Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Please help with question 11 and provide calculations and formulas of how you solved for 11 Maintenance Management Case Study Synopsis: Vacation Express Airlines is
Please help with question 11 and provide calculations and formulas of how you solved for 11 
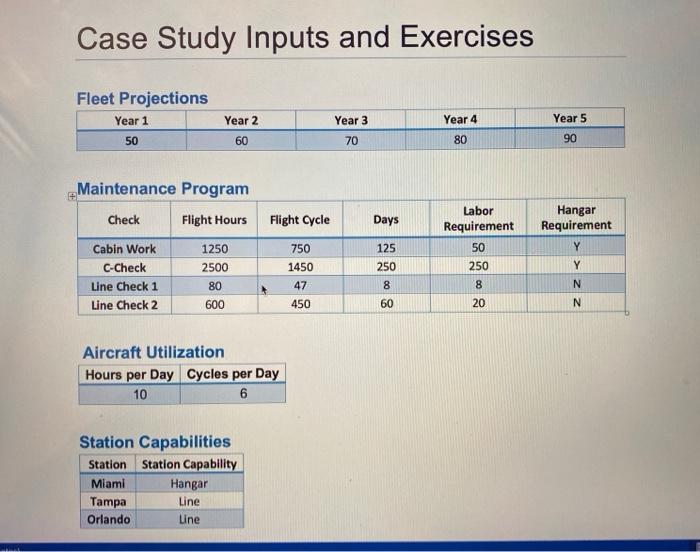
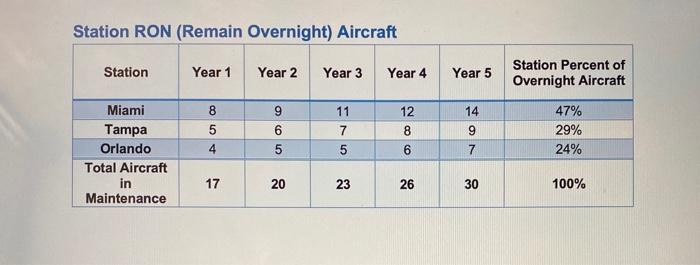

Maintenance Management Case Study Synopsis: Vacation Express Airlines is the latest in up and coming Ultra-Low Cost Carriers (ULCCs) that have been steadily building on a niche market for low fare travel to vacation destinations. The company strategy involves being aggressive, nimble and innovative by identifying opportunities to grow the business and make quick but well thought out decisions. The current fleet consists of 50 B737-700 but if more aircraft can be acquired at the right price point, there could be significant growth opportunities over the next five years. The Fleet Transactions department is working on a deal to acquire aircraft coming off lease in in the next five years. You are the Manager of Line Maintenance Planning and the senior leadership of Maintenance & Engineering has confirmed that Vacation Express will almost be doubling its fleet over the next five years to support aggressive growth in along the northeast to vacation destinations in Florida. You have been tasked with producing a forecast of maintenance demand to assist senior leadership developing a plan for adding the needed capacity and designing a maintenance footprint that will support the Network Plan as the fleet grows. Learning Objectives: 1. Gain a basic understanding of check intervals and Maintenance Planning concepts 2. Provide students with a method for estimating resource requirements for a RON (remain overnight) maintenance 3. Gain the ability to generate forecasts and make recommendations to support management decision making Concepts Demonstrated in Exercises Aircraft utilization and the relationship with the driving time limit of check intervals Event based forecasting using check intervals Check yield management and the associated implications within an RON setting Labor demand distribution across a network of maintenance bases with varying capabilities Estimating hangar and labor capacity . . Case Study Inputs and Exercises Fleet Projections Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Year 5 90 50 60 70 80 Days Maintenance Program Check Flight Hours Cabin Work 1250 C-Check 2500 Line Check 1 80 Line Check 2 600 Labor Requirement 50 250 Hangar Requirement Y Flight Cycle 750 1450 47 125 250 8 Y 8 N N 450 60 20 Aircraft Utilization Hours per Day Cycles per Day 10 6 Station Capabilities Station Station Capability Miami Hangar Tampa Line Orlando Line Station RON (Remain Overnight) Aircraft Station Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Year 5 Station Percent of Overnight Aircraft 12 8 5 4 Miami Tampa Orlando Total Aircraft in Maintenance 9 6 5 11 7 5 8 14 9 7 47% 29% 24% 6 17 20 23 26 30 100% Case Study Questions 1. Convert flight hour and cycle interval to day terms using the provided utilization. 2. Determine the driving time limit for each check. 3. Determine the actual frequency each check will be accomplished using a 95% yield on driving interval. 4. With 1 aircraft what is the average number events that need to be accomplished each year for each check? 5. With 1 aircraft what is the average events per month for each check? 6. With 1 aircraft what is the average events per day for each check? 7. What is the average number of events for each check that must be accomplished each day considering the fleet size in years 1 to 5? 8. What are the total man-hours required for hangar and line maintenance checks considering the fleet counts in years 1 to 5? 9. How many mechanics are required to generate to the forecasted man-hours required? 10. Assuming that there are 30 mechanics on staff in what years will the company need to hire additional mechanics and how many? 11. Assuming that you currently have only one hangar bay in what year will need to add more hangar capacity? 12. What is the current net for mechanics in each maintenance location? 