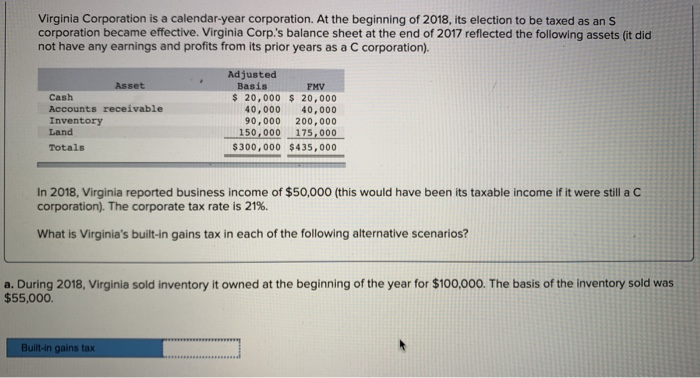
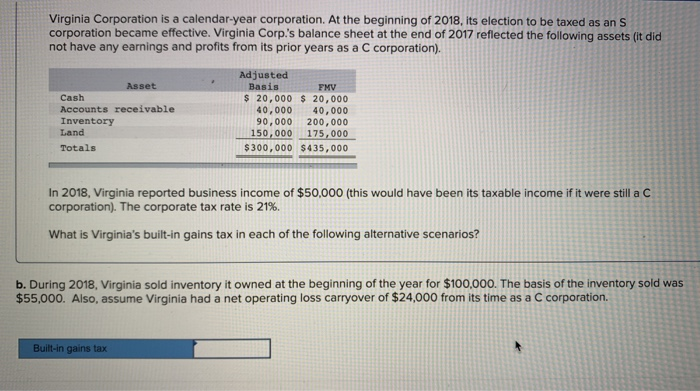
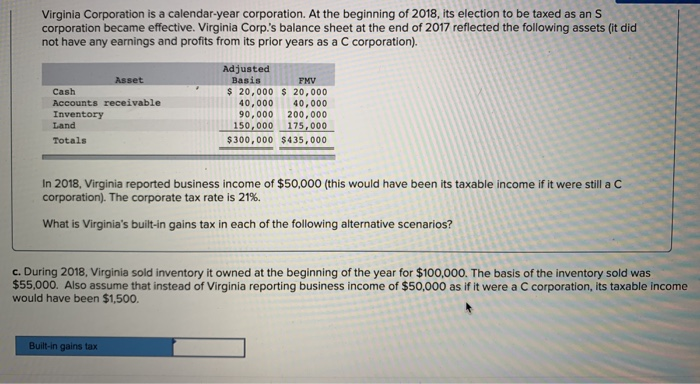
Virginia Corporation is a calendar-year corporation. At the beginning of 2018, its election to be taxed as an S corporation became effective. Virginia Corp's balance sheet at the end of 2017 reflected the following assets (it did not have any earnings and profits from its prior years as a C corporation). Adjusted Basis Asset FMV Cash Accounts receivable Inventory Land Totals $ 20,000 20,000 40,000 40,000 90,000 200,000 150,000 175,000 $300,000 $435,000 In 2018, Virginia reported business income of $50,000 (this would have been its taxable income if it were still a C corporation). The corporate tax rate is 21%. What is Virginia's built-in gains tax in each of the following alternative scenarios? a. During 2018, Virginia sold inventory it owned at the beginning of the year for $100,000. The basis of the inventory sold was $55,000 Built-in gains tax Virginia Corporation is a calendar-year corporation. At the beginning of 2018, its election to be taxed as an S corporation became effective. Virginia Corp.'s balance sheet at the end of 2017 reflected the following assets (it did not have any earnings and profits from its prior years as a C corporation). Adjusted Basis Asset FMV Cash Accounts receivable Inventory Land Totals $ 20,000 20,000 40,000 40,000 90,000 200,000 150,000175,000 $300,000 $435,000 In 2018, Virginia reported business income of $50,000 (this would have been its taxable income if it were still a C corporation). The corporate tax rate is 21%. What is Virginia's built-in gains tax in each of the following alternative scenarios? b. During 2018, Virginia sold inventory it owned at the beginning of the year for $100.000. The basis of the inventory sold was $55,000. Also, assume Virginia had a net operating loss carryover of $24,000 from its time as a C corporation. Built-in gains tax Virginia Corporation is a calendar-year corporation. At the beginning of 2018, its election to be taxed as an S corporation became effective. Virginia Corp.'s balance sheet at the end of 2017 reflected the following assets (it did not have any earnings and profits from its prior years as a C corporation). Adjusted Basis Asset FMV Cash Accounts receivable Inventory Land Totals $ 20,000 20,000 40,00040,000 90,000 200,000 150,000 175,000 $300,000 $435,000 In 2018, Virginia reported business income of $50,000 (this would have been its taxable income if it were still a C corporation). The corporate tax rate is 21%. What is Virginia's built-in gains tax in each of the following alternative scenarios? c. During 2018, Virginia sold inventory it owned at the beginning of the year for $100,000. The basis of the inventory sold was $55,000. Also assume that instead of Virginia reporting business income of $50,000 as if it were a C corporation, its