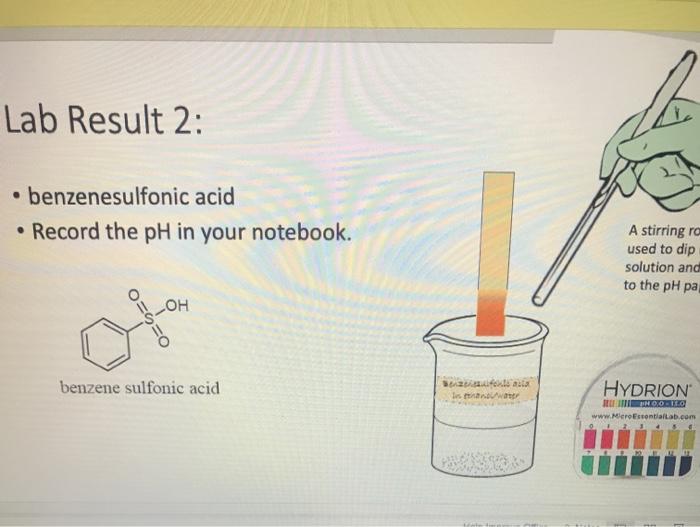
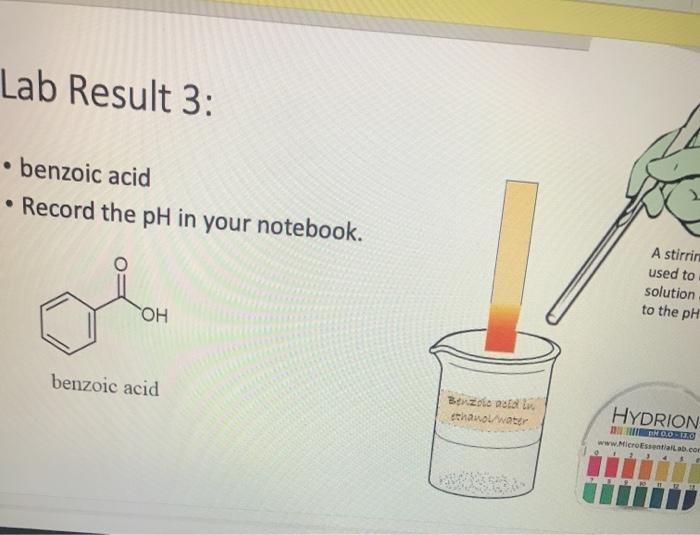













Lab Result 1: OH benzyl alcohol . In this experiment, the pH of benzyl alcohol is set to neutral, e.g., if a solution has a pH less than benzyl alcohol, it is acidic; pH higher than benzyl alcohol, it is basic. The pH of benzyl alcohol is represented at right, so use this as your new 7... Make your best estimate of the value (you can use 0.5 to represent between two values). Record the pH in your notebook A stirring rod was used to dip in the solution and touch to the pH paper HYDRION Benzyt nicohol i ethanol water PRODUTO www.Micronantailab.com Help Improve Oce Notes 8871% 24 dtv 4 09 MacBook Air Lab Result 2: benzenesulfonic acid Record the pH in your notebook. A stirring ra used to dip solution and to the pH pa LOH O==0 benzene sulfonic acid HYDRION TEHNOLOLO www.Mere Essentiallab.com Lab Result 3: . benzoic acid Record the pH in your notebook. . A stirrin used to solution to the pH benzoic acid Related thanol/water HYDRION BERODSKO www.Micro Essentiailab.com Lab Result 4: benzyl amine Record the pH in your notebook. A stirring rod was used to dip in the solution and touch to the pH paper NH2 benzyl amine HYDRION Helbimprovec N Lab Result 5: cresol Record the pH in your notebook. A stirrin used to solution to the pH HO cresol Crest the water HYDRION ORLD www.Microsentillah.com Lab Result 6: aniline Record the pH in your notebook. NH2 A stirring used to dig solution an to the pH pa aniline du thanol water HYDRION www.Microlab.com Lab Result 7: pyridine . Record the pH in your notebook. A stirring used to dig solution an to the pH pa Pyridine Paroista th HYDRION www.Microlab.com Lab Result 8: Picric acid Record the pH in your notebook. = A stirrir used to solution to the pH 0- HO P. that picric acid HYDRION www.Micro Errentarlab.com Writing the Equations Now that you have your data recorded, it is time to interpret it. . For this lab, we will determine structure based upon pH and represent it in an equation. . First, draw the structure of the molecule on the left-hand side. Note that benzene can be represented as a circle inside a hexagon as shown on the left; this represents the hybrid form of benzene since the double bonds alternate around the ring . Since we are studying acid-base reactions, show all H (potential acids) and lone pairs (potential bases). Show it in reaction with water or ethanol since both were in the mixture. 30-50 Predicting the Product Since we have the pH, we know one of the products of the reactio Hopefully, you found a pH ~2 for benzenesulfonic acid. This pH indicates that hydronium is present in solution. Draw hydronium on the right-hand side. :0-S=0 H Hoc 0 H H H H H Predicting the Product Now, we know how the compound reacted. If hydronium is produced, water must have obtained H* from the benzenesulfon acid. Therefore, we can draw the conjugate base of benzenesulfonic aci the other product. There are two possible H to remove from benzenesulfonic acid (shown in orange and blue). To decide which is more acidic, examine the stability of each conjugate base 30-S=0 H . C C Predicting the Product . Which negative charge is more stable? :0: -H : 0=S=0: H :0=$=0: H Hugo " H H : H Since O is more electronegative than C, it is better able to stabilize the anion that forms. Consider the factors for acidity from Chapter 2. Predicting the Product Draw