Please help me answer the following questions. Thanks in advance.
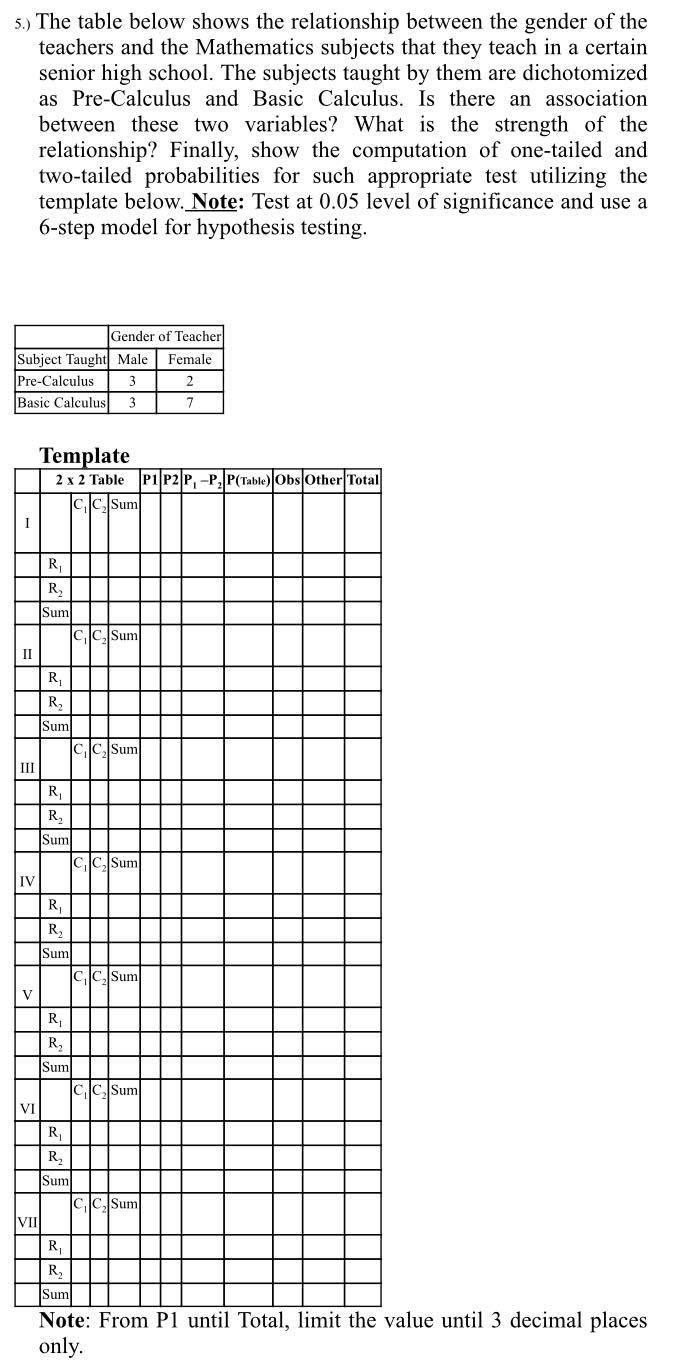
Presented here is the proposed 6-Step Model for hypothesis testing that the group must consider in working out every situation problem, to enumerate: > State the null hypothesis, H. > Choose a statistical test (for this one, it is being identified already) Select the level of significance and the sample size, N, (if necessitated only) - Select the sampling distribution and establishing the critical region/value. Collect the data (given already) and compute the statistical test. - Make a decision.5.) The table below shows the relationship between the gender of the teachers and the Mathematics subjects that they teach in a certain senior high school. The subjects taught by them are dichotomized as Pre-Calculus and Basic Calculus. Is there an association between these two variables? What is the strength of the relationship? Finally, show the computation of one-tailed and two-tailed probabilities for such appropriate test utilizing the template below. Note: Test at 0.05 level of significance and use a 6-step model for hypothesis testing. Gender of Teacher Subject Taught Male Female Pre-Calculus 3 2 Basic Calculus 3 7 Template 2 x 2 Table PI P2 P, -P, P(Table) |Obs Other Total CC, Sum R R Sum CC, Sum II R Sum C C, Sum III R R Sum CC Sum IV R R Sum CC, Sum V R Sum CC Sum VI R R Sum CC, Sum VII R R, Sun Note: From Pl until Total, limit the value until 3 decimal places only.4.} A random sample often neophyte Subject Teachers (it e. those who served for less than 5 years) had been given a skill test on computer literacy with the following results: 35, 32, 74, 93, 37, 86, T5, 80, T9, 8.: 85. A random sample of eight seasoned Subject Teachers (if; those who have been in the service for 20-30 years already) in from the same school had been likewise given the same test with these scores resulting: 88, Ti, 93, 94, 83, 91, T8, 3c 30, respectively. Is there a difference in the computer literacy between these two groups, as measured by the test? Note: Test at {10] level of signicance and use a 6-step model for hypothesis testing Situational Problems & Data Set: 1.) Mrs. Pachill-chillang, a secondary level Mathematics Teacher, claims that the median grade on a test was 72. A sample of her 25 students had the following grades. You, having enrolled in the Graduate Teacher Education with major in Mathematics, must check the teacher's claim with an assumption that the population is not normal. Note: Test at 0.01 level of significance and use a 6- step model for hypothesis testing. Data: 68, 72, 74, 69, 52, 52, 81, 72, 78, 86, 76, 91, 42, 85, 73, 92, 61, 87, 73, 78, 96, 94, 72, 81, 75 2.) With the consolidated results of the 3"d quarterly examination from the Grade-11, Mr. Reklamador defensively pointed out that the low mean percentage scores garnered by his students in General Mathematics is caused by their degree of anxiety. Hence, his School Principal and Middle Managers ask him if the female students are more anxious than male students under his tutelage. With the data below, is the difference between male and female students statistically significant? Note: Test at 0.05 level of significance and use a 6-step model for hypothesis testing. Degree of Anxiety Data Female students: 50, 38, 49, 41, 39, 45, 46 Male students: 43, 32, 42, 35, 37, 40 3.) In Walaklaro National High School, it was reported by the Division that the senior high school students were not adept in terms of Scientific Literacy. During their in-service training last October 2021, the principal has ordered all Mathematics, Science and English Teachers to collaboratively conduct an action research to address the incumbent issue. The challenge for these teachers was to infer whether or not there is significant relationship between the Scientific Literacy and class standing? Additionally, this joint venture must present the outcome of such empirical investigation to the Principal and Resource Mangers - if the upperclass significantly different from the underclass on such articulated variable. Note: Test at 0.05 level of significance and use a 6-step model for hypothesis testing. Scientific Class Standing Literacy Combined Underclass Upperclass High 10 33 43 Average 30 40 70 Low 54 30 84 Total 94 103 197