taxable income would have been $1,500 Built-in gains tax Virginia Corporation is a calendar-year corporation. At the beginning of 2018, its election to be taxed as an S corporation became effective. Virginia Corp's balance sheet at the end of 2017 reflected the following assets (it did not have any earnings and profits from its prior years as a C corporation). Adjusted Basis Asset FMV Cash Accounts receivable Inventory Land Totals $ 20,000 20,000 40,000 40,000 90,000 200,000 150,000 175,000 $300,000 $435,000 In 2018, Virginia reported business income of $50,000 (this would have been its taxable income if it were still a C corporation). The corporate tax rate is 21%. What is Virginia's built-in gains tax in each of the following alternative scenarios? a. During 2018, Virginia sold inventory it owned at the beginning of the year for $100,000. The basis of the inventory sold was $55,000 Built-in gains tax Virginia Corporation is a calendar-year corporation. At the beginning of 2018, its election to be taxed as an S corporation became effective. Virginia Corp.'s balance sheet at the end of 2017 reflected the following assets (it did not have any earnings and profits from its prior years as a C corporation). Adjusted Basis Asset FMV Cash Accounts receivable Inventory Land Totals $ 20,000 20,000 40,000 40,000 90,000 200,000 150,000175,000 $300,000 $435,000 In 2018, Virginia reported business income of $50,000 (this would have been its taxable income if it were still a C corporation). The corporate tax rate is 21%. What is Virginia's built-in gains tax in each of the following alternative scenarios? b. During 2018, Virginia sold inventory it owned at the beginning of the year for $100.000. The basis of the inventory sold was $55,000. Also, assume Virginia had a net operating loss carryover of $24,000 from its time as a C corporation. Built-in gains tax Virginia Corporation is a calendar-year corporation. At the beginning of 2018, its election to be taxed as an S corporation became effective. Virginia Corp.'s balance sheet at the end of 2017 reflected the following assets (it did not have any earnings and profits from its prior years as a C corporation). Adjusted Basis Asset FMV Cash Accounts receivable Inventory Land Totals $ 20,000 20,000 40,00040,000 90,000 200,000 150,000 175,000 $300,000 $435,000 In 2018, Virginia reported business income of $50,000 (this would have been its taxable income if it were still a C corporation). The corporate tax rate is 21%. What is Virginia's built-in gains tax in each of the following alternative scenarios? c. During 2018, Virginia sold inventory it owned at the beginning of the year for $100,000. The basis of the inventory sold was $55,000. Also assume that instead of Virginia reporting business income of $50,000 as if it were a C corporation, its taxable income would have been $1,500 Built-in gains tax