the conjugate base as the second product. This is the complete and balanced chemical equation. . Check to make sure all atoms and charges are balanced on the left- and righ hand side of the arrow. Since benzenesulfonic acid acted as acid, water (or ethanol) must have been the base. Hydronium is the conjugate acid. . :0=S=0 HCc. H :0 :0-S=O: CH H H HH Check equilibrium Most organic compounds are weak acids or bases, so we use equilibrium arrows most of the time. However, benzenesulfonic acid is a strong acid (pka ~-2.5), so we use a right arrow since most of the molecules are dissociated. It is a stronger acid than hydronium (more negative than pKa -1.7), so equilibrium pushes away from it. Side note: you will find different pka's reported online for this molecule. Pick one, indicate it on your paper, and draw your arrows consistent with it. You can read more on using pka's here: Reusch's Virtual Textbook Acidity pka -2.5 Stronger acid, push away! pka ~ 1.7 :0 S 0 : :0 :0-S=0 :O: H H H H 0 H anol v. Water Recall that the solution of reagent was prepared in a mixture of ethanol and water. . Since these have similar pka's (15.9 v. 15.7) and therefore similar acid- base reactivity, either could act as the base in the equation. o H TO$ OCH HO . 20: OS: H 0 0 $0 Note the similarity in structure between the hydronium and alkoxonium ions! H DO 10 SO 30 SEO Adding Mechanism Arrows Finally, we can draw mechanism arrows to show the bond breaking and bond forming in the reaction. Always start from the base (electrons) and attack the acid (positive charge). 0 H :0: TOSHO: . The arrow from water shows the lone pair e-turning into a bonding pair to form the new O-H bond in the hydronium product (blue arrow and bond). Lab Result 1: OH benzyl alcohol . In this experiment, the pH of benzyl alcohol is set to neutral, e.g., if a solution has a pH less than benzyl alcohol, it is acidic; pH higher than benzyl alcohol, it is basic. The pH of benzyl alcohol is represented at right, so use this as your new 7... Make your best estimate of the value (you can use 0.5 to represent between two values). Record the pH in your notebook A stirring rod was used to dip in the solution and touch to the pH paper HYDRION Benzyt nicohol i ethanol water PRODUTO www.Micronantailab.com Help Improve Oce Notes 8871% 24 dtv 4 09 MacBook Air Lab Result 2: benzenesulfonic acid Record the pH in your notebook. A stirring ra used to dip solution and to the pH pa LOH O==0 benzene sulfonic acid HYDRION TEHNOLOLO www.Mere Essentiallab.com Lab Result 3: . benzoic acid Record the pH in your notebook. . A stirrin used to solution to the pH benzoic acid Related thanol/water HYDRION BERODSKO www.Micro Essentiailab.com Lab Result 4: benzyl amine Record the pH in your notebook. A stirring rod was used to dip in the solution and touch to the pH paper NH2 benzyl amine HYDRION Helbimprovec N Lab Result 5: cresol Record the pH in your notebook. A stirrin used to solution to the pH HO cresol Crest the water HYDRION ORLD www.Microsentillah.com Lab Result 6: aniline Record the pH in your notebook. NH2 A stirring used to dig solution an to the pH pa aniline du thanol water HYDRION www.Microlab.com Lab Result 7: pyridine . Record the pH in your notebook. A stirring used to dig solution an to the pH pa Pyridine Paroista th HYDRION www.Microlab.com Lab Result 8: Picric acid Record the pH in your notebook. = A stirrir used to solution