please help
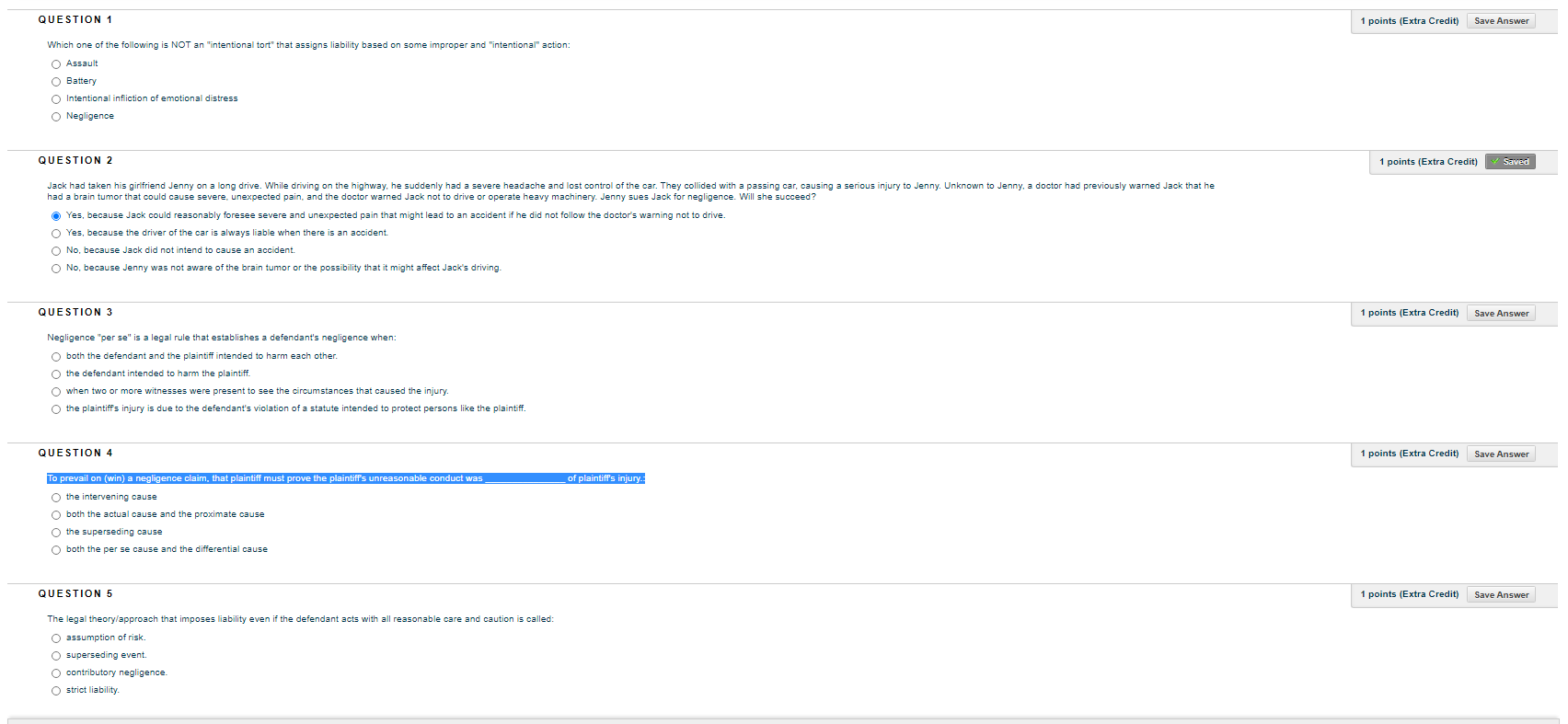
QUESTION 1 1 points (Extra Credit) Save Answer Which one of the following is NOT an "intentional tort" that assigns liability based on some improper and "intentional" action: Assault Battery O Intentional infliction of emotional distress Negligence QUESTION 2 1 points (Extra Credit) * Saved Jack had taken his girlfriend Jenny on a long drive. While driving on the highway, he suddenly had a severe headache and lost control of the car. They collided with a passing car, causing a serious injury to Jenny. Unknown to Jenny, a doctor had previously warned Jack that he had a brain tumor that could cause severe, unexpected pain, and the doctor warned Jack not to drive or operate heavy machinery. Jenny sues Jack for negligence. Will she succeed? Yes, because Jack could reasonably foresee severe and unexpected pain that might lead to an accident if he did not follow the doctor's warning not to drive. Yes, because the driver of the car is always liable when there is an accident. No. because Jack did not intend to cause an accident. No, because Jenny was not aware of the brain tumor or the possibility that it might affect Jack's driving. QUESTION 3 1 points (Extra Credit) Save Answer Negligence "per se" is a legal rule that establishes a defendant's negligence when: O both the defendant and the plaintiff intended to harm each other. O the defendant intended to harm the plaintiff. O when two or more witnesses were present to see the circumstances that caused the injury. O the plaintiff's injury is due to the defendant's violation of a statute intended to protect persons like the plaintiff. QUESTION 4 1 points (Extra Credit) Save Answer To prevail on (win) a negligence claim. that plaintiff must prove the plaintiff's unreasonable conduct was of plaintiff's injury. the intervening cause O both the actual cause and the proximate cause O the superseding cause O both the per se cause and the differential cause QUESTION 5 1 points (Extra Credit) Save Answer The legal theory/approach that imposes liability even if the defendant acts with all reasonable care and caution is called: assumption of risk. superseding event. contributory negligence. O strict liability