13. What will be the staffing demand for each location as the fleet grows? Assume that any additional hangar space will be added in Miami. Final Exercise Using the data produced by answering the above questions produce an outline for a potential presentation for Maintenance & Engineering senior leadership to accomplish the following: 1) A summary of the forecasting methodology and key inputs to the forecast 2) A summary of the forecast outputs that would be of interest to senior leadership 3) Recommendations for the timing and amount of resources to be added Maintenance Management Case Study Synopsis: Vacation Express Airlines is the latest in up and coming Ultra-Low Cost Carriers (ULCCs) that have been steadily building on a niche market for low fare travel to vacation destinations. The company strategy involves being aggressive, nimble and innovative by identifying opportunities to grow the business and make quick but well thought out decisions. The current fleet consists of 50 B737-700 but if more aircraft can be acquired at the right price point, there could be significant growth opportunities over the next five years. The Fleet Transactions department is working on a deal to acquire aircraft coming off lease in in the next five years. You are the Manager of Line Maintenance Planning and the senior leadership of Maintenance & Engineering has confirmed that Vacation Express will almost be doubling its fleet over the next five years to support aggressive growth in along the northeast to vacation destinations in Florida. You have been tasked with producing a forecast of maintenance demand to assist senior leadership developing a plan for adding the needed capacity and designing a maintenance footprint that will support the Network Plan as the fleet grows. Learning Objectives: 1. Gain a basic understanding of check intervals and Maintenance Planning concepts 2. Provide students with a method for estimating resource requirements for a RON (remain overnight) maintenance 3. Gain the ability to generate forecasts and make recommendations to support management decision making Concepts Demonstrated in Exercises Aircraft utilization and the relationship with the driving time limit of check intervals Event based forecasting using check intervals Check yield management and the associated implications within an RON setting Labor demand distribution across a network of maintenance bases with varying capabilities Estimating hangar and labor capacity . . Case Study Inputs and Exercises Fleet Projections Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Year 5 90 50 60 70 80 Days Maintenance Program Check Flight Hours Cabin Work 1250 C-Check 2500 Line Check 1 80 Line Check 2 600 Labor Requirement 50 250 Hangar Requirement Y Flight Cycle 750 1450 47 125 250 8 Y 8 N N 450 60 20 Aircraft Utilization Hours per Day Cycles per Day 10 6 Station Capabilities Station Station Capability Miami Hangar Tampa Line Orlando Line Station RON (Remain Overnight) Aircraft Station Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Year 5 Station Percent of Overnight Aircraft 12 8 5 4 Miami Tampa Orlando Total Aircraft in Maintenance 9 6 5 11 7 5 8 14 9 7 47% 29% 24% 6 17 20 23 26 30 100% Case Study Questions 1. Convert flight hour and cycle interval to day terms using the provided utilization. 2. Determine the driving time limit for each check. 3. Determine the actual frequency each check will be accomplished using a 95% yield on driving interval. 4. With 1 aircraft what is the average number events that need to be accomplished each year for each check? 5. With 1 aircraft what is the average events per month for each check? 6. With 1 aircraft what is the average events per day for each check? 7. What is the average number of events for each check that must be accomplished each day considering the fleet size in years 1 to 5? 8. What are the total man-hours required for hangar and line maintenance checks considering the fleet counts in years 1 to 5? 9. How many mechanics are required to generate to the forecasted man-hours required? 10. Assuming that there are 30 mechanics on staff in what years will the company need to hire additional mechanics and how many? 11. Assuming that you currently have only one hangar bay in what year will need to add more hangar capacity? 12. What is the current net for mechanics in each maintenance location? 13. What will be the staffing demand for each location as the fleet grows? Assume that any additional hangar space will be added in Miami. Final Exercise Using the data produced by answering the above questions produce an outline for a potential presentation for Maintenance & Engineering senior leadership to accomplish the following: 1) A summary of the forecasting methodology and key inputs to the forecast 2) A summary of the forecast outputs that would be of interest to senior leadership 3) Recommendations for the timing and amount of resources to be added 



Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