to the pH 0- HO P. that picric acid HYDRION www.Micro Errentarlab.com Writing the Equations Now that you have your data recorded, it is time to interpret it. . For this lab, we will determine structure based upon pH and represent it in an equation. . First, draw the structure of the molecule on the left-hand side. Note that benzene can be represented as a circle inside a hexagon as shown on the left; this represents the hybrid form of benzene since the double bonds alternate around the ring . Since we are studying acid-base reactions, show all H (potential acids) and lone pairs (potential bases). Show it in reaction with water or ethanol since both were in the mixture. 30-50 Predicting the Product Since we have the pH, we know one of the products of the reactio Hopefully, you found a pH ~2 for benzenesulfonic acid. This pH indicates that hydronium is present in solution. Draw hydronium on the right-hand side. :0-S=0 H Hoc 0 H H H H H Predicting the Product Now, we know how the compound reacted. If hydronium is produced, water must have obtained H* from the benzenesulfon acid. Therefore, we can draw the conjugate base of benzenesulfonic aci the other product. There are two possible H to remove from benzenesulfonic acid (shown in orange and blue). To decide which is more acidic, examine the stability of each conjugate base 30-S=0 H . C C Predicting the Product . Which negative charge is more stable? :0: -H : 0=S=0: H :0=$=0: H Hugo " H H : H Since O is more electronegative than C, it is better able to stabilize the anion that forms. Consider the factors for acidity from Chapter 2. Predicting the Product Draw the conjugate base as the second product. This is the complete and balanced chemical equation. . Check to make sure all atoms and charges are balanced on the left- and righ hand side of the arrow. Since benzenesulfonic acid acted as acid, water (or ethanol) must have been the base. Hydronium is the conjugate acid. . :0=S=0 HCc. H :0 :0-S=O: CH H H HH Check equilibrium Most organic compounds are weak acids or bases, so we use equilibrium arrows most of the time. However, benzenesulfonic acid is a strong acid (pka ~-2.5), so we use a right arrow since most of the molecules are dissociated. It is a stronger acid than hydronium (more negative than pKa -1.7), so equilibrium pushes away from it. Side note: you will find different pka's reported online for this molecule. Pick one, indicate it on your paper, and draw your arrows consistent with it. You can read more on using pka's here: Reusch's Virtual Textbook Acidity pka -2.5 Stronger acid, push away! pka ~ 1.7 :0 S 0 : :0 :0-S=0 :O: H H H H 0 H anol v. Water Recall that the solution of reagent was prepared in a mixture of ethanol and water. . Since these have similar pka's (15.9 v. 15.7) and therefore similar acid- base reactivity, either could act as the base in the equation. o H TO$ OCH HO . 20: OS: H 0 0 $0 Note the similarity in structure between the hydronium and alkoxonium ions! H DO 10 SO 30 SEO Adding Mechanism Arrows Finally, we can draw mechanism arrows to show the bond breaking and bond forming in the reaction. Always start from the base (electrons) and attack the acid (positive charge). 0 H :0: TOSHO: . The arrow from water shows the lone pair e-turning into a bonding pair to form the new O-H bond in the hydronium product (blue arrow and bond)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


