Question: Please kindly write out all output Section 3:- Process and System Monitoring Linux has several ways of telling you about processes or tasks in the
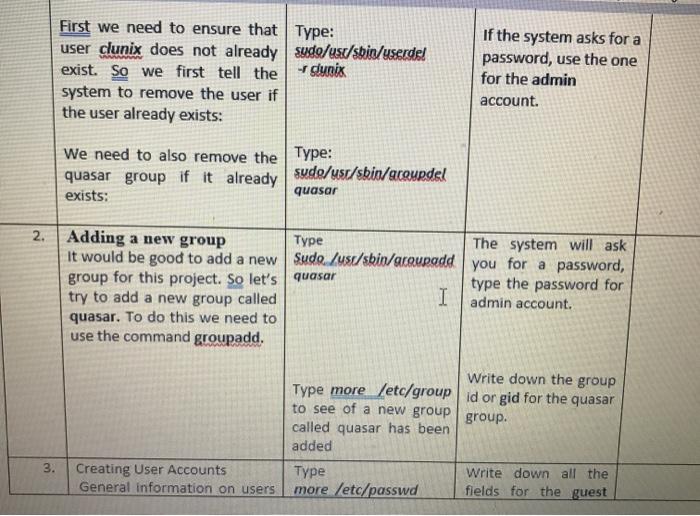
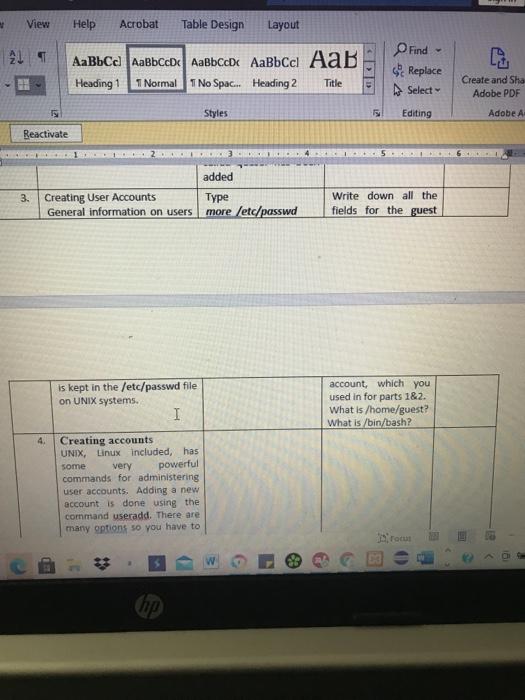
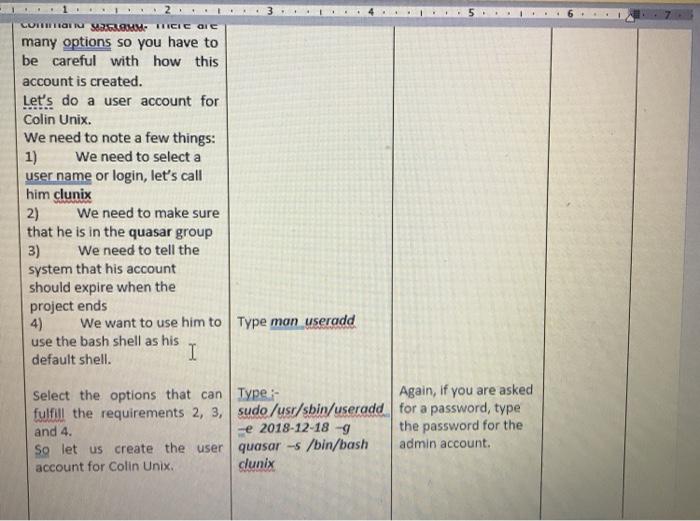
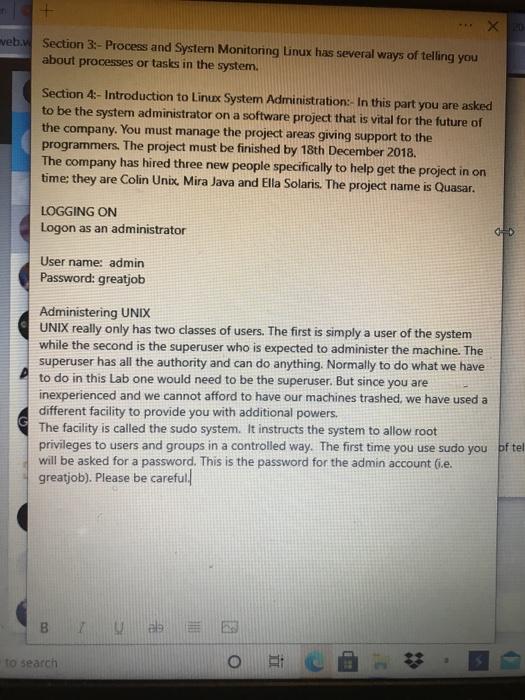
2. top Using the top command The top command is also used to report on processes or tasks as well as other system info. I Find out what is the total number of processes or tasks running in the system? How many processes or tasks are sleeping? The id parameter stands for the idle status. Find out what percentage of time the processor is idle? Look at the individual processes, find out the process or task using 1) The most memory 2)the most CPU time? Answer the following questions: (Hint: use the cpuinfo 3. Using /proc:- Both the ps and Type: cd /proc top commands use a special Type: Is to see the directory called /proc. files This directory contains system information. Let's go to the Use the more /proc directory command to look at the contents of the following files cpuinfo, meminfo and interrupts. I file) What type of processor is running (Pentium, Celeron, Intel Core Duo, etc.)? What is its speed? What is the? How many size of the processor cache CPUs does your computer have? (Hint: use the meminfo file) What is the total amount of memory in the system? How much memory is being used? How much memory has been allocated for swap space? How much swap space is actually being used? (Hint: use the interrupts file) Which interrupts are T Focus I Tids been allocated TUI swap space? How much swap space is actually being used? (Hint: use the interrupts file) Which interrupts are being used by the timer and the Ethernet NIC (eth1 or eml)? Note: The interrupt number is in the first column on your left. The smaller the interrupt number, the more important the interrupt and thus it is usually given a higher priority. Explain why the timer interrupt is very important. LOGGING ON Logon as an administrator Username: admin Password: greatiob Administering UNIX UNIX really only has two classes of users. The first is simply a user of the system while the second is the superuser who is expected to administer the machine. The superuser has all the authority and can do anything. Normally to do what we have to do in this Lab one would need to be the superuser. But since you are inexperienced and we cannot afford to have our machines trashed, we have used a different facility to provide you with additional powers. The facility is called the sudo system. It instructs the system to allow root privileges to users and groups in a controlled way. The first time you use sudo you will be asked for a password. This is the password for the admin account (ie, greatiob). Please be careful. 1. Understanding Groups UNIX has the concept of groups for people doing collaborative work or for people or services that need certain privileges. Open a terminal window Type: man groups write a brief summary of how groups are managed. Users can see the group(s) to Type groups which they belong. write down the answer you get for the admin account. First we need to ensure that Type: user clunix does not already sude/us/sbin/userde! exist. So we first tell the dunix system to remove the user if the user already exists: If the system asks for a password, use the one for the admin account. We need to also remove the Type: quasar group if it already sude/usr/sbin/acourdel quasar exists: 2. Adding a new group Type The system will ask it would be good to add a new Sudo./usr/sbin/groupadd you for a password, group for this project. So let's quasar type the password for try to add a new group called I admin account. quasar. To do this we need to use the command groupadd. Write down the group Type more /etc/group id orgid for the quasar to see of a new group group. called quasar has been added Type Write down all the more /etc/passwd fields for the guest 3. Creating User Accounts General information on users View Help Acrobat Table Design Layout ALS Heading 1 1 No Spac... Heading 2 C D Find Replace Select T Normal Title Create and Sha Adobe PDF Styles Editing Adobe A Reactivate added 3. Creating User Accounts General information on users Type more /etc/passwd Write down all the fields for the guest is kept in the /etc/passwd file on UNIX systems. I account, which you used in for parts 1&2. What is /home/guest? What is /bin/bash? 4. Creating accounts UNIX, Linux included, has some very powerful commands for administering user accounts. Adding a new account is done using the command useradd. There are many options so you have to roc & 3 hp 3 LORITI SAM ICIC OIC many options so you have to be careful with how this account is created. Let's do a user account for Colin Unix. We need to note a few things: 1) We need to select a user name or login, let's call him clunix 2) We need to make sure that he is in the quasar group 3) We need to tell the system that his account should expire when the project ends 4) We want to use him to Type man useradd use the bash shell as his default shell. I Select the options that can Type: Again, if you are asked fulfill the requirements 2, 3, sudo /usr/sbin/useradd for a password, type and 4. e 2018-12-18 -9 the password for the So let us create the user quasar -s /bin/bash admin account. account for Colin Unix. dunix XRD veb. Section 3:- Process and System Monitoring Linux has several ways of telling you about processes or tasks in the system. Section 4:- Introduction to Linux System Administration:- In this part you are asked to be the system administrator on a software project that is vital for the future of the company. You must manage the project areas giving support to the programmers. The project must be finished by 18th December 2018 The company has hired three new people specifically to help get the project in on time: they are Colin Unix, Mira Java and Ella Solaris. The project name is Quasar. LOGGING ON Logon as an administrator OD User name: admin Password: greatjob Administering UNIX UNIX really only has two classes of users. The first is simply a user of the system while the second is the superuser who is expected to administer the machine. The superuser has all the authority and can do anything. Normally to do what we have to do in this Lab one would need to be the superuser. But since you are inexperienced and we cannot afford to have our machines trashed, we have used a different facility to provide you with additional powers, The facility is called the sudo system. It instructs the system to allow root privileges to users and groups in a controlled way. The first time you use sudo you of tel will be asked for a password. This is the password for the admin account (e. greatjob). Please be careful. B TES to search
